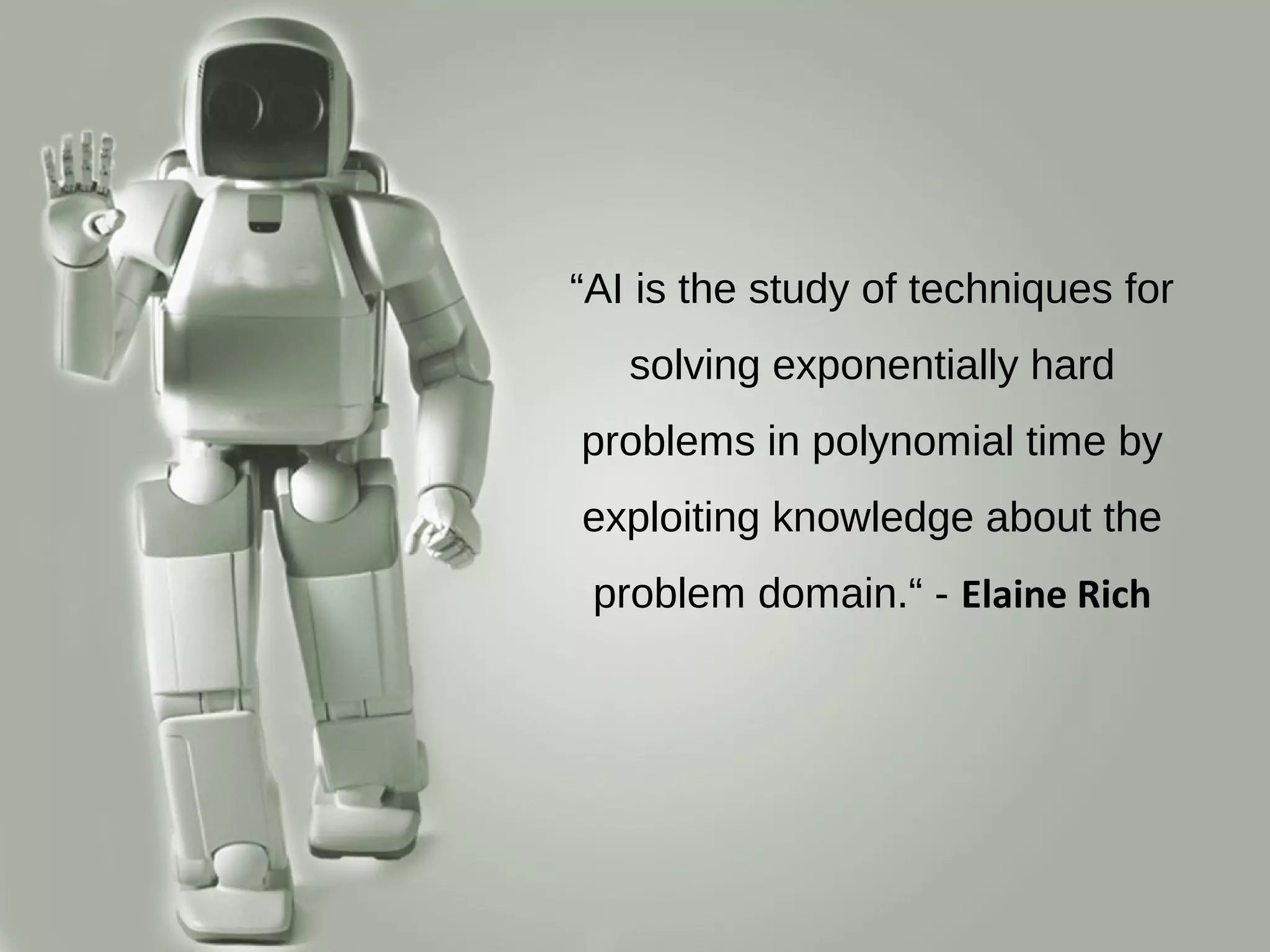
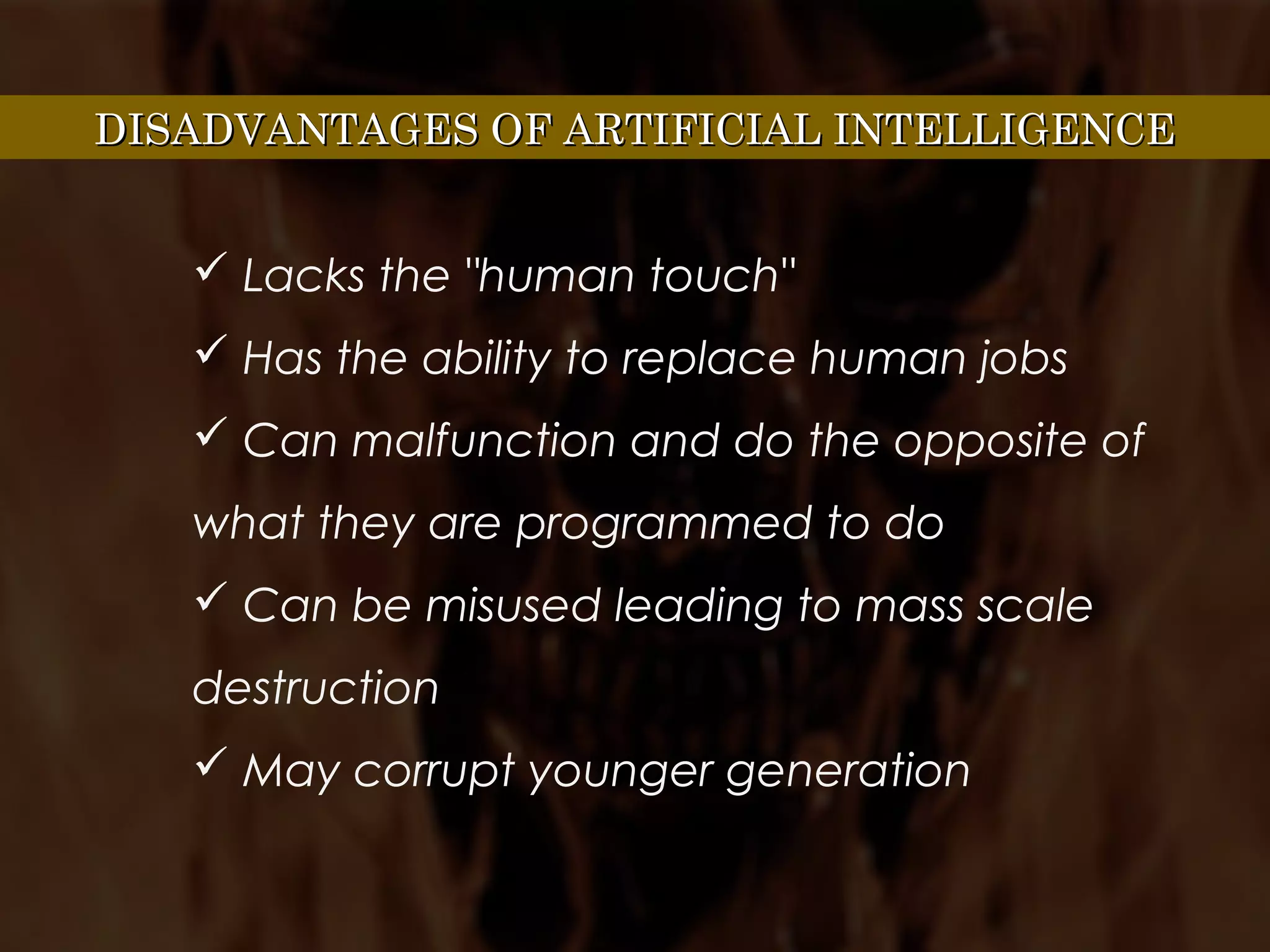
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI). It defines AI as techniques for solving exponentially hard problems in polynomial time by exploiting domain knowledge. It then briefly discusses the history of AI, including its roots in logic developed by Aristotle and its modern conception introduced by Alan Turing and John McCarthy. The document also lists some common applications of AI like game playing, automated reasoning, expert systems, natural language processing, planning and robotics. It provides advantages of AI such as taking on complex work, completing tasks faster, and making fewer errors, but also disadvantages like lacking human qualities, potential job replacement, and possible misuse. Finally, it outlines four possible goals for AI systems: thinking like humans, thinking rationally, acting like