1. The document discusses logical operators and functions in MATLAB. It describes element-wise and short-circuit logical operators like &, |, ~, &&, and ||.
2. Various logical functions are also covered, including find to find indices of non-zero elements, all to check if all elements are non-zero, and any to check if any elements are non-zero.
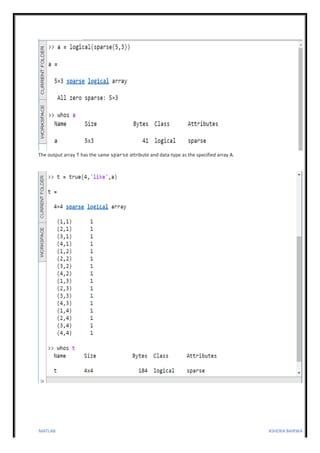
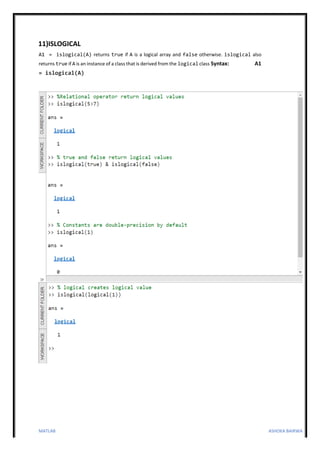
3. Functions are also described to represent true and false values using true and false, convert numeric values to logical using logical, and check if a variable is logical using islogical.



![MATLAB ASHOKA BAIRWA
7)ALL
Determine if all array elements are nonzero or true
Syntax: B = all(A)
B = all(A,'all')
B = all(A,dim)
B = all(A,vecdim)
B = all(A) tests along the first array dimension of A whose size does not equal 1, and determines if the
elements are all nonzero or logical 1 (true). In practice, all is a natural extension of the logical AND operator.
• If A is a vector, then all(A) returns logical 1 (true) if all the elements are nonzero and returns
logical 0 (false) if one or more elements are zero.
• If A is a nonempty matrix, then all(A) treats the columns of A as vectors and returns a row
vector of logical 1s and 0s.
• If A is an empty 0-by-0 matrix, then all(A) returns logical 1 (true).
• If A is a multidimensional array, then all(A) acts along the first array dimension whose size does
not equal 1 and returns an array of logical values. The size of this dimension becomes 1, while the
sizes of all other dimensions remain the same.
B = all(A,'all') tests over all elements of A. This syntax is valid for MATLAB® versions R2018b and later.
B = all(A,dim) tests elements along dimension dim. The dim input is a positive integer scalar.
B = all(A,vecdim) tests elements based on the dimensions specified in the vector vecdim.
For example, if A is a matrix, then all(A,[1 2]) tests over all elements in A, since every element of a matrix is
contained in the array slice defined by dimensions 1 and 2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabpractical-4-230126105309-7849b744/85/Matlab-practical-4-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![MATLAB ASHOKA BAIRWA
8)ANY
Determine if any array elements are nonzero
Syntax: B = any(A)
B = any(A,'all')
B = any(A,dim)
B = any(A,vecdim)
B = any(A) tests along the first array dimension of A whose size does not equal 1, and determines if any
element is a nonzero number or logical 1 (true). In practice, any is a natural extension of the logical OR
operator.
• If A is a vector, then B = any(A) returns logical 1 (true) if any of the elements of A is a nonzero
number or is logical 1, and returns logical 0 (false) if all the elements are zero.
• If A is a nonempty, nonvector matrix, then B = any(A) treats the columns of A as vectors,
returning a row vector of logical 1s and 0s.
• If A is an empty 0-by-0 matrix, any(A) returns logical 0 (false).
• If A is a multidimensional array, any(A) acts along the first array dimension whose size does not
equal 1 and returns an array of logical values. The size of this dimension becomes 1, while the sizes
of all other dimensions remain the same.
B = any(A,'all') tests over all elements of A. This syntax is valid for MATLAB® versions R2018b and later.
B = any(A,dim) tests elements along dimension dim. The dim input is a positive integer scalar.
B = any(A,vecdim) tests elements based on the dimensions specified in the vector vecdim.
For example, if A is a matrix, then any(A,[1 2]) tests over all elements in A, since every element of a matrix
is contained in the array slice defined by dimensions 1 and 2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabpractical-4-230126105309-7849b744/85/Matlab-practical-4-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![MATLAB ASHOKA BAIRWA
9)FALSE
Logical 0 (false)
Syntax: false
F = false(n)
F = false(sz)
F = false(sz1,...,szN)
F = false(___,'like',p)
false is shorthand for the logical value 0. F =
false(n) is an n-by-n array of logical zeros.
F = false(sz) is an array of logical zeros where the size vector, sz, defines size(F). For example,
false([2 3]) returns a 2-by-3 array of logical zeros.
F = false(sz1,...,szN) is a sz1-by-...-by-szN array of logical zeros where sz1,...,szN indicates
the size of each dimension. For example, false(2,3) returns a 2-by-3 array of logical zeros.
F = false(___,'like',p) returns an array of logical zeros of the same sparsity as the logical variable p
using any of the previous size syntaxes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabpractical-4-230126105309-7849b744/85/Matlab-practical-4-pdf-7-320.jpg)
![MATLAB ASHOKA BAIRWA
10)FIND
Find indices and values of nonzero elements
Syntax: k = find(X)
k = find(X,n) k =
find(X,n,direction)
[row,col] = find(___)
[row,col,v] = find(___)
k = find(X) returns a vector containing the linear indices of each nonzero element in array X.
• If X is a vector, then find returns a vector with the same orientation as X.
• If X is a multidimensional array, then find returns a column vector of the linear indices of the
result.
k = find(X,n) returns the first n indices corresponding to the nonzero elements in X.
k = find(X,n,direction), where direction is 'last', finds the last n indices corresponding to
nonzero elements in X. The default for direction is 'first', which finds the first n indices corresponding
to nonzero elements.
[row,col] = find(___) returns the row and column subscripts of each nonzero element in array X
using any of the input arguments in previous syntaxes.
[row,col,v] = find(___) also returns vector v, which contains the nonzero elements of X.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabpractical-4-230126105309-7849b744/85/Matlab-practical-4-pdf-8-320.jpg)



![MATLAB ASHOKA BAIRWA
13)TRUE
true(n) is much faster and more memory efficient than logical(true(n)). Logical 1
(true)
Syntax: true
T = true(n)
T = true(sz)
T = true(sz1,...,szN)
T = true(___,'like',p)
true is shorthand for the logical value 1. T =
true(n) is an n-by-n matrix of logical ones.
T = true(sz) is an array of logical ones where the size vector, sz, defines size(T). For example,
true([2 3]) returns a 2-by-3 array of logical ones.
T = true(sz1,...,szN) is a sz1-by-...-by-szN array of logical ones where sz1,...,szN indicates the
size of each dimension. For example, true(2,3) returns a 2-by-3 array of logical ones.
T = true(___,'like',p) returns an array of logical ones of the same sparsity as the logical variable p using
any of the previous size syntaxes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabpractical-4-230126105309-7849b744/85/Matlab-practical-4-pdf-13-320.jpg)