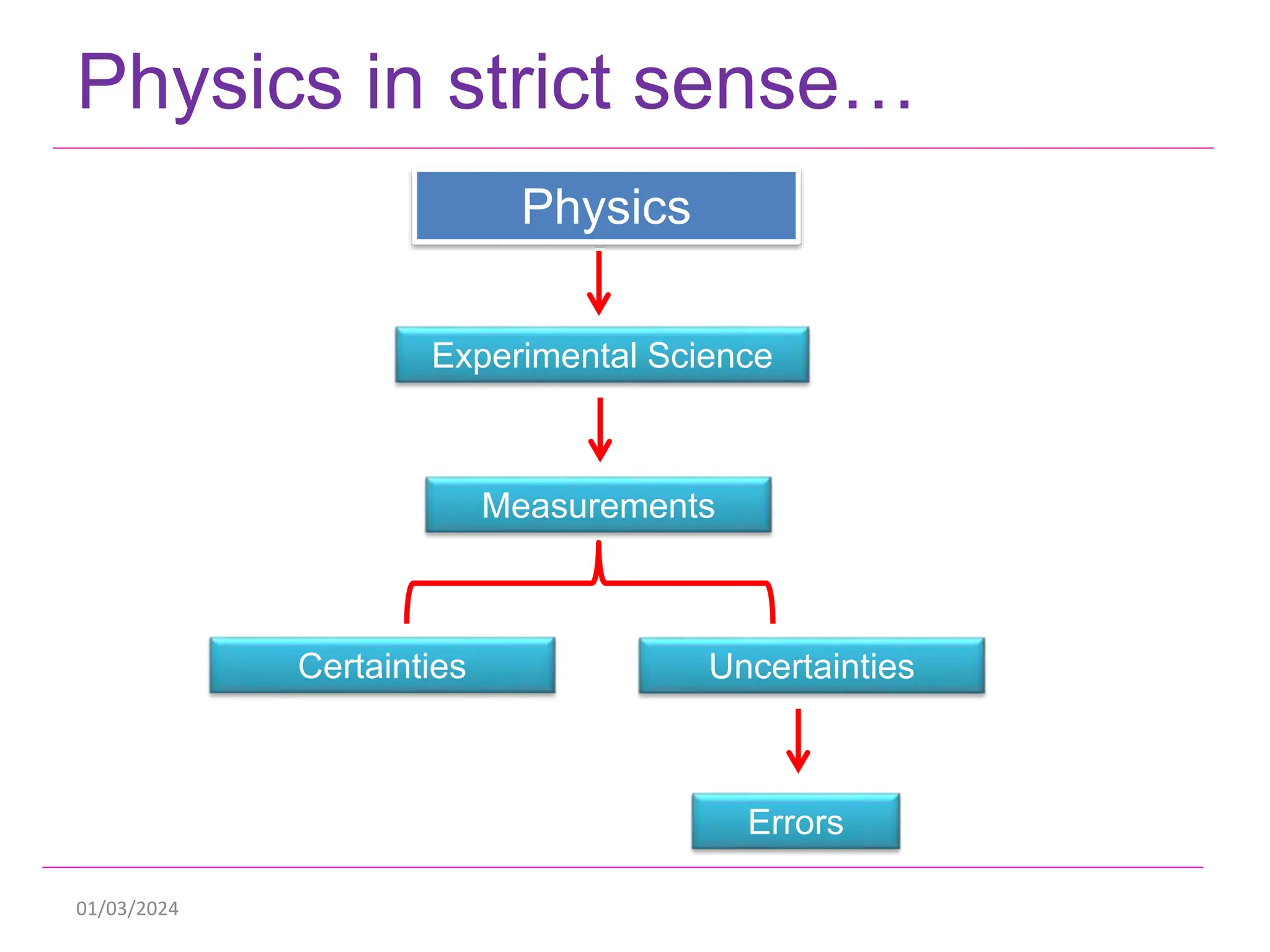
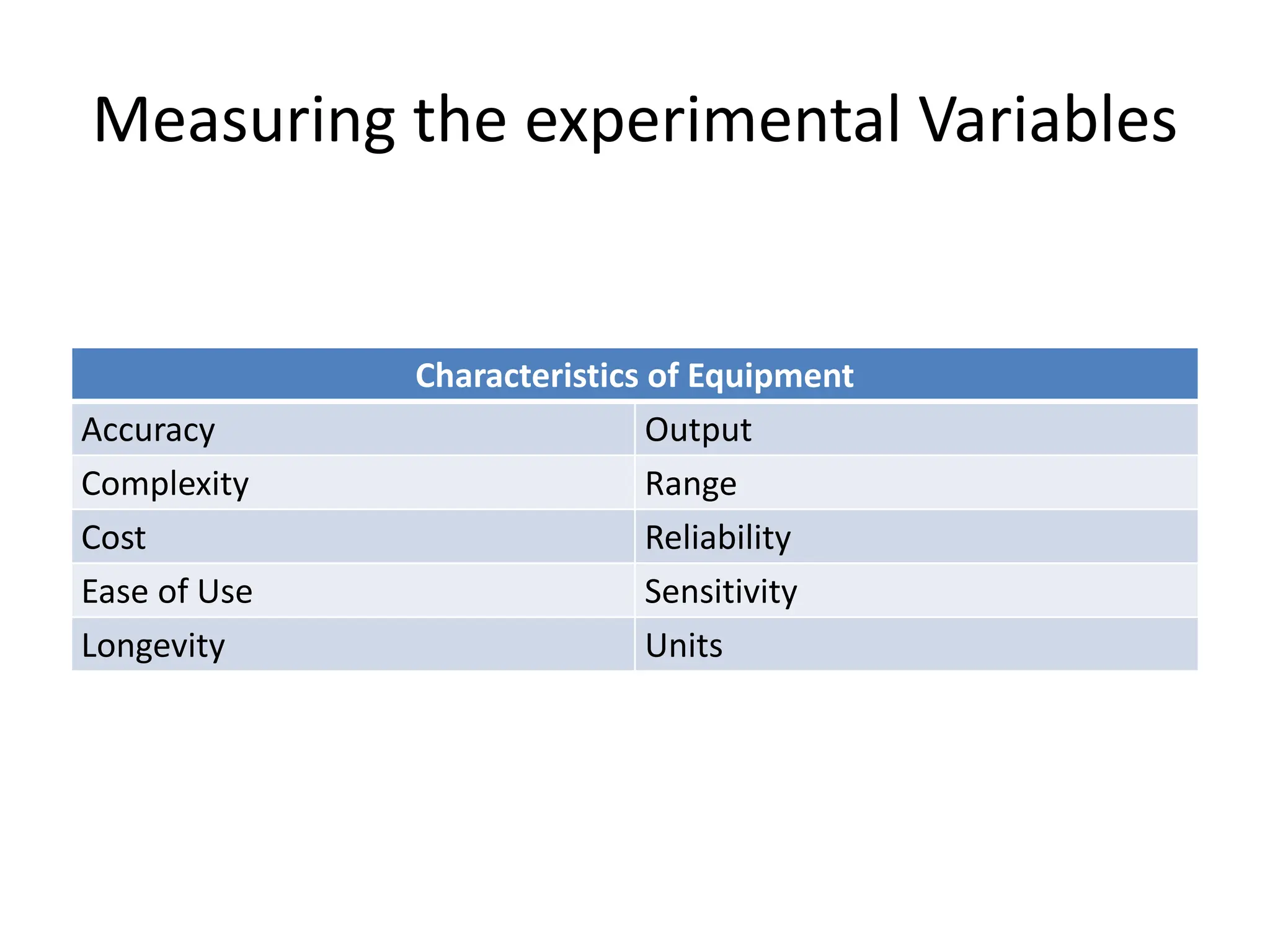
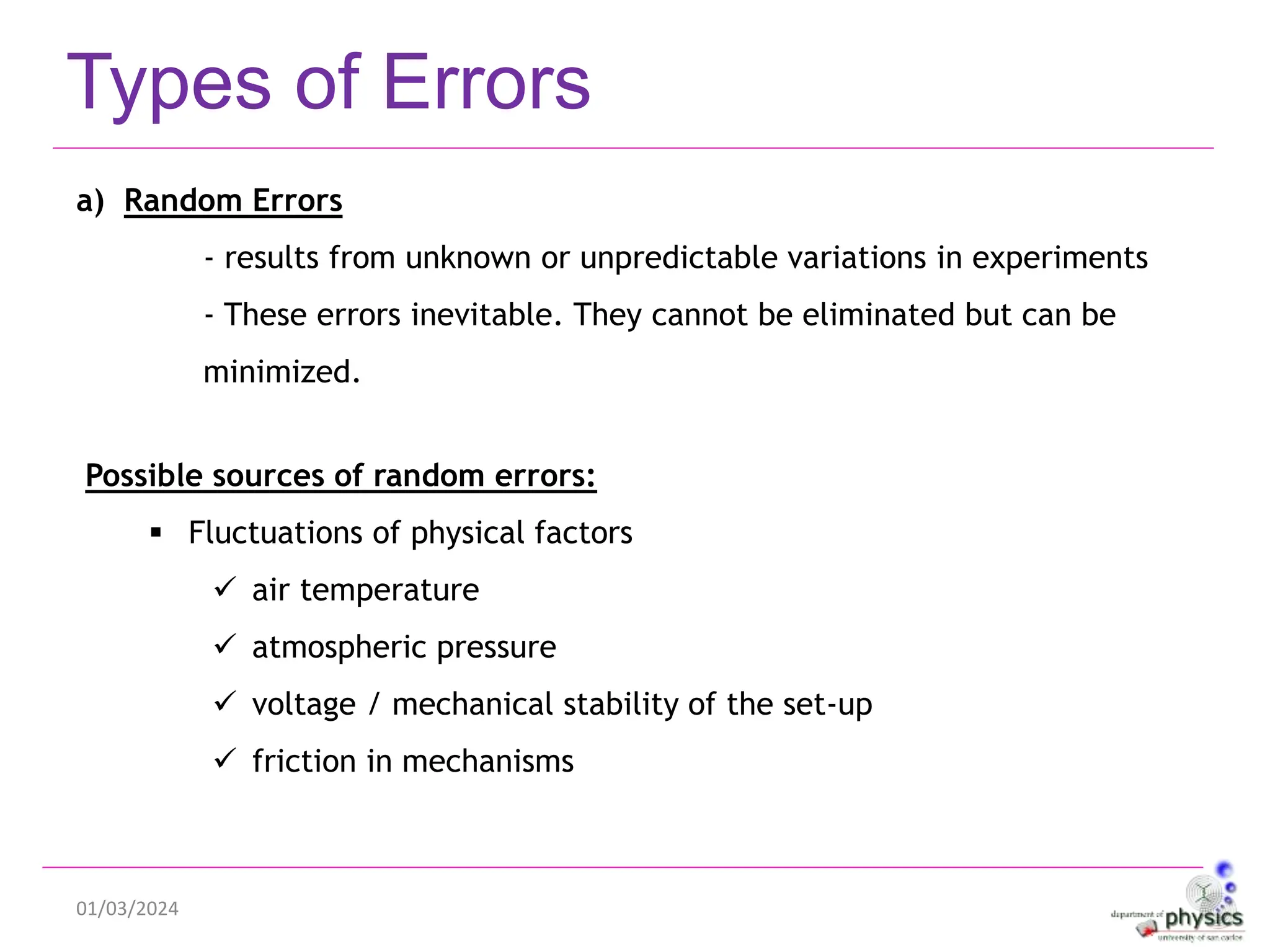
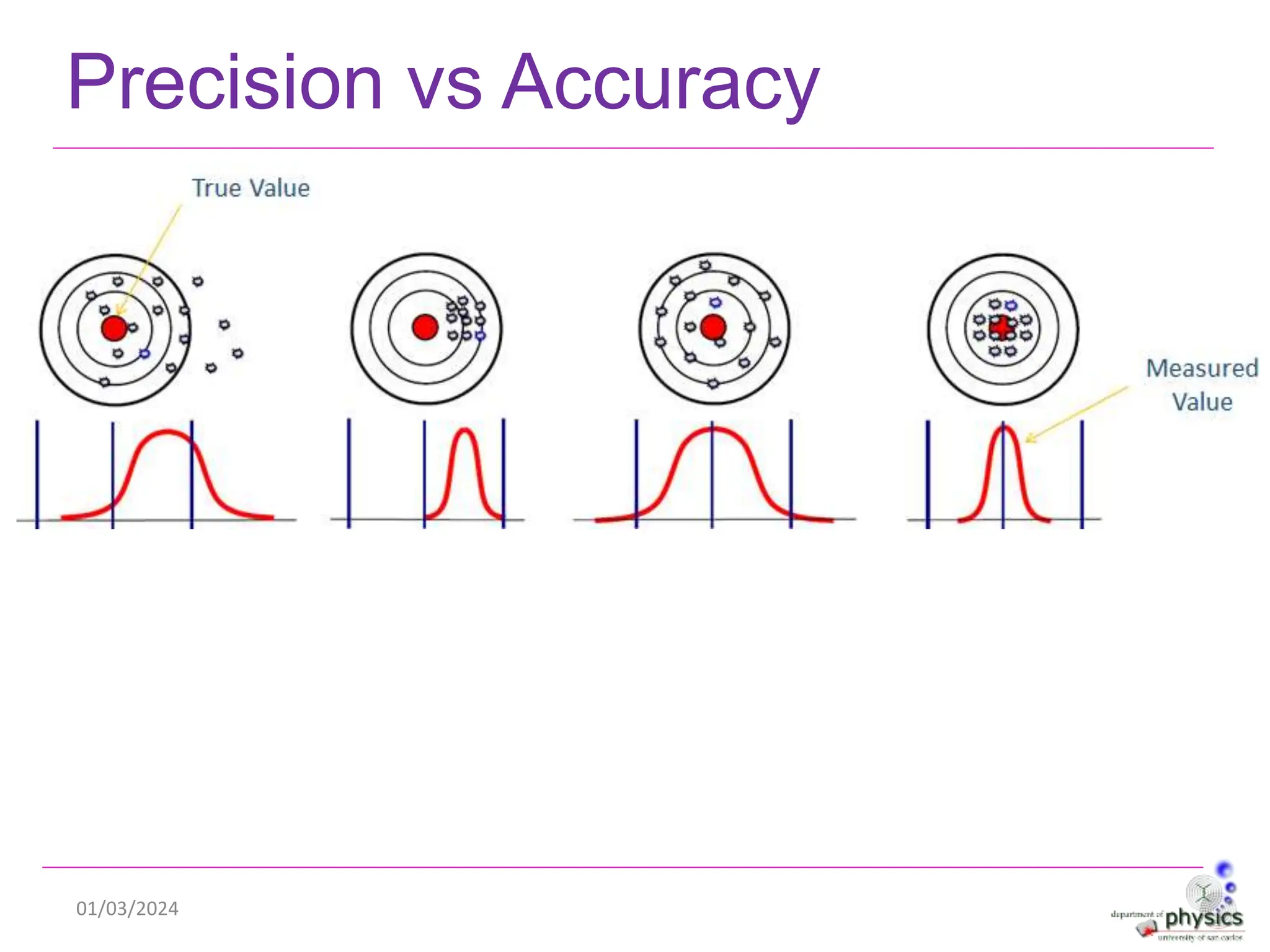
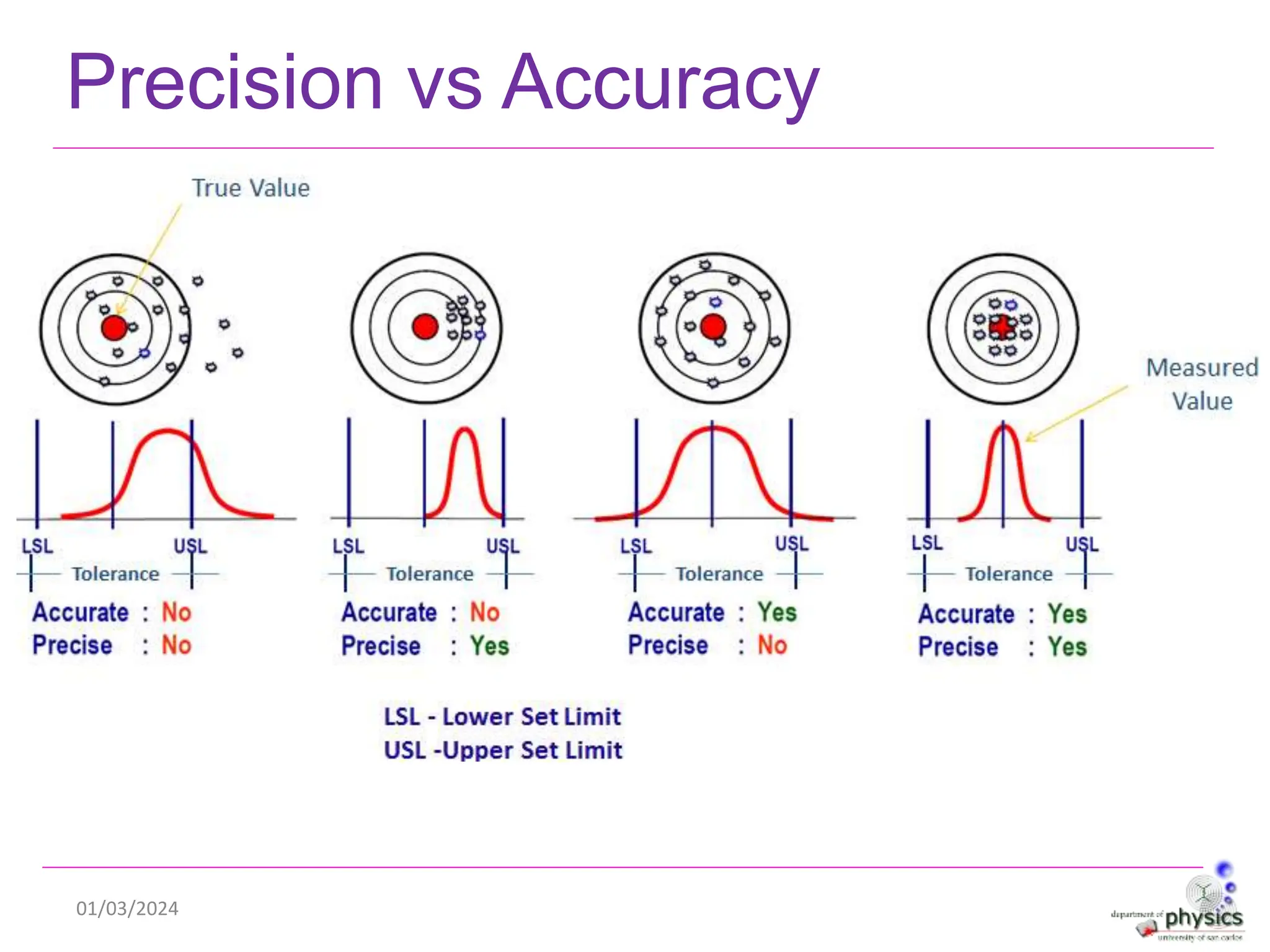
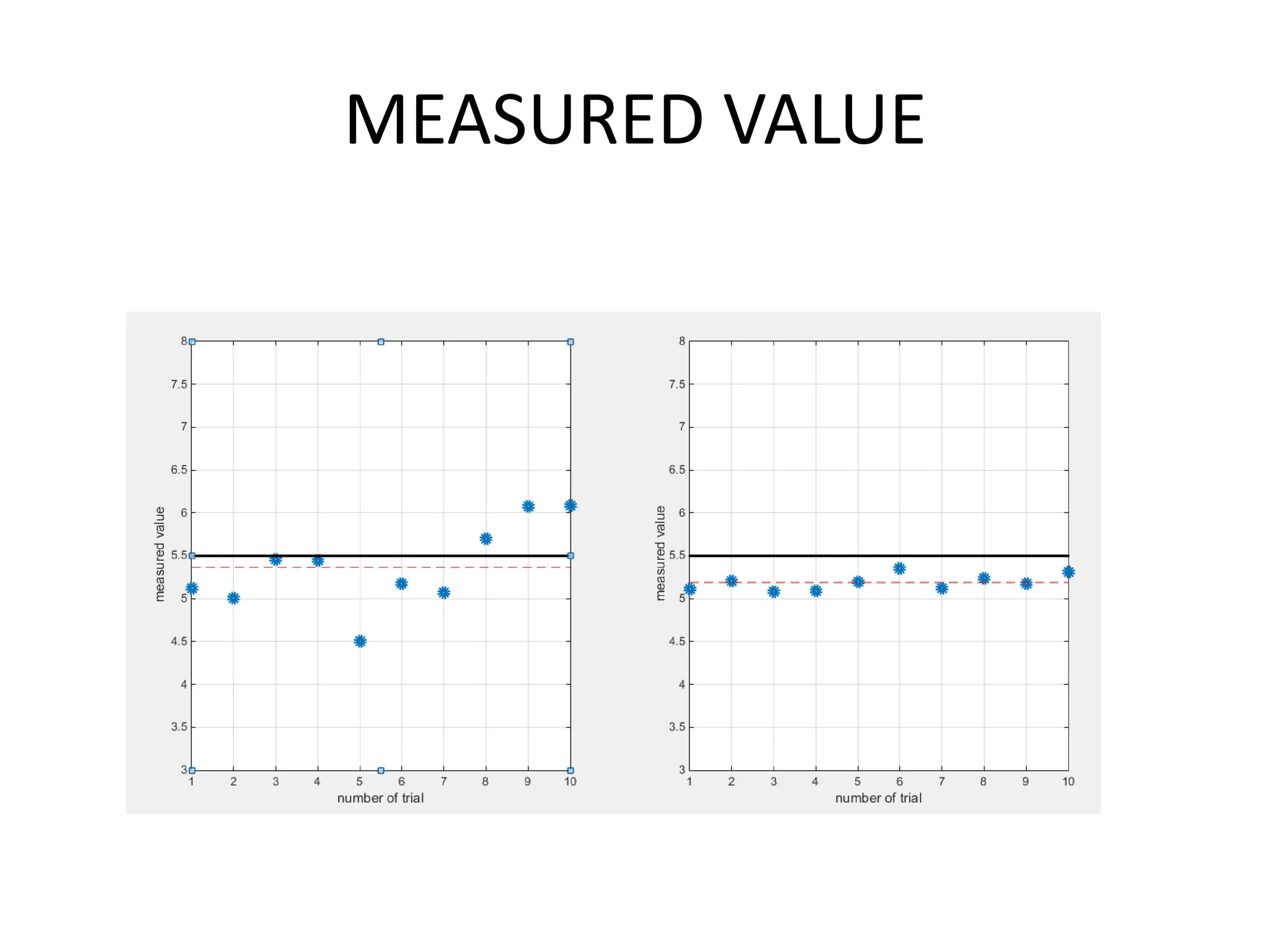
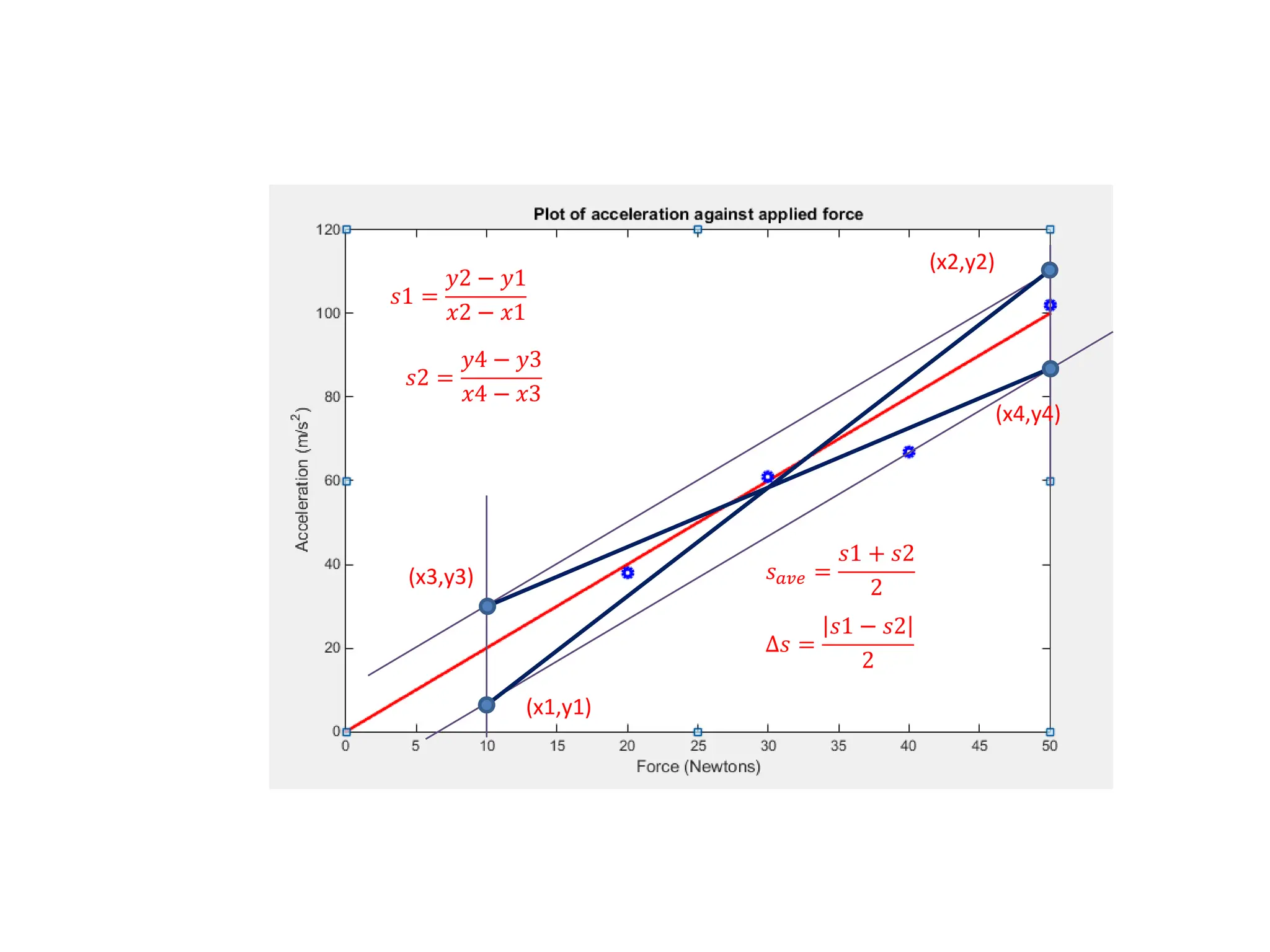
This document discusses measurements, errors, and precision vs accuracy in experimental science. It describes two main types of errors: random errors which are inevitable but can be minimized, and systematic errors which can be eliminated. Random errors result from unpredictable variations and can be reduced by taking multiple independent measurements. Systematic errors are associated with issues like improper instrument calibration, use of the wrong equipment or procedures. The document also explains that precision refers to the reproducibility of measurements but does not guarantee accuracy, which is defined as closeness to the true value.