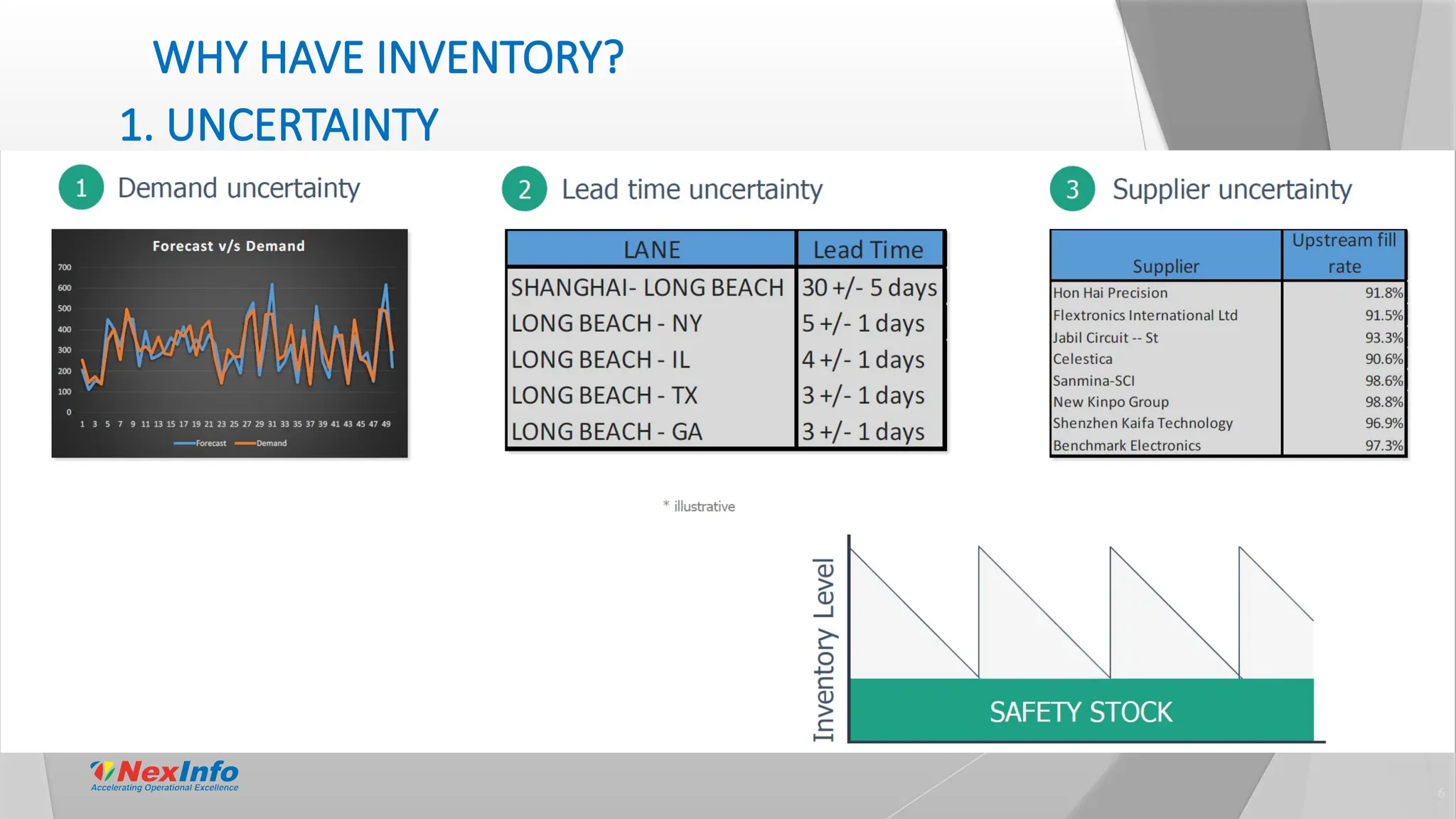
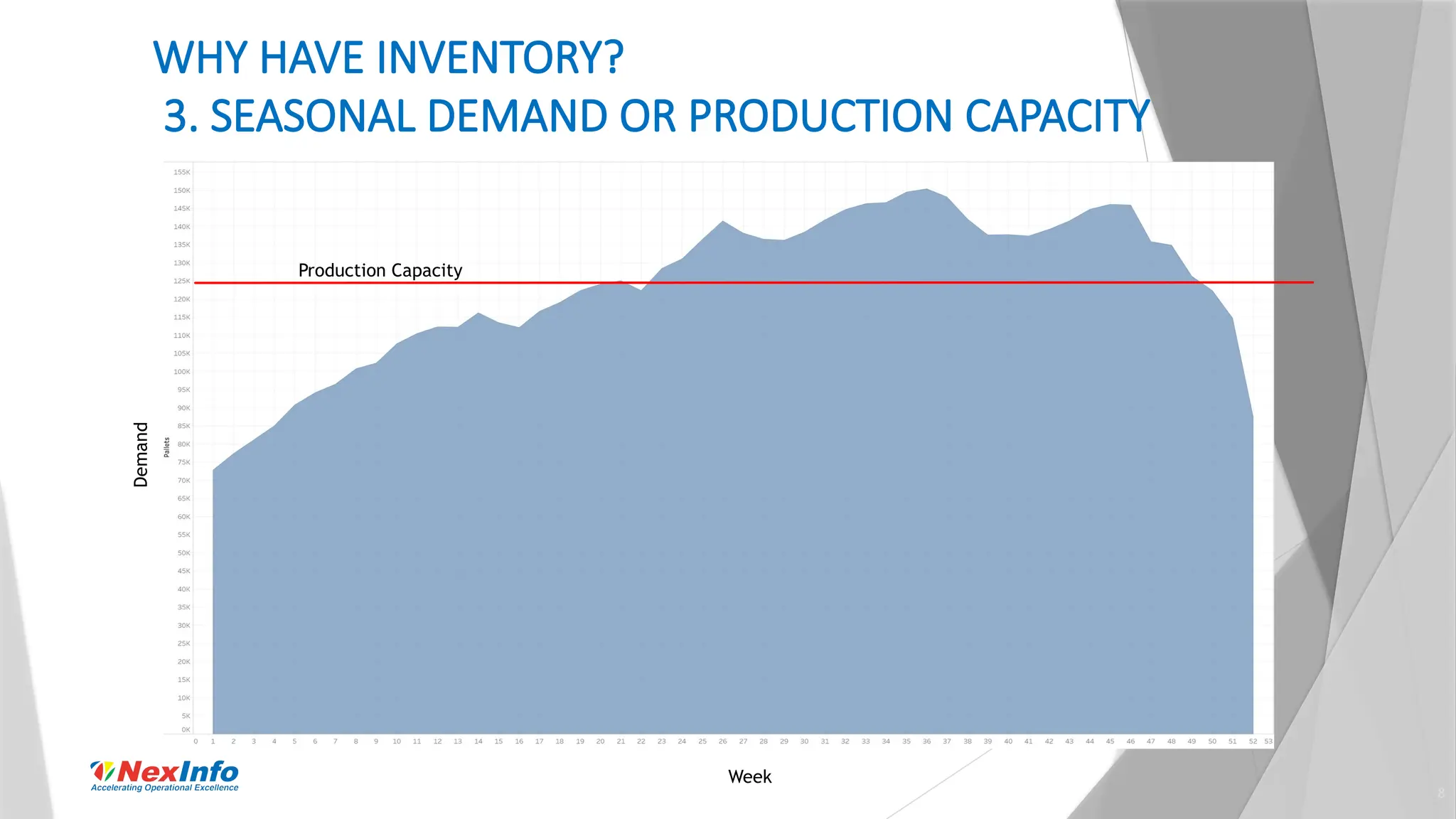
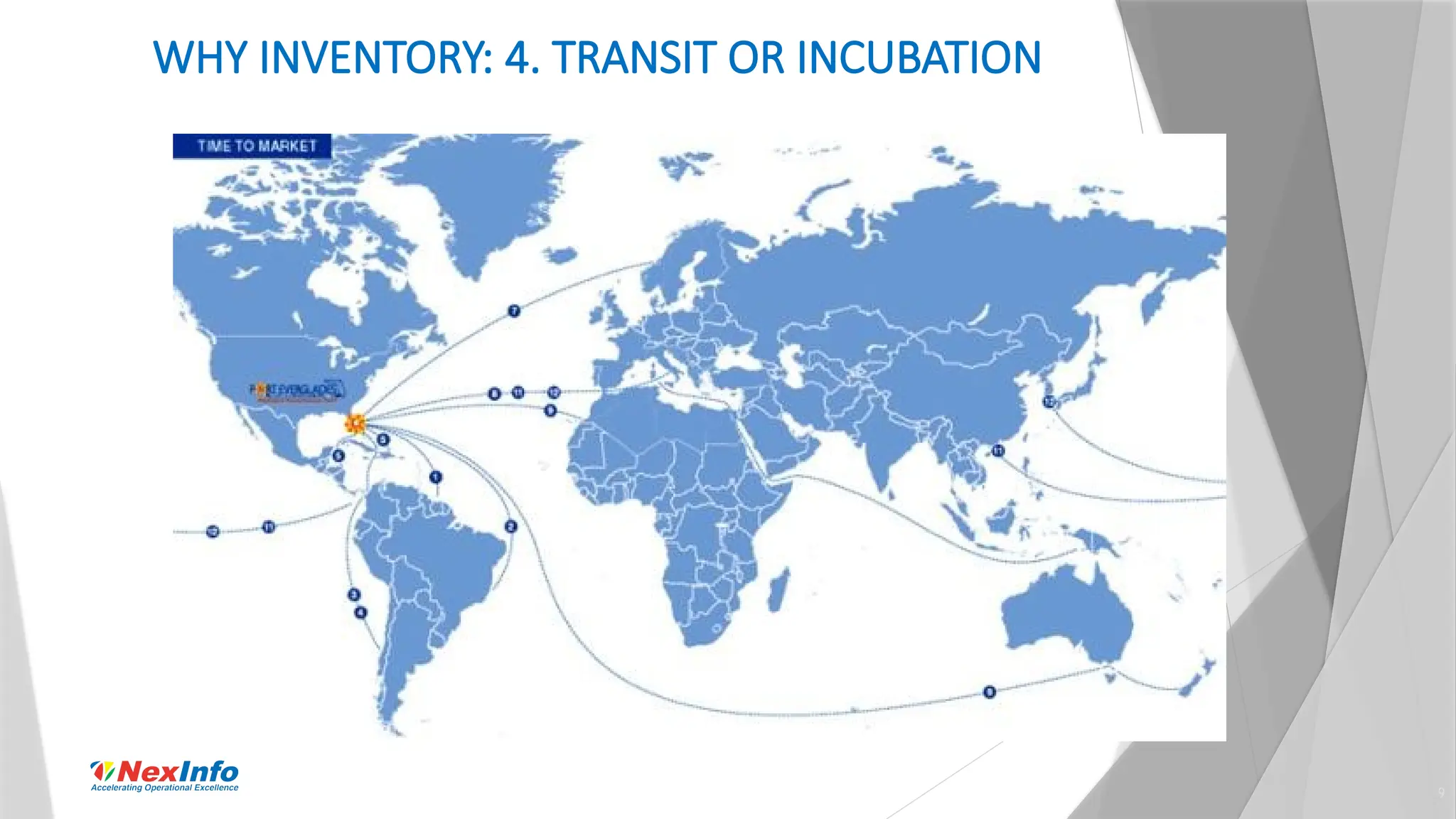
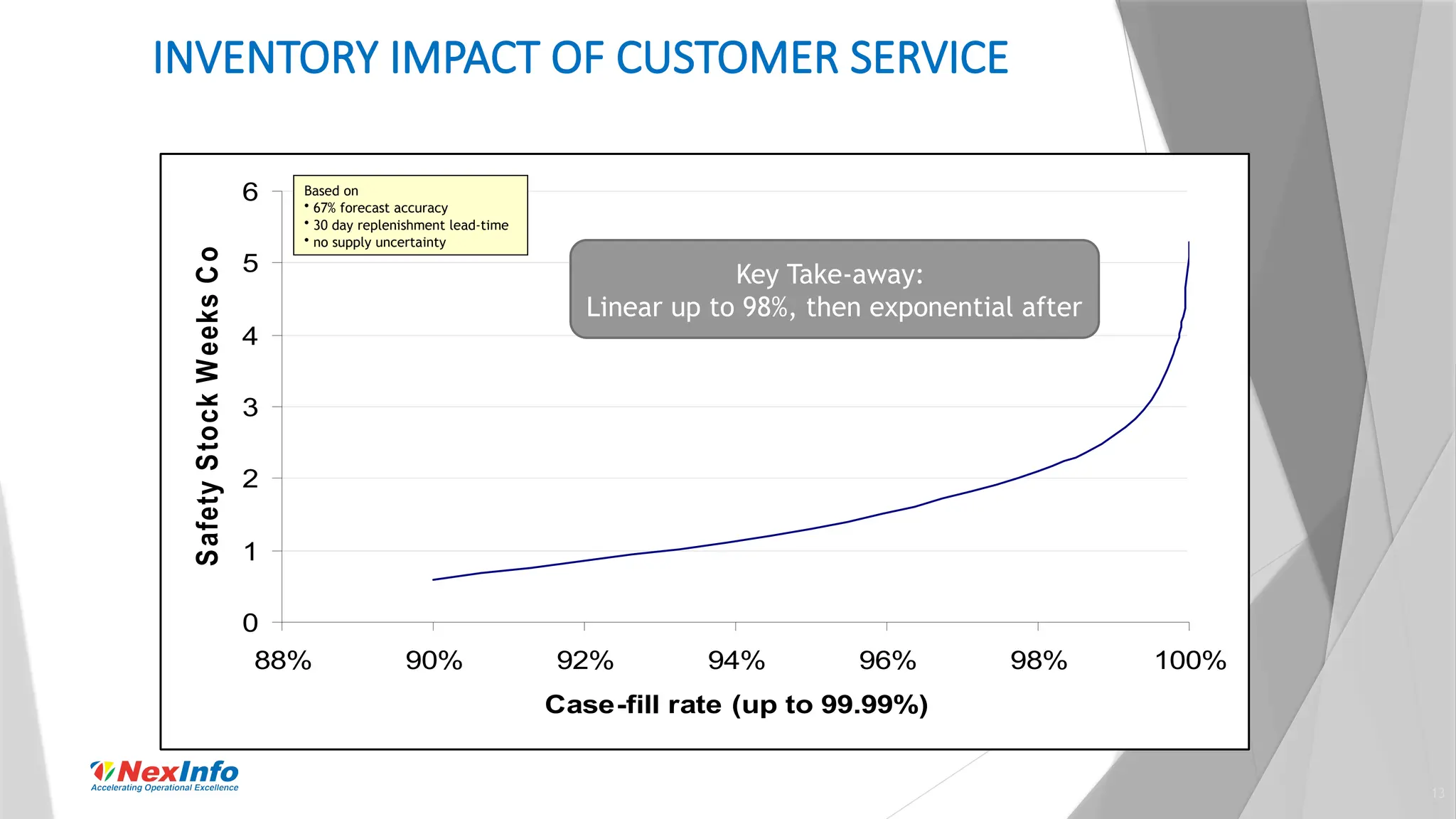
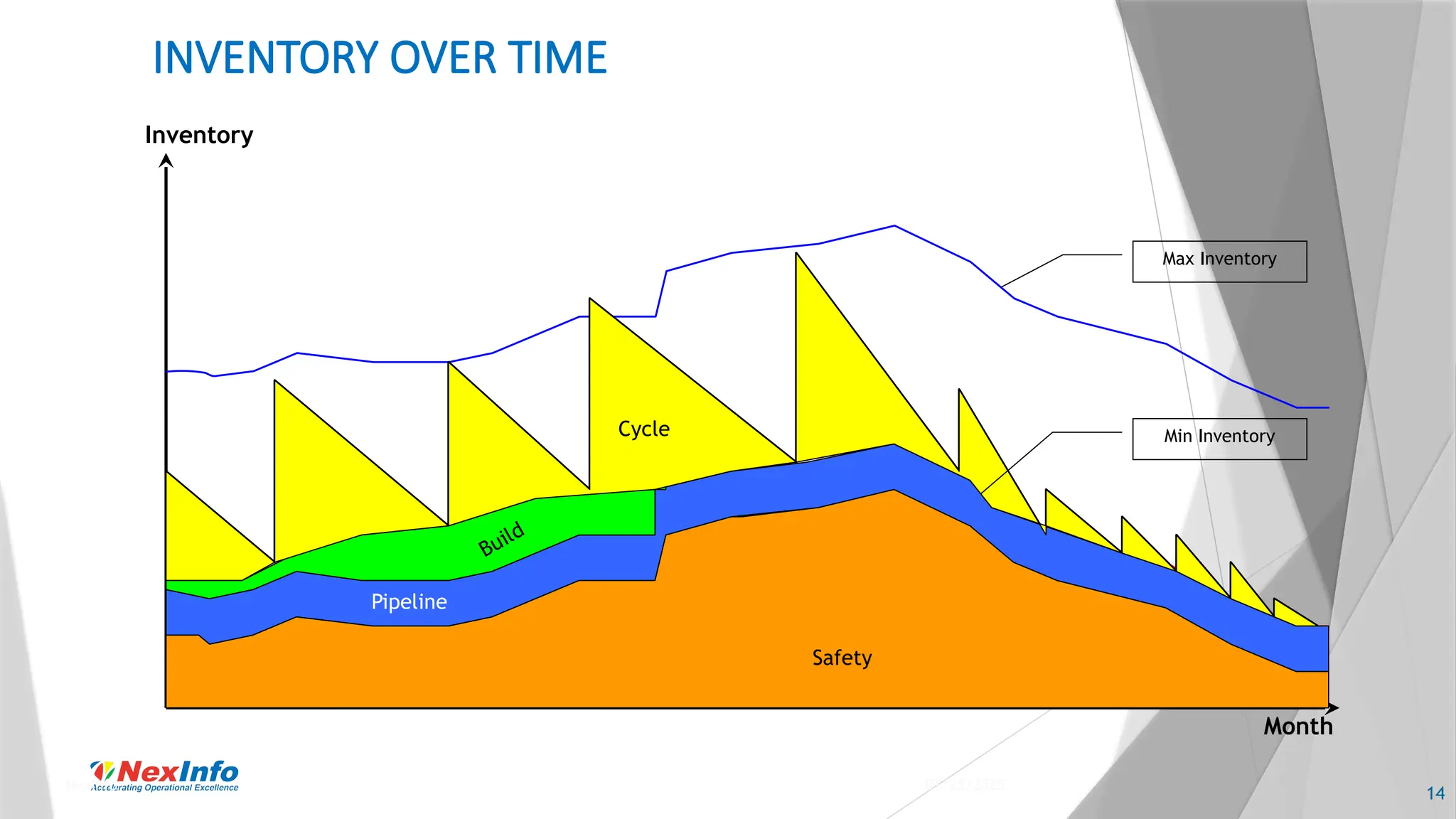
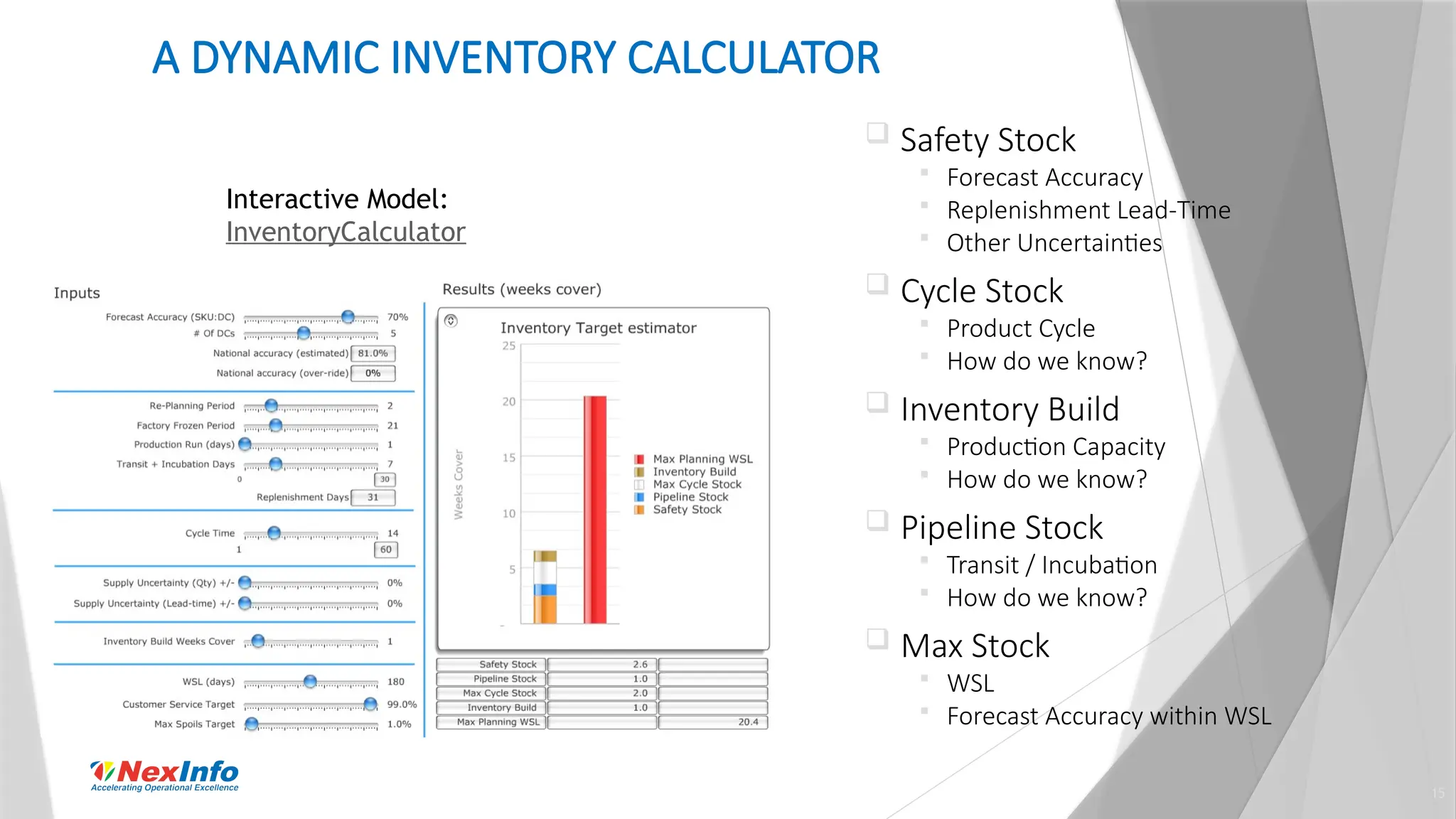
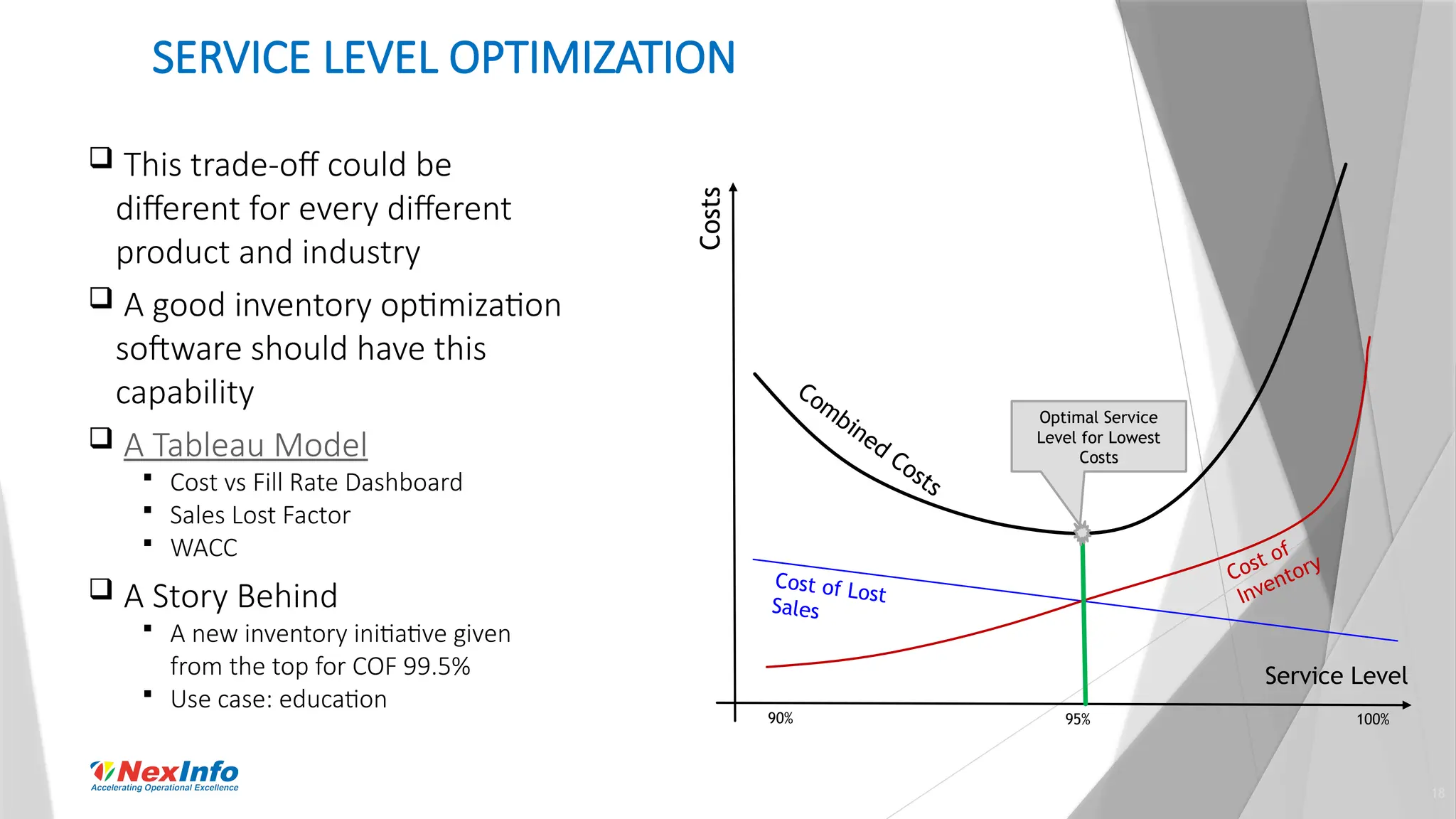
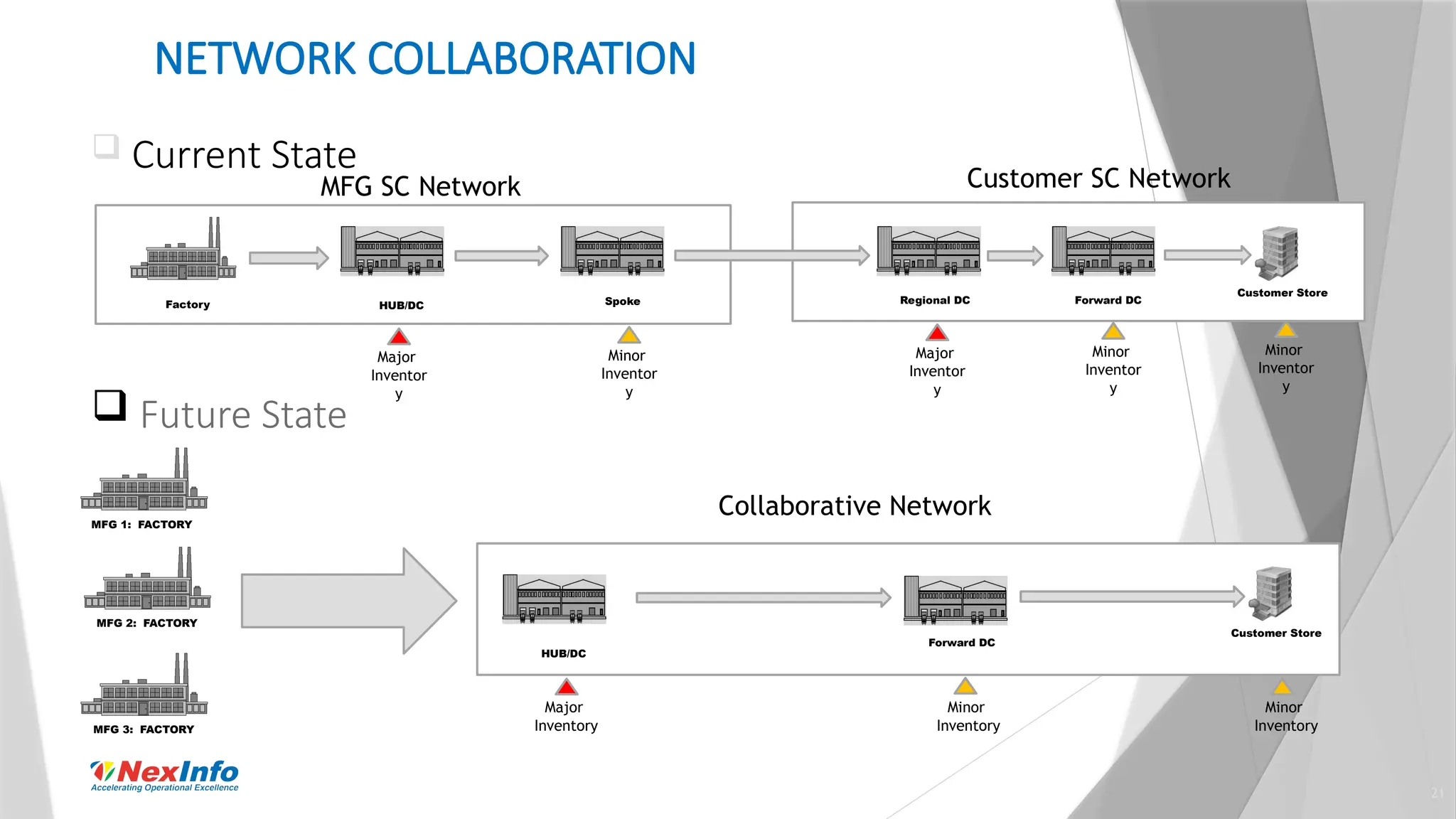
NexInfo is a consulting firm founded in 1999, specializing in operational excellence through business process and software consulting services, with a focus on areas such as supply chain optimization and inventory management. Robert Wang, a key presenter, is an expert in utilizing various analytic techniques to solve complex business challenges, having experience in management consulting and academia. The document discusses the significance of inventory management, types of inventory, measurement methods, and strategies for optimization to enhance customer service and reduce operational costs.