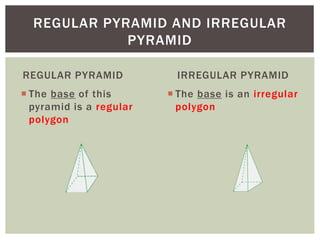
This document defines and provides details about different types of pyramids in mathematics. It begins with a brief history of pyramids and Egyptian mathematics. It then defines what a pyramid is and describes right pyramids, oblique pyramids, regular pyramids, irregular pyramids, convex pyramids, and concave pyramids. The document also covers types of pyramids based on their base, surface area, volume, frustums of pyramids, and includes examples and formulas. References for additional information on pyramids are provided at the end.