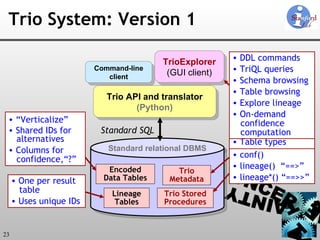
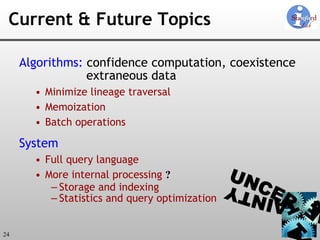
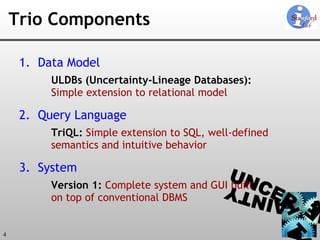
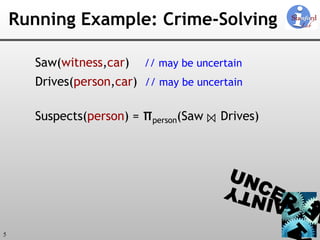
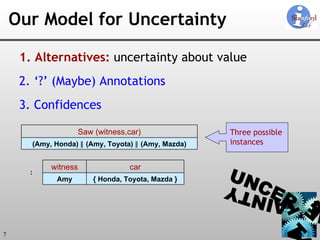
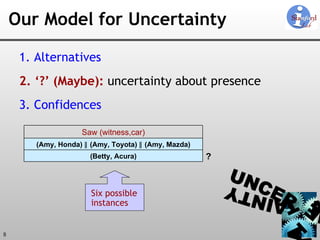
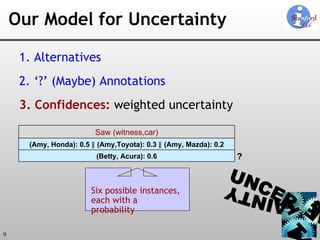
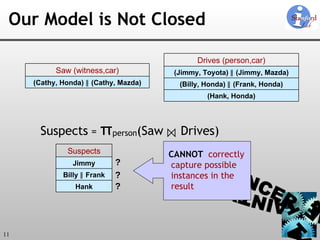
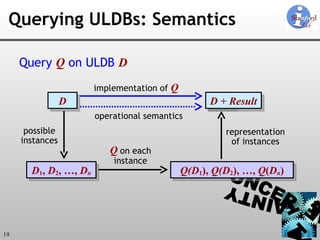
The document discusses 'Trio', a system designed for handling data uncertainty and lineage, utilizing uncertainty-lineage databases (ULDBs) and a query language called TriQL. It highlights the necessity of lineage for efficient and consistent representation of uncertain data, while detailing the system's components, operational semantics, and the models for managing uncertainty. Additionally, it outlines the current functionalities and future enhancements planned for the Trio system.


![Models for Uncertainty Our model (so far) is not especially new We spent some time exploring the space of models for uncertainty [ICDE 06, journal] Tension between understandability and expressiveness Our model is understandable But it is not complete, or even closed under common operations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trio-meeting-091227233850-phpapp01/85/Mazda-Trio-Meeting-10-320.jpg)

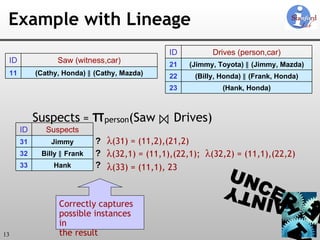
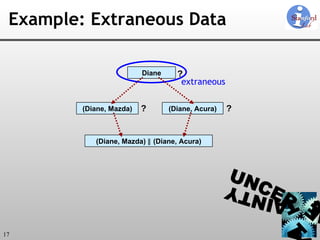
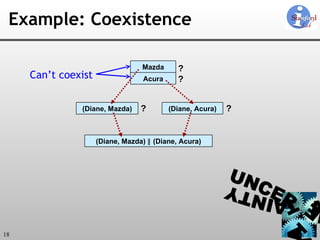
![Uncertainty-Lineage Databases (ULDBs) 1. Alternatives 2. ‘?’ (Maybe) Annotations 3. Confidences 4. Lineage ULDBs are closed and complete [VLDB 06]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trio-meeting-091227233850-phpapp01/85/Mazda-Trio-Meeting-14-320.jpg)


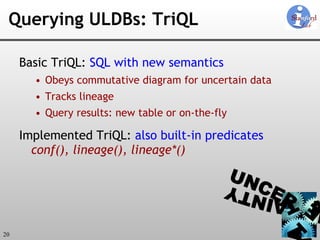
![Additional TriQL Constructs [Language manual on web site] “ Horizontal subqueries” Refer to tuple alternatives as a relation Unmerged (horizontal duplicates) Flatten , GroupAlts NoLineage , NoConf , NoMaybe Query-specified confidences [done] Data modification statements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trio-meeting-091227233850-phpapp01/85/Mazda-Trio-Meeting-21-320.jpg)