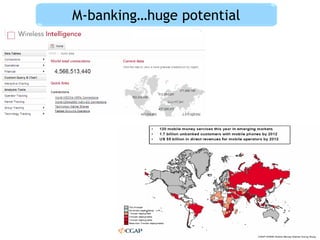
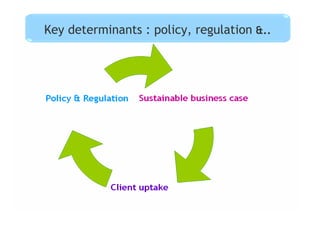
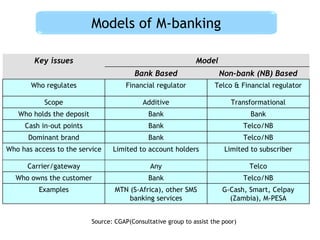
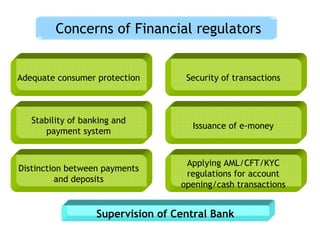
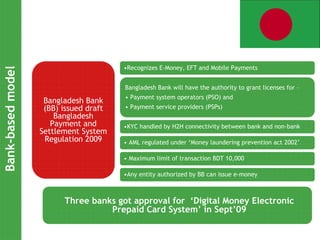
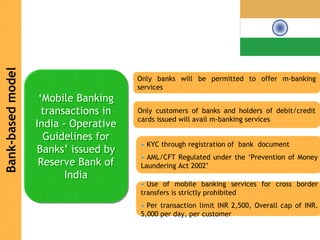
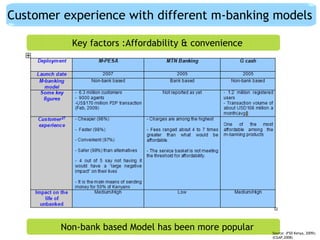
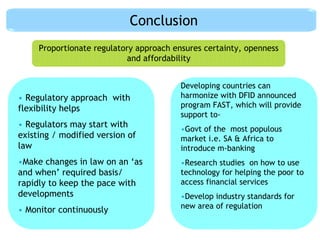
This document discusses regulatory frameworks for mobile banking (m-banking) in emerging markets. It outlines key models including bank-based models where banks regulate m-banking and non-bank based models where telecommunications companies and non-banks regulate m-banking. It provides examples of regulatory approaches and guidelines in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Kenya, and South Africa that illustrate considerations around know-your-customer (KYC) procedures, anti-money laundering (AML), transaction limits, and which entities can issue electronic money.