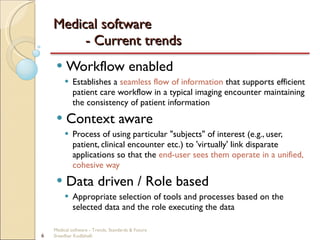
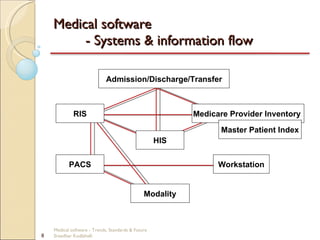
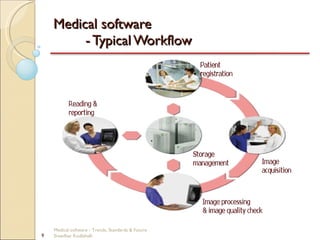
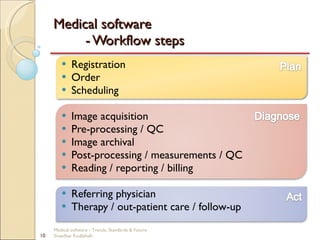
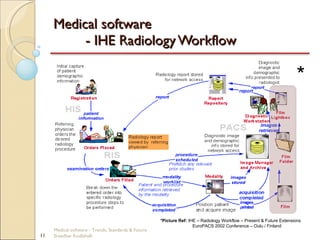
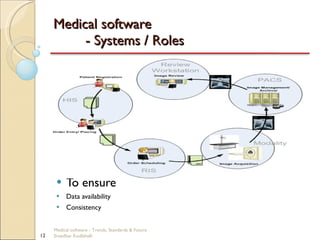
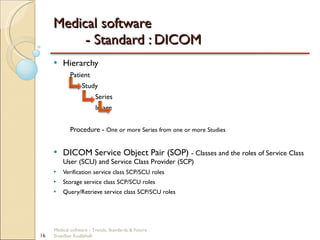
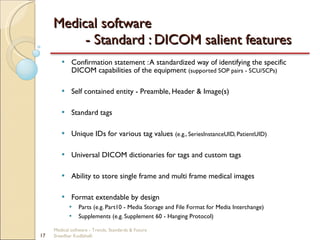
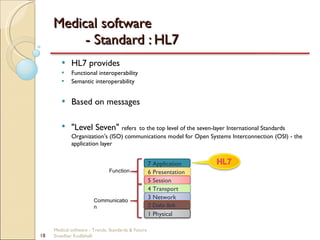
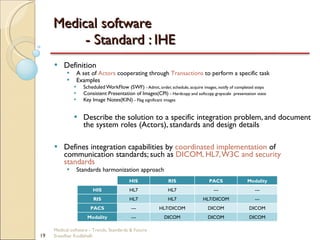
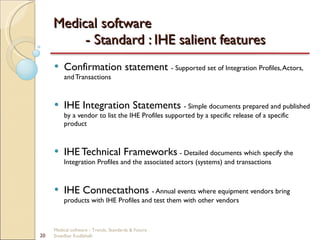
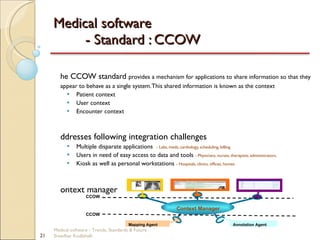
This document discusses trends, standards, and the future of medical software. It covers definitions of medical devices and various medical software systems. Standards like DICOM, HL7, IHE, and CCOW that promote medical data sharing are summarized. Development challenges and future trends involving cloud storage, remote diagnosis, and integrated multimodality workflows are outlined in less than 3 sentences.














![Thank YOU Medical software - Trends, Standards & Future Sreedhar Kodlahalli SREEDHAR KODLAHALLI BANGALORE, INDIA [email_address] [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medicalsoftware-111012090934-phpapp02/85/Medical-software-Trends-Standards-Future-29-320.jpg)