The document provides an overview of a session on linguistic analysis of media texts for journalism students. It covers several key points:
1. The objectives of the session are for students to understand grammar concepts needed to analyze English print media, describe rhetorical features used in media texts, and analyze different genres of journalistic writing.
2. The session will include a discussion on frameworks for text analysis and revising grammatical terms, as well as rhetorical devices used in texts.
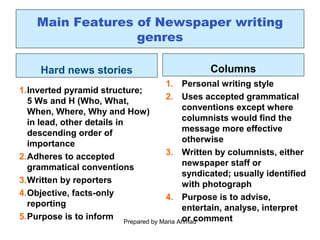
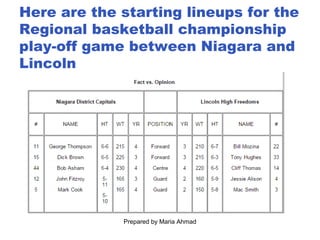
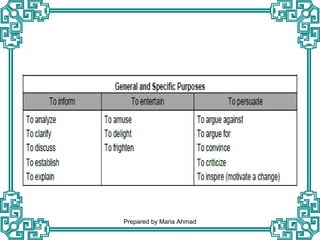
3. The document outlines various frameworks and concepts to help students analyze media texts, including examining headlines, genres, rhetorical patterns, word choice, and identifying facts versus opinions.