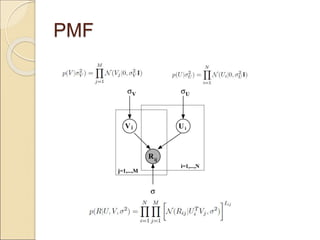
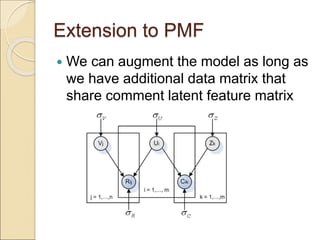
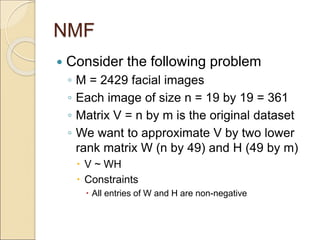
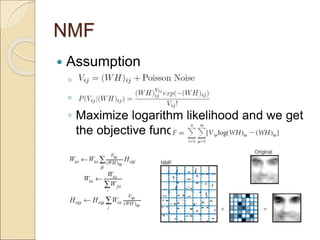
This document discusses different matrix factorization methods and their applications. It covers nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) and probabilistic matrix factorization (PMF) in more detail. For NMF, it describes using the method to learn the parts of objects from a dataset of facial images. For PMF, it discusses how the technique can be used for recommendation systems by factorizing a user-item rating matrix to predict unknown ratings.