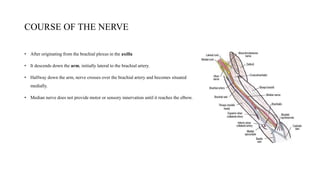
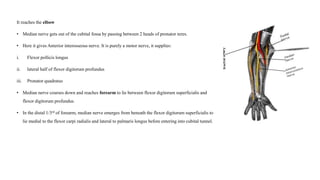
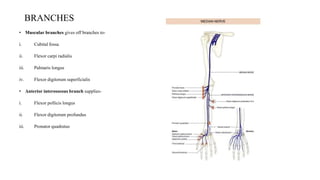
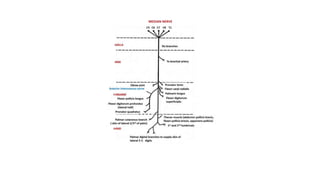
The median nerve is a crucial nerve of the forearm, responsible for motor control of hand movements and sensory innervation of specific fingers. It originates from the brachial plexus and travels through the arm and forearm to reach the hand, where it branches into divisions supplying various muscles and sensory innervation. Compression of the median nerve can result in syndromes such as carpal tunnel syndrome, anterior interosseous syndrome, and pronator teres syndrome, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected areas.