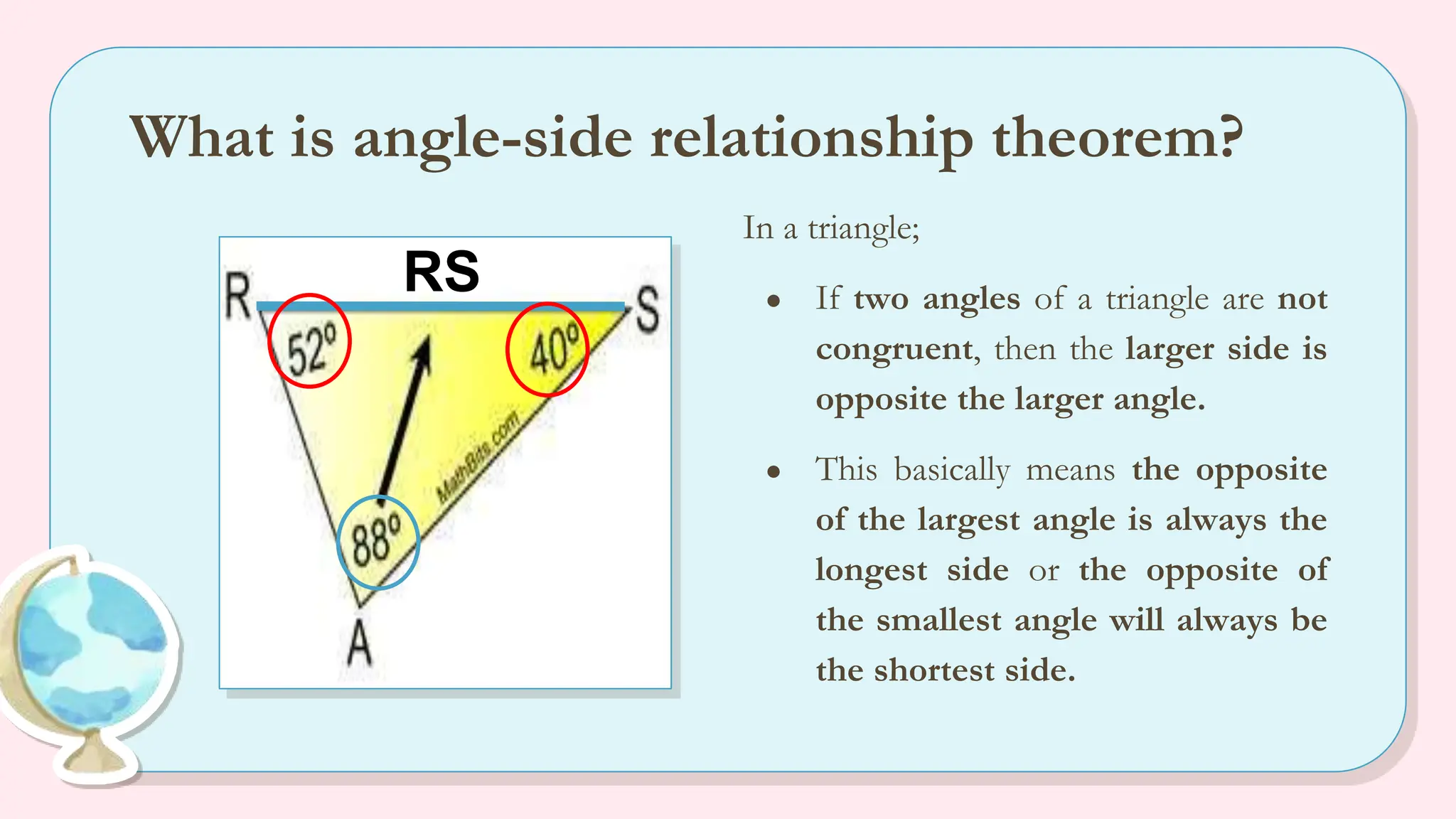
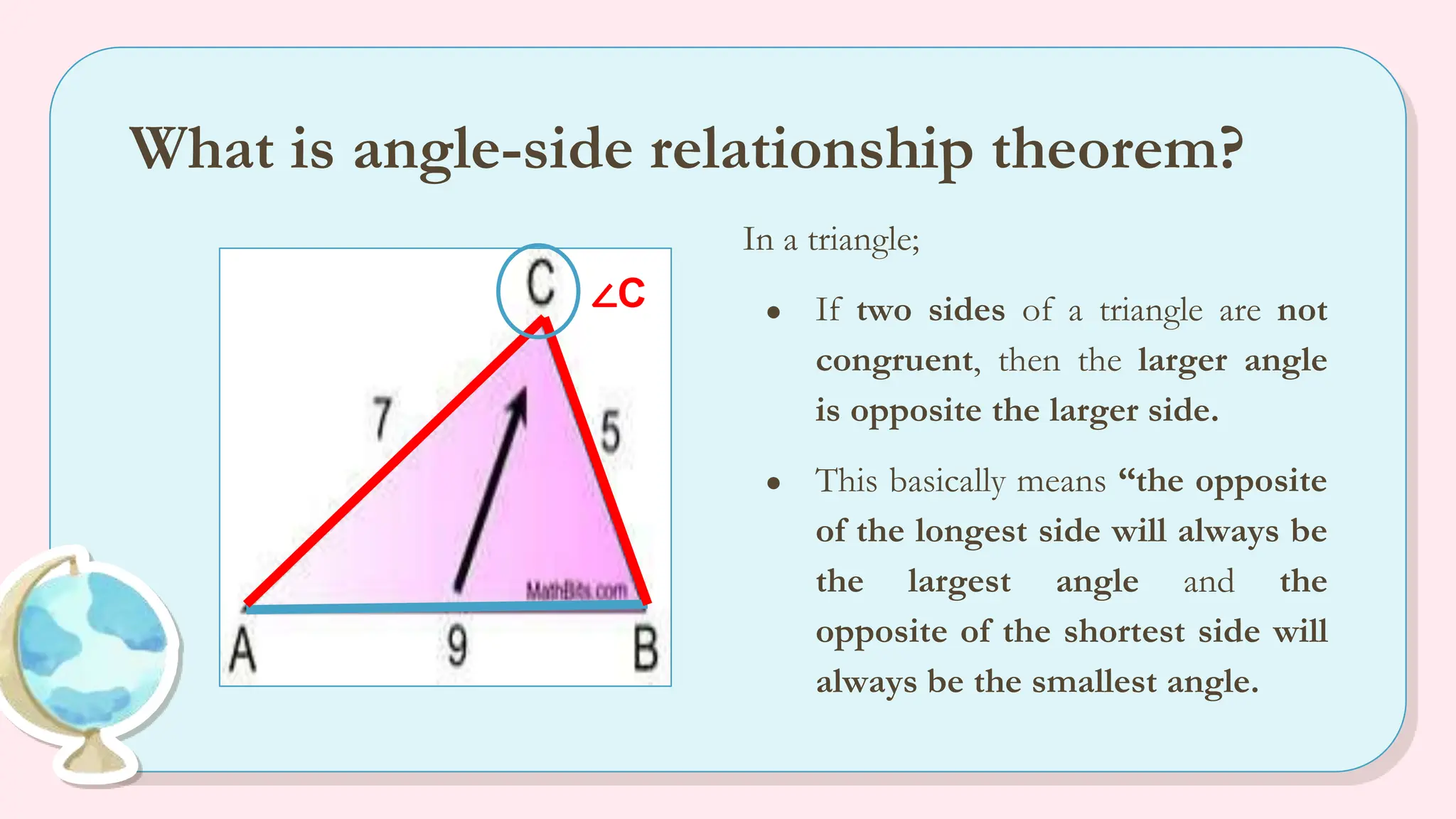
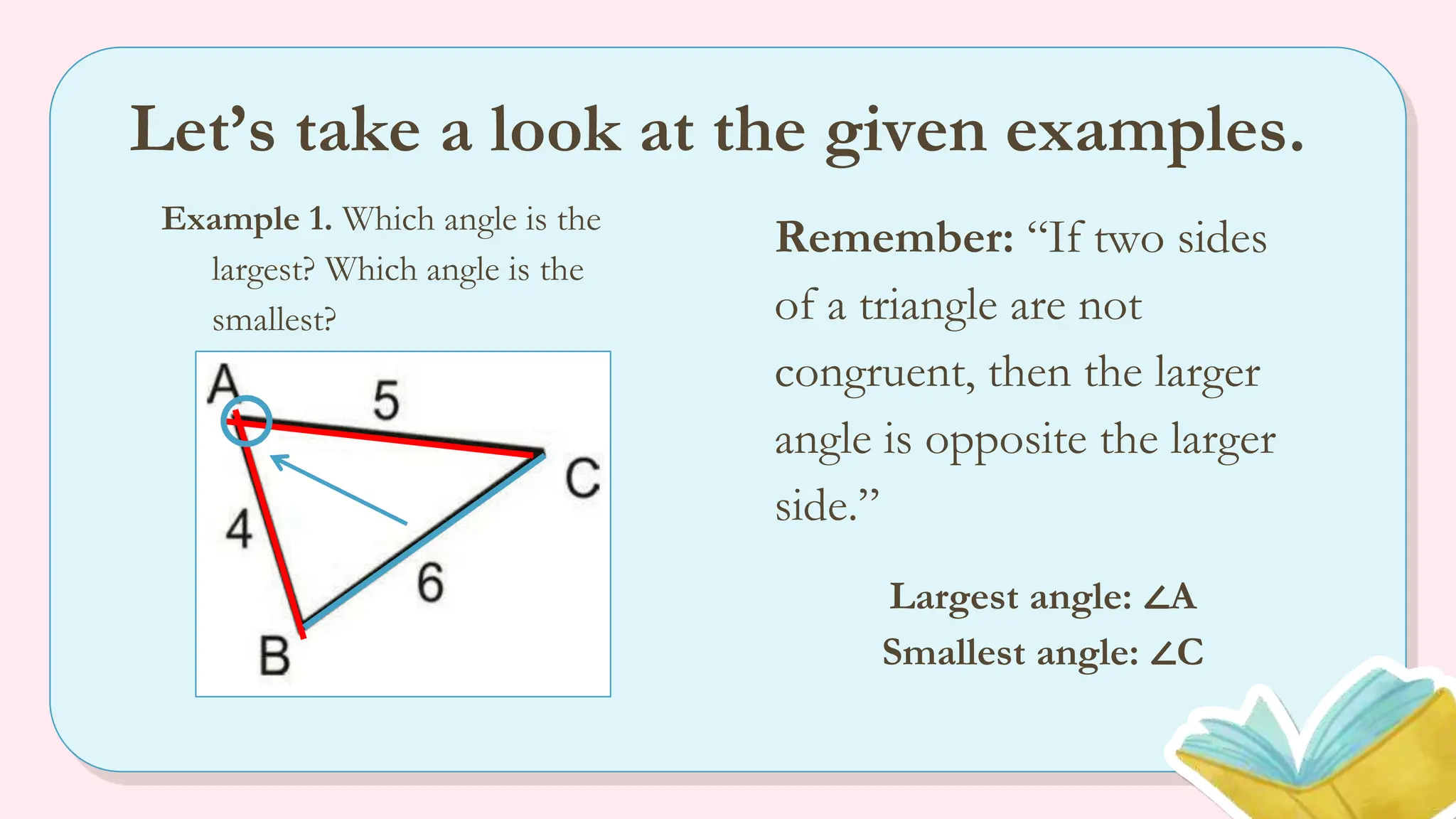
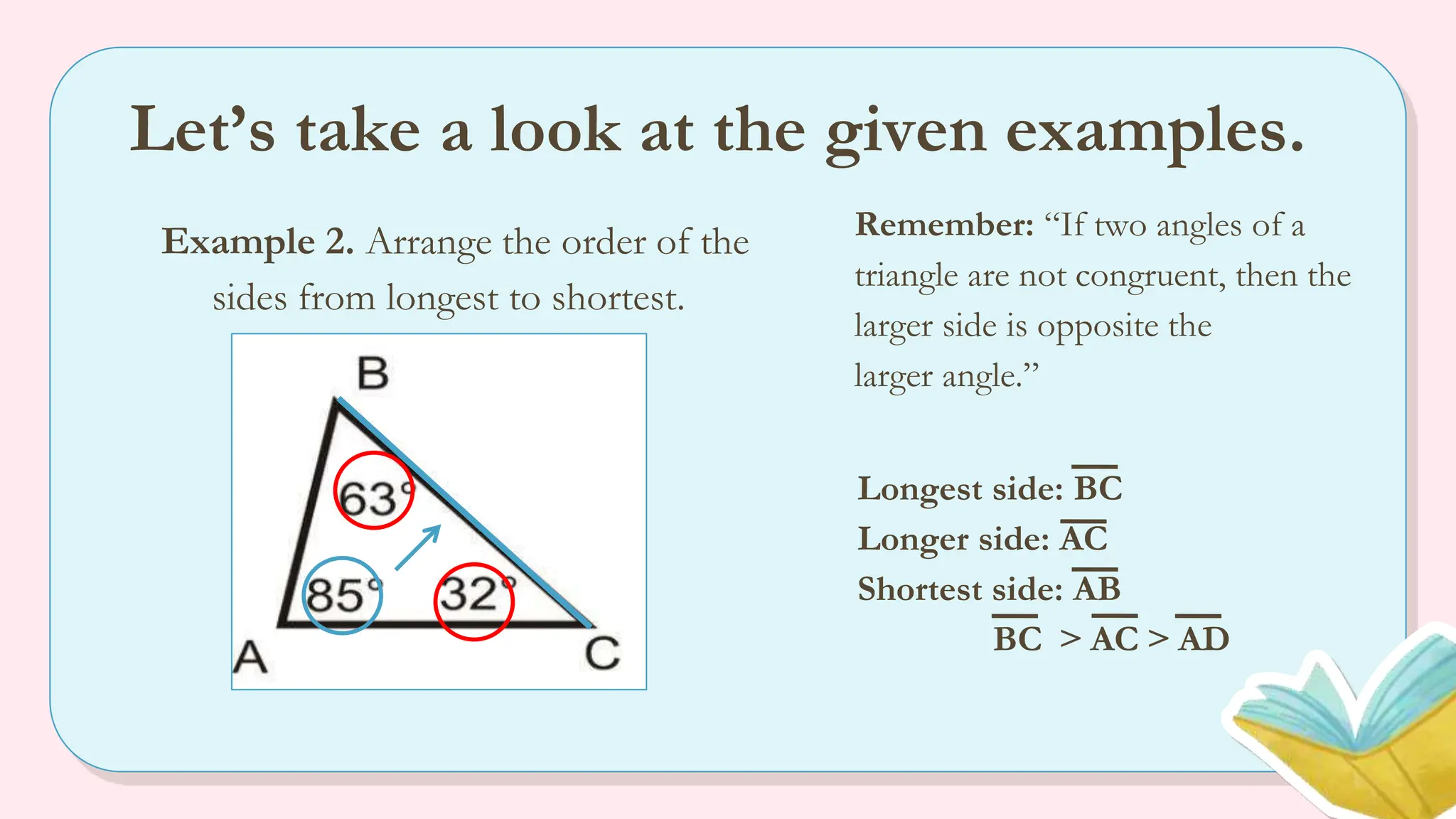
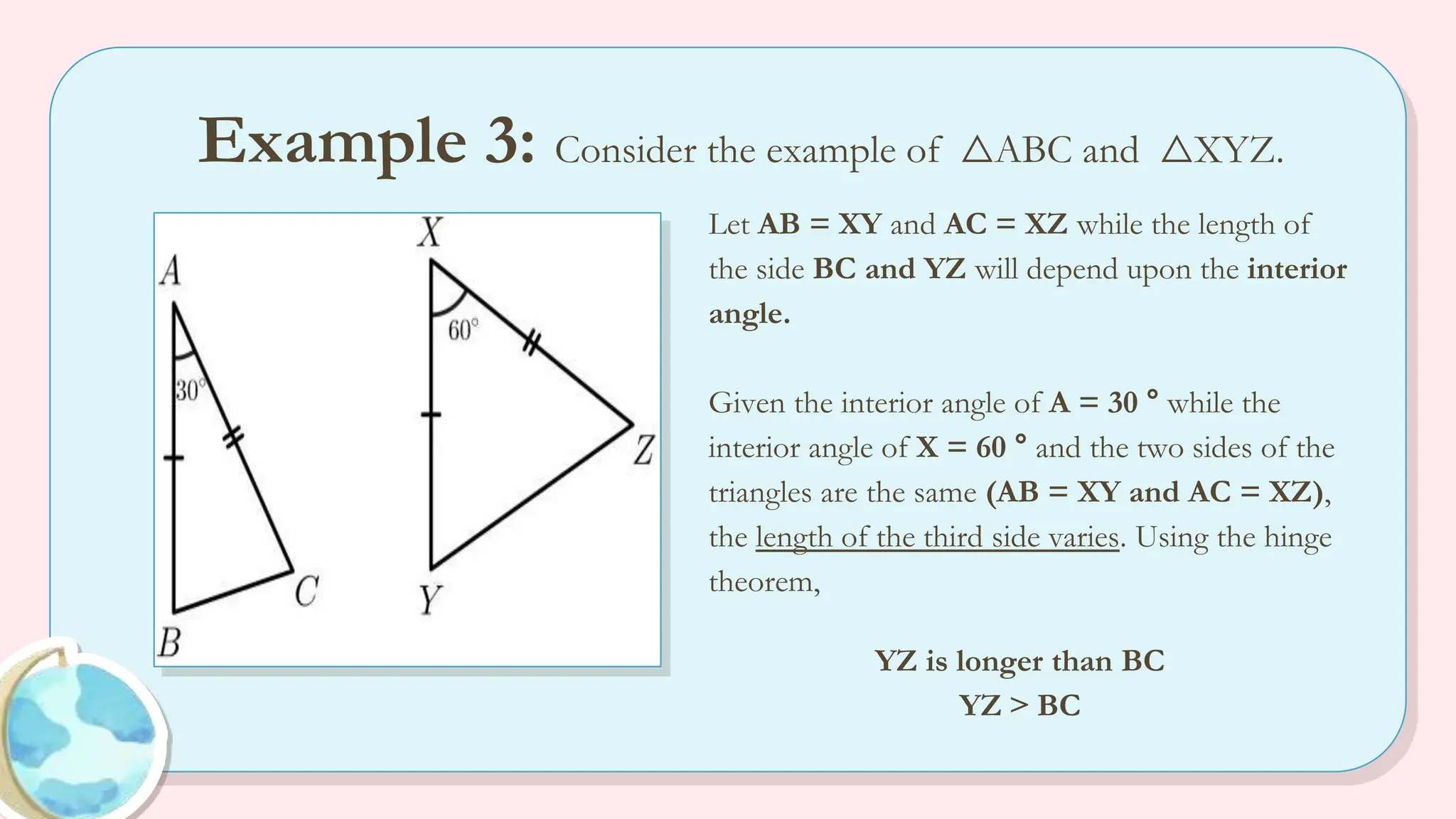
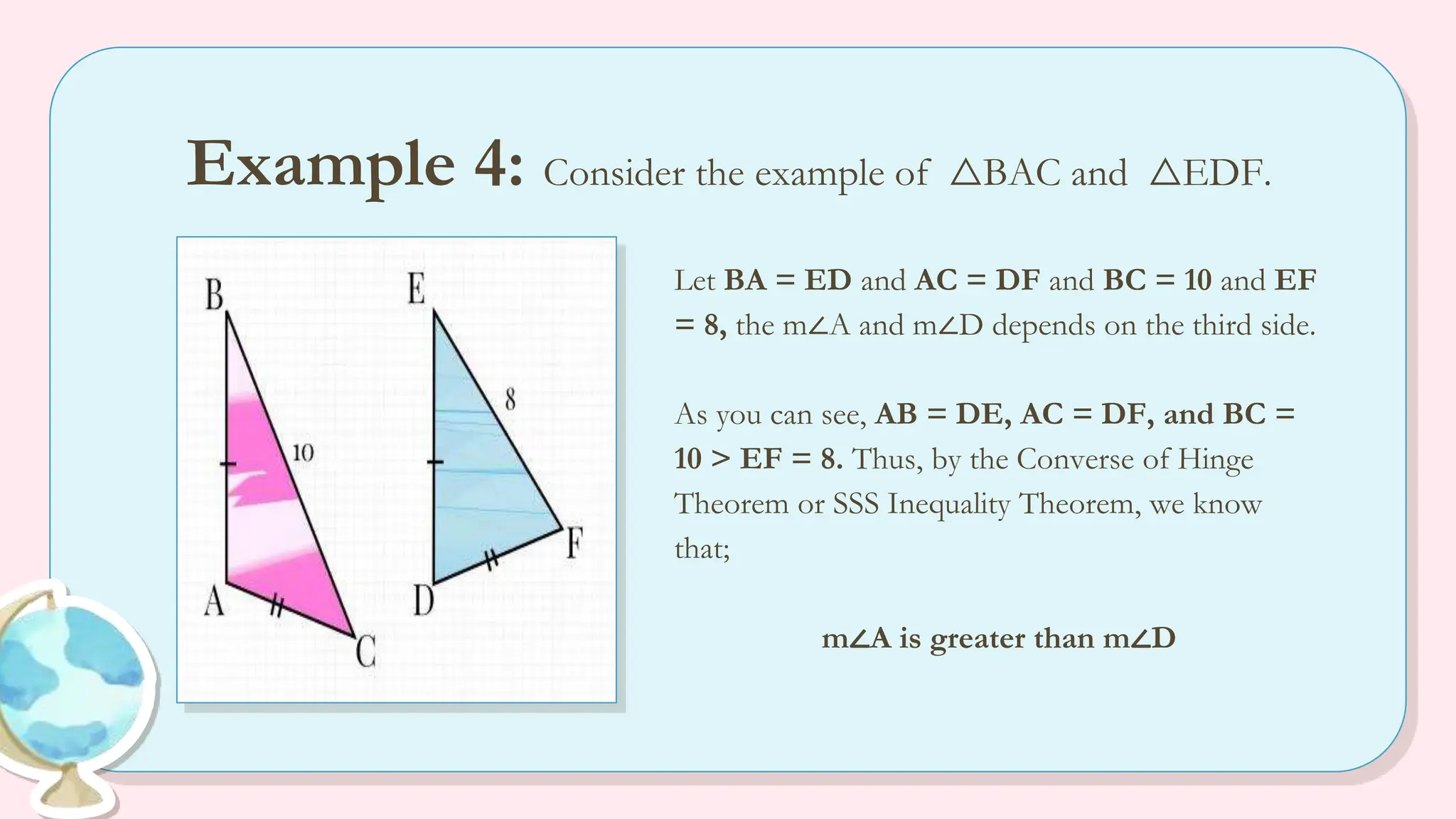
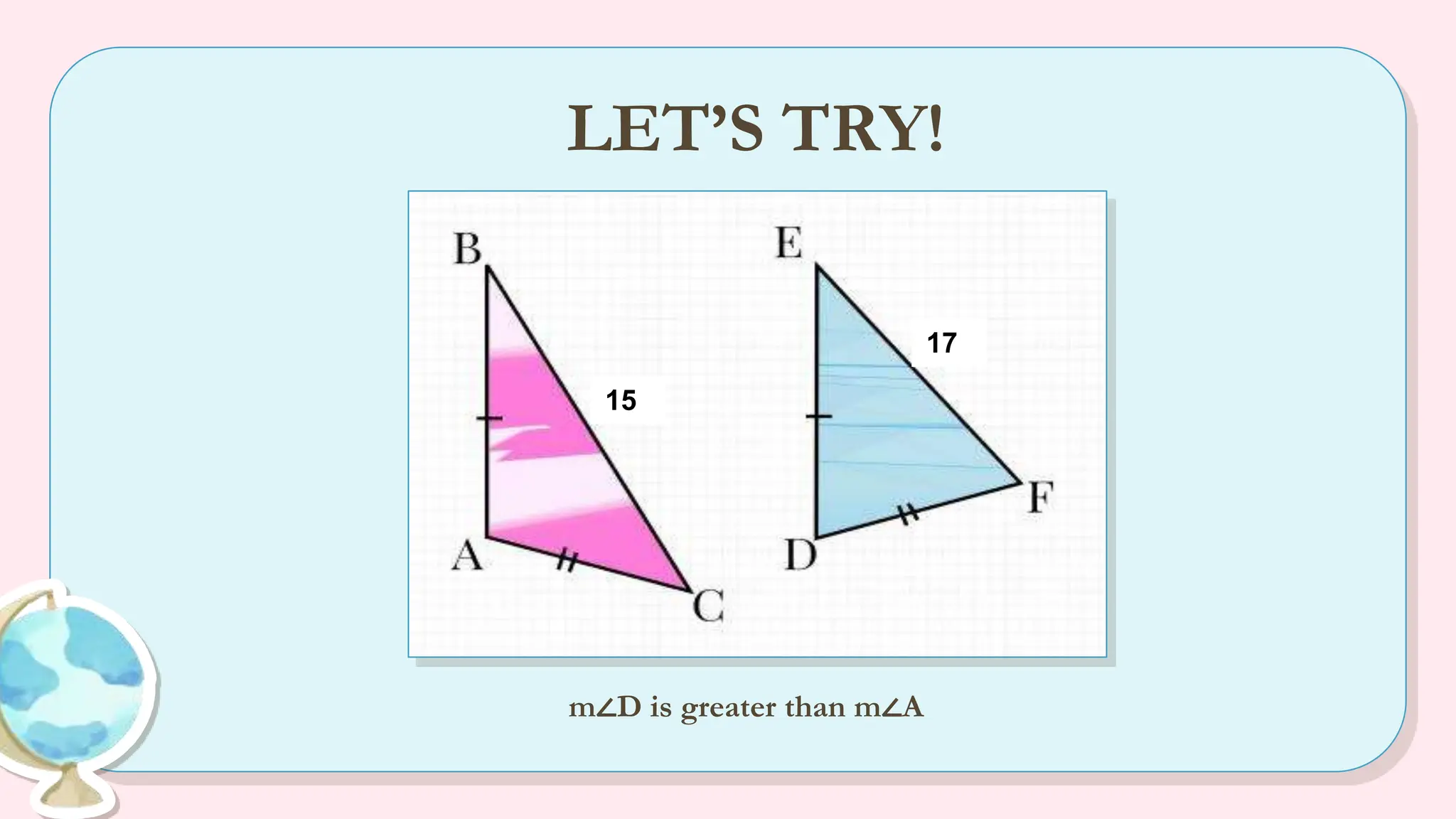
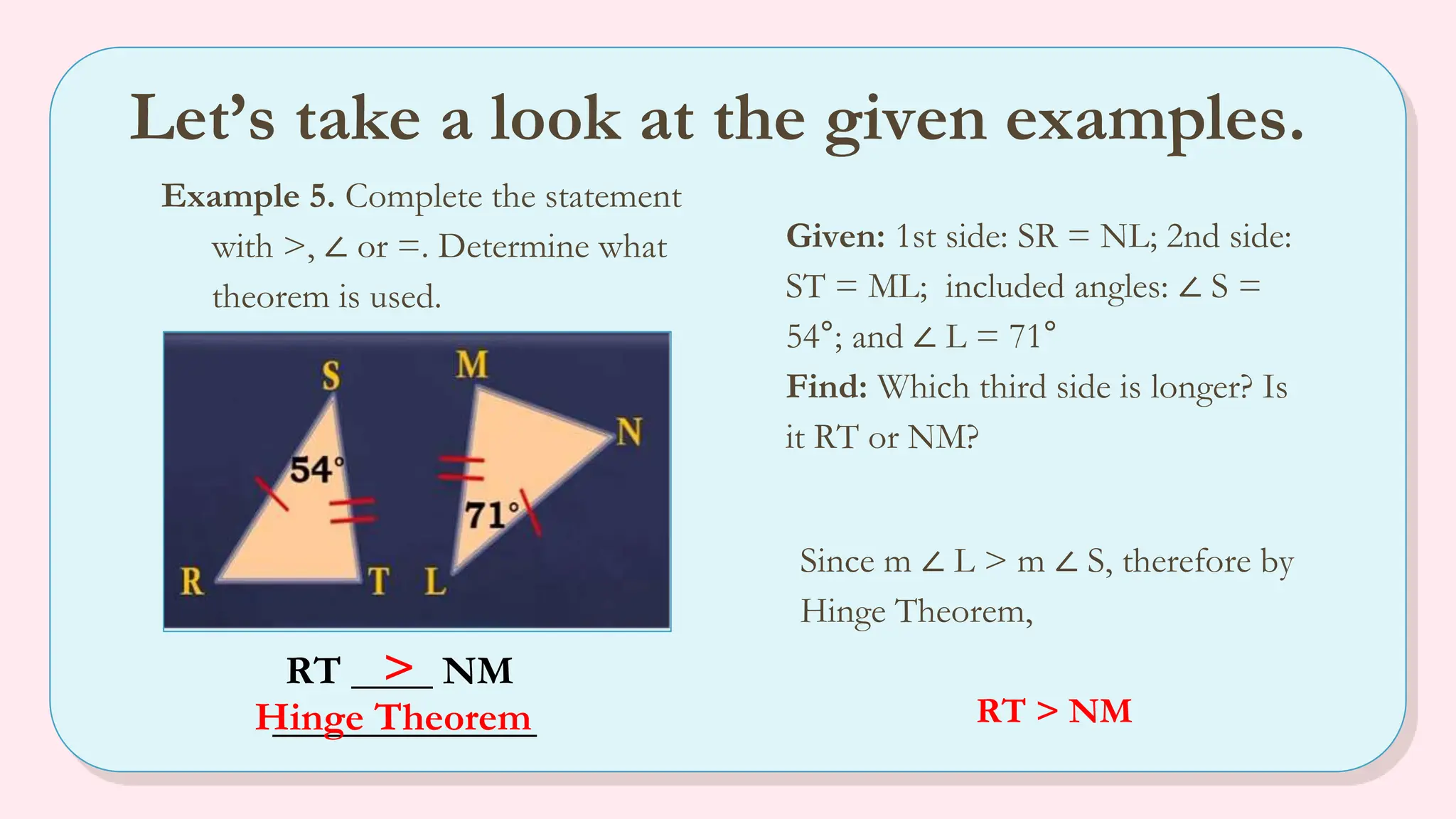
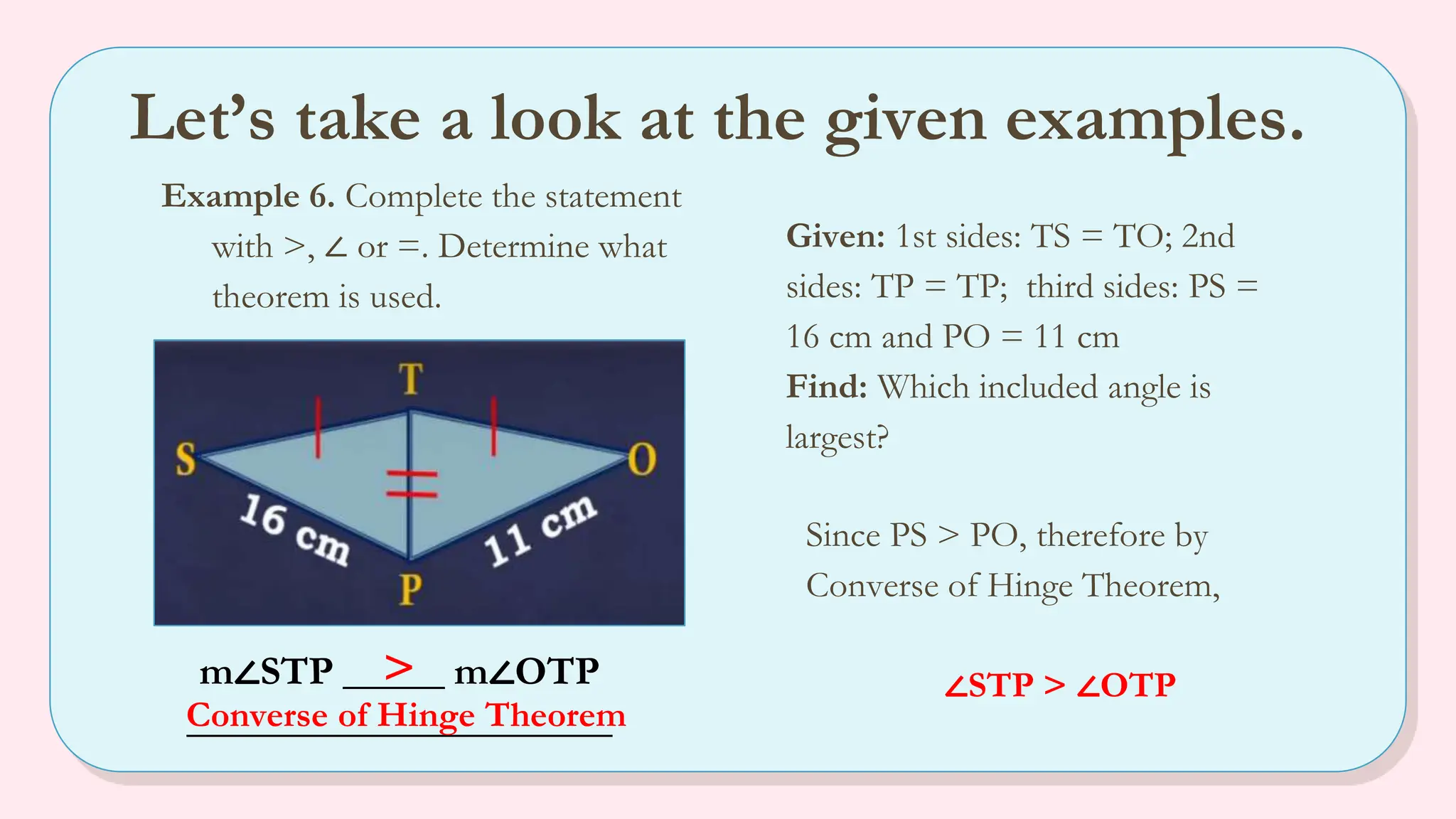
The document explains the angle-side relationship theorem, which states that in a triangle, the larger angle is opposite the longer side and vice versa. It also covers the hinge theorem, illustrating how two congruent sides and a greater included angle indicates a longer third side, and the converse hinge theorem, which states that a longer third side correlates with a larger included angle. Multiple examples are provided to clarify these concepts, along with links to informative videos.