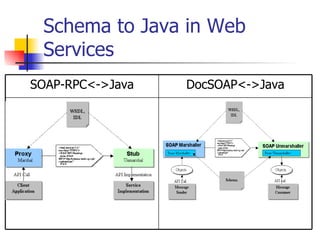
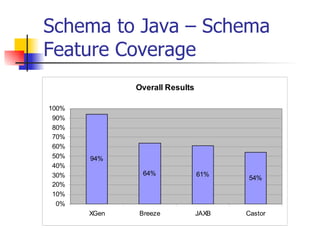
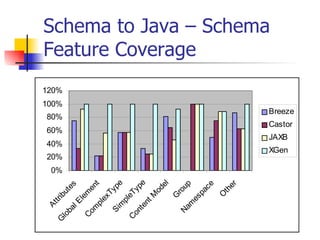
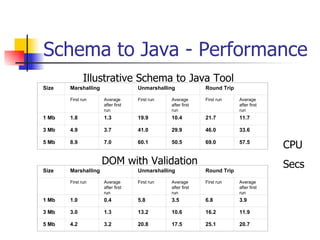
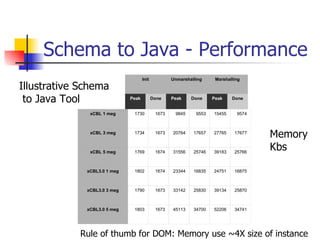
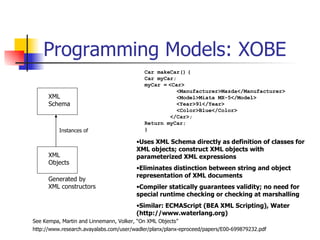
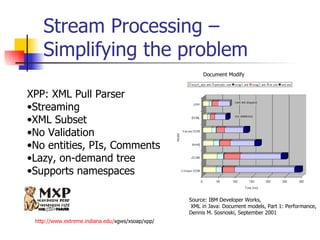
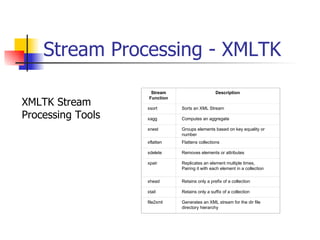
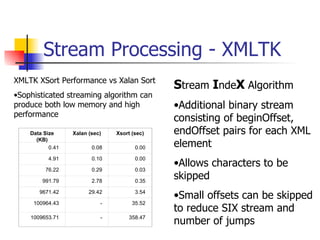
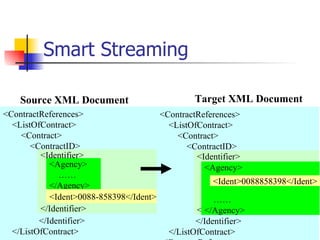
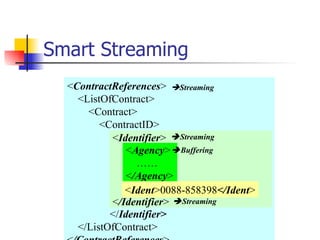
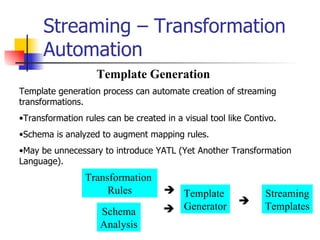
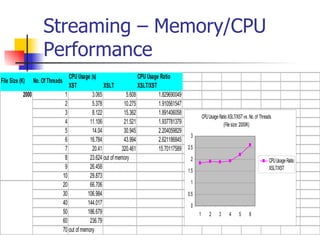
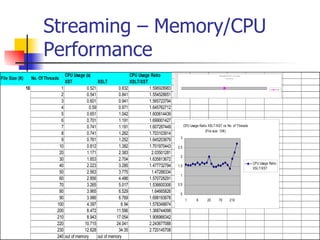
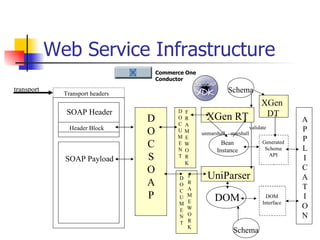
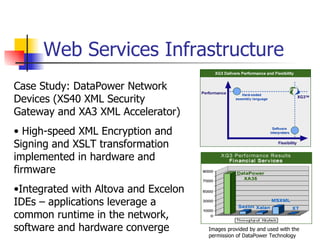
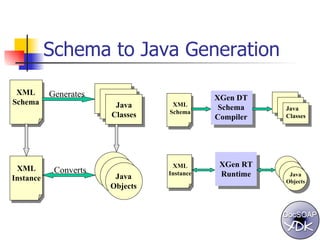
The document discusses the evolution of XML tools, focusing on third-generation tools that enhance programming models and performance, particularly through schema to Java generation. It highlights the simplification of the development process by reducing the need for XML experience while improving type checking and reliability. Performance comparisons of various XML processing approaches, including streaming and DOM, are also provided, demonstrating memory efficiency and execution time.
![Third Generation XML Tools Michael Leventhal [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thirdgenerationxmltools-091227233845-phpapp01/85/Mazda-Use-of-Third-Generation-Xml-Tools-1-320.jpg)





![Schema to Java Example package com.commerceone.samples.xdk; import com.commerceone.schemas.xdk.samples.Car_xsd.Car; import com.commerceone.schemas.xdk.samples.Car_xsd.types.CarType; import com.commerceone.xdk.castor.types.*; import com.commerceone.xdk.castor.excp.ConstraintValidationException; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.io.Writer; public class CarCreator { public static void main(String[] args) { try { CarCreator cc = new CarCreator(); Car car = cc.makeCar(); car.marshal(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public Car makeCar() throws ConstraintValidationException { Car car = new Car(); CarType ct = car.getCarTypeComplexType(); ct.setColor(new XString("Blue")); ct.setManufacturer(new XString("Mazda")); ct.setModel(new XString("Miata MX-5")); ct.setYear(new XInt(91)); ct.setForSale_Attribute(new XBoolean(true)); return car; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thirdgenerationxmltools-091227233845-phpapp01/85/Mazda-Use-of-Third-Generation-Xml-Tools-9-320.jpg)
![public class CarCreator { public static void main(String[] args) { try { CarCreator cc = new CarCreator(); Car car = cc.makeCar(); car.marshal(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public Car makeCar()throws ConstraintValidationException { Car car = new Car(); CarType ct = car.getCarTypeComplexType(); ct.setColor(new XString("Blue")); ct.setManufacturer(new XString("Mazda")); ct.setModel(new XString("Miata MX-5")); ct.setYear(new XInt(91)); ct.setForSale_Attribute(new XBoolean(true)); return car; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thirdgenerationxmltools-091227233845-phpapp01/85/Mazda-Use-of-Third-Generation-Xml-Tools-10-320.jpg)