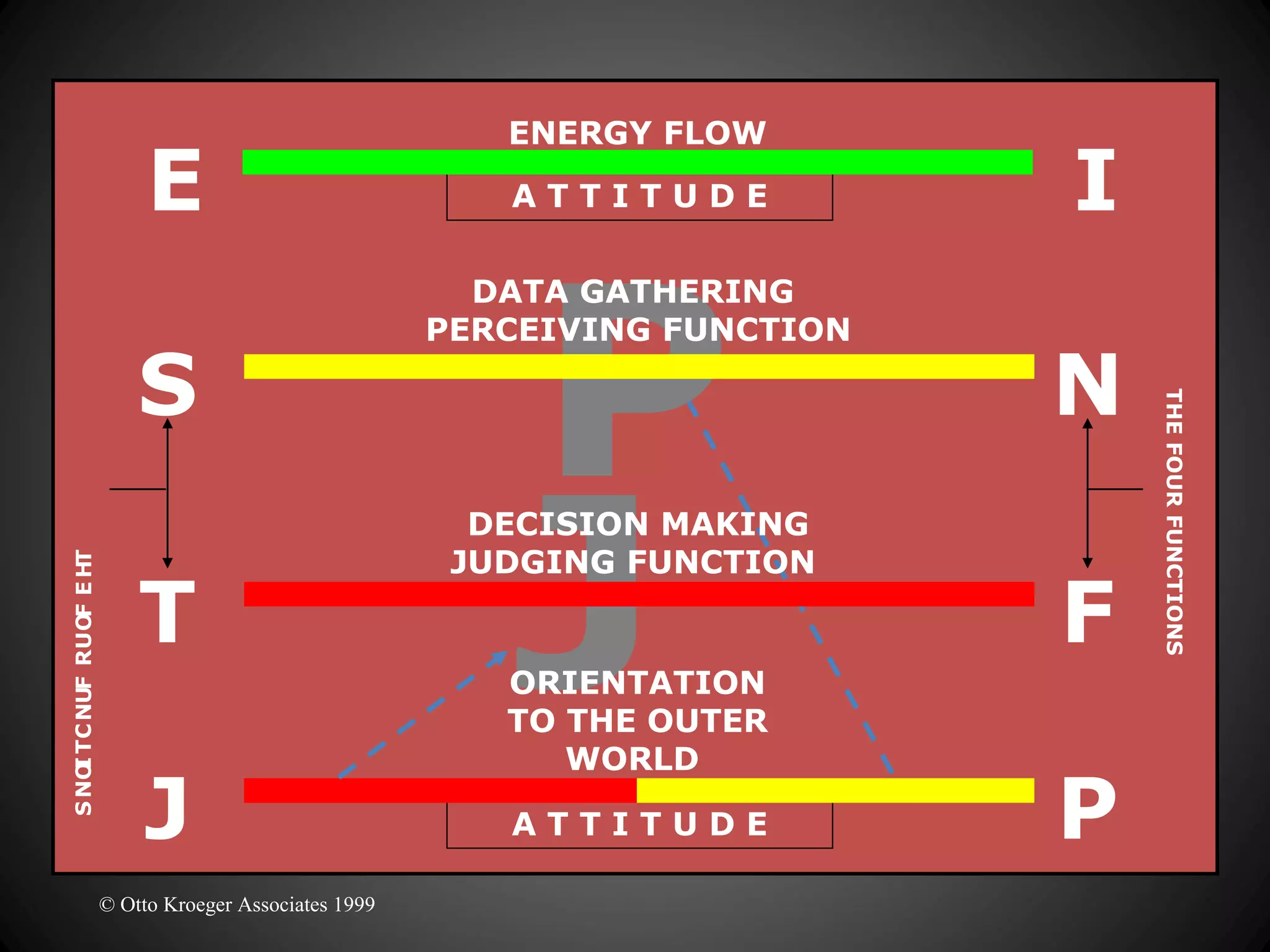
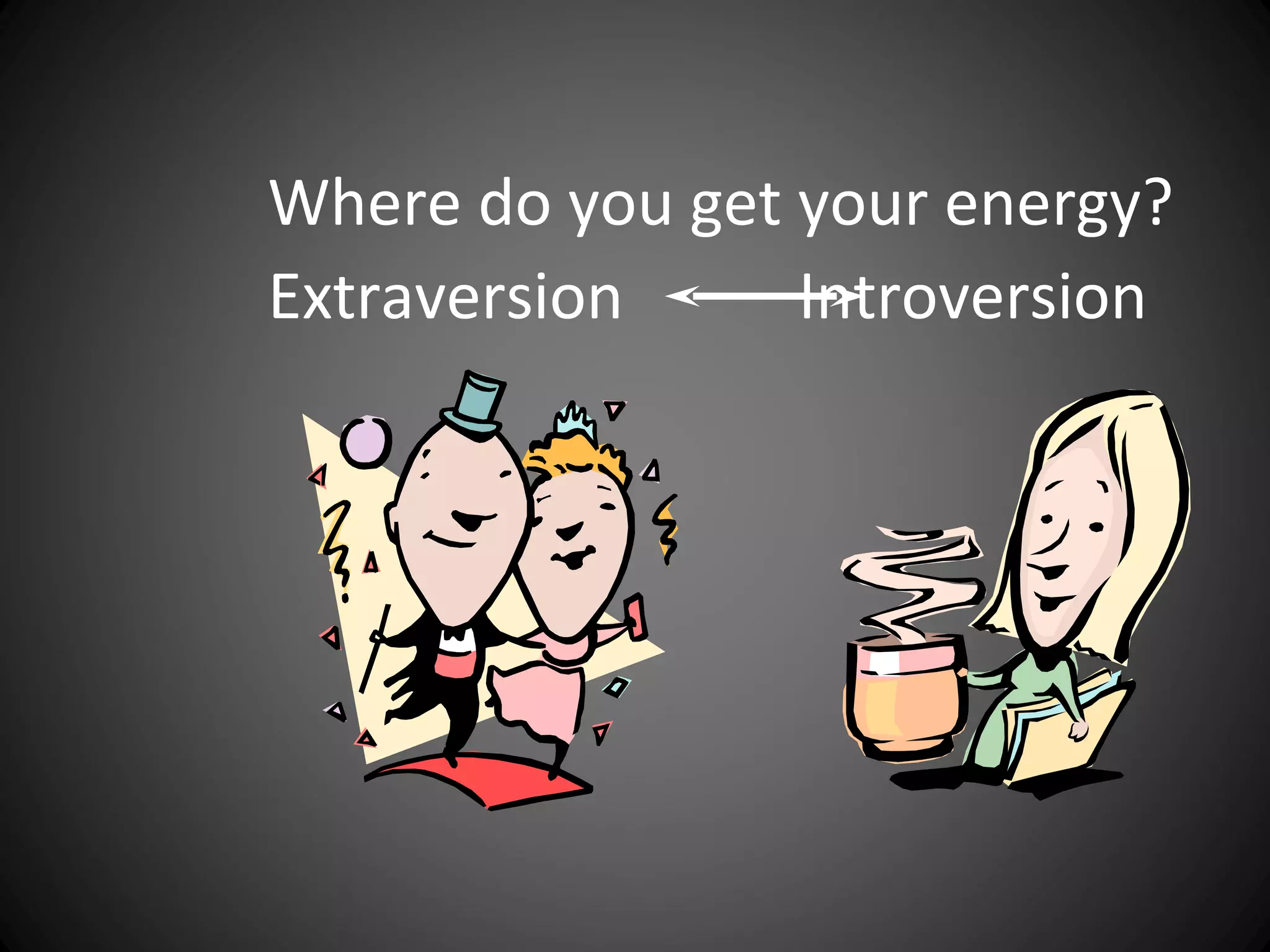
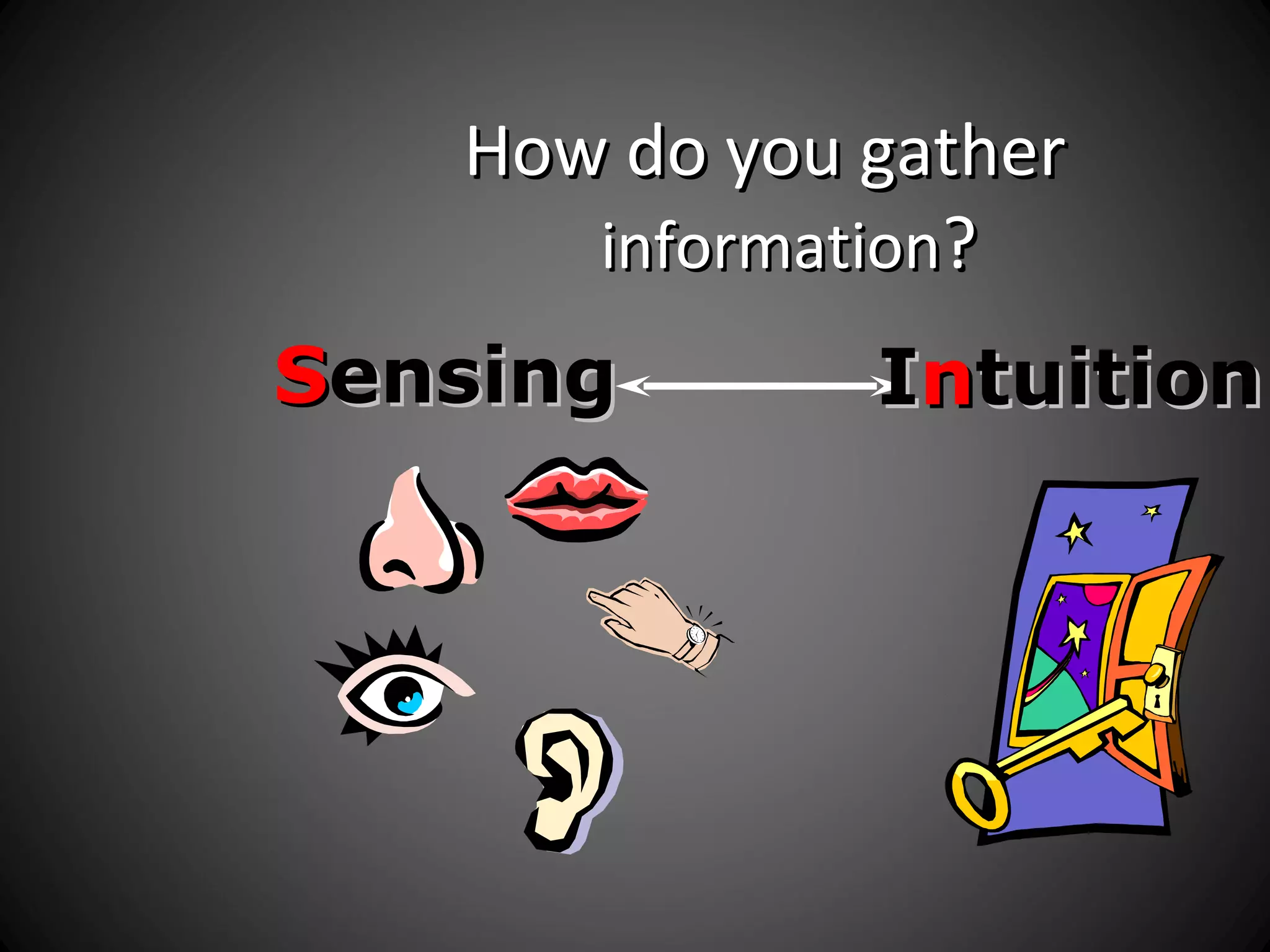
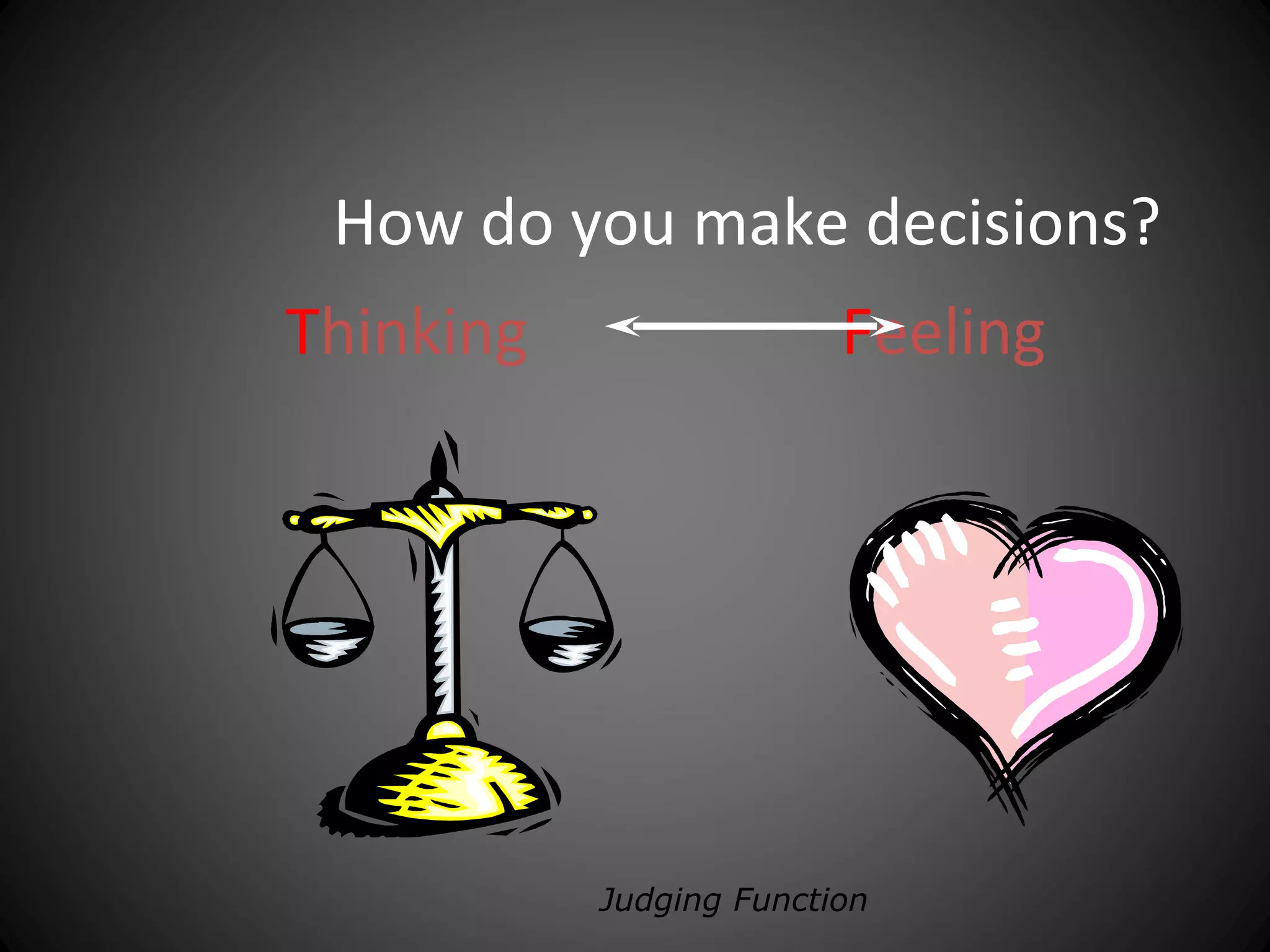
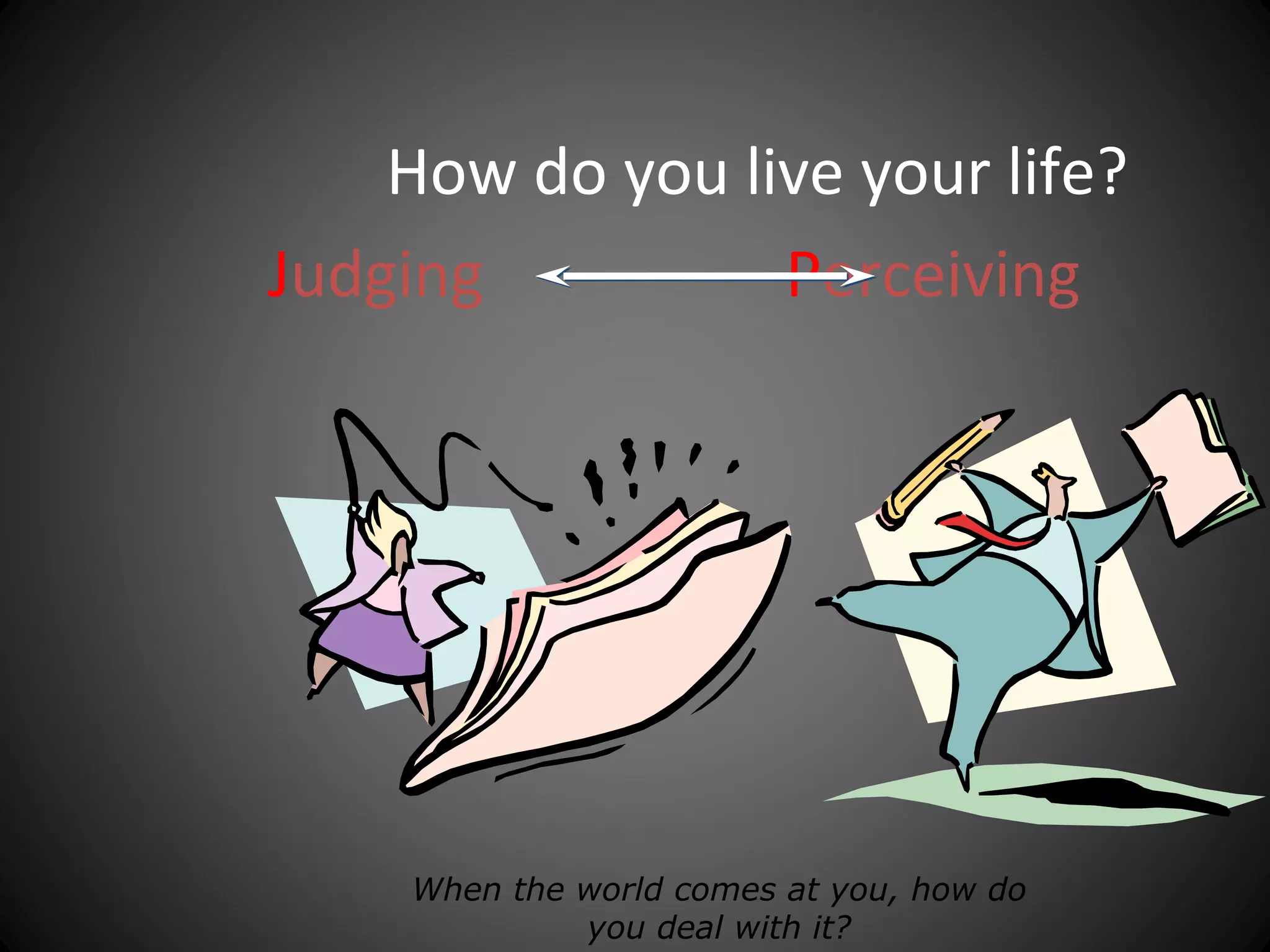
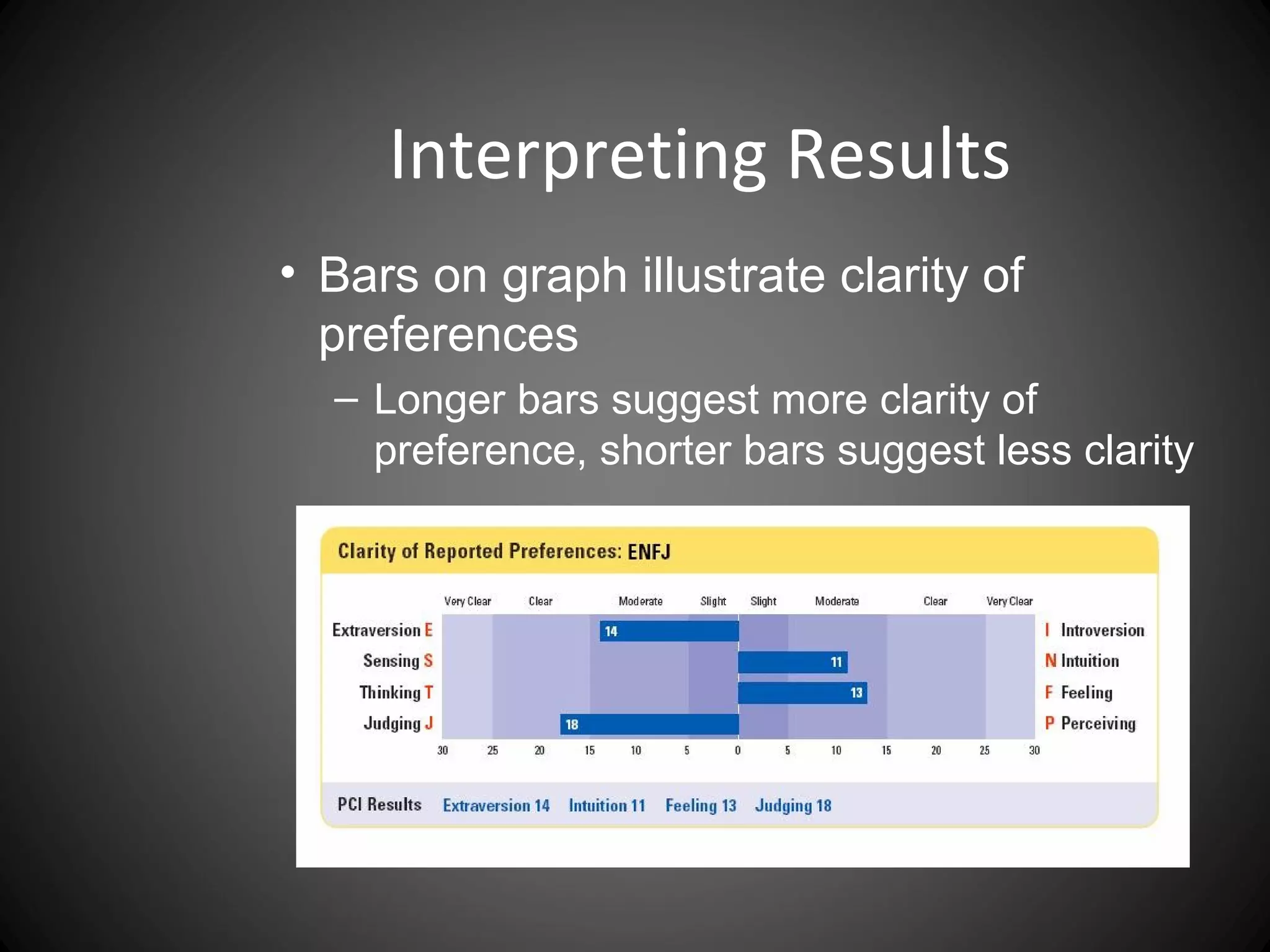
The document discusses the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality assessment. It explains that the MBTI is based on Carl Jung's theory of psychological types and assesses four dichotomies: Extraversion vs Introversion, Sensing vs Intuition, Thinking vs Feeling, and Judging vs Perceiving. It provides descriptions of each dichotomy and estimates of their prevalence in the US population. It notes that the MBTI aims to make Jung's theory of types understandable and useful for understanding personality differences.