The document summarizes several theories related to media audiences:
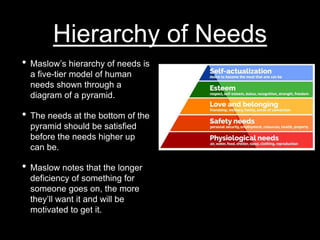
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that basic physiological needs must be met before higher-level needs.
- Passive audience theory suggests audiences directly receive media messages and are influenced without response.
- The hypodermic needle model views audiences as directly and powerfully impacted by media like advertisements.
- Cultivation theory examines television's long-term influence on viewers' perspectives without their awareness.
- The two-step flow theory proposes opinions spread from media to opinion leaders and then to others.
- Active audience and reader response theories see audiences as interpreting media based on their own experiences.
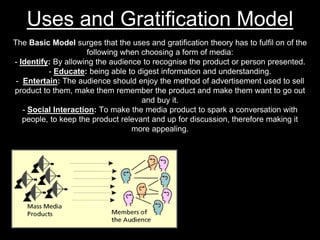
- Uses and gratifications model focuses on what audiences do with