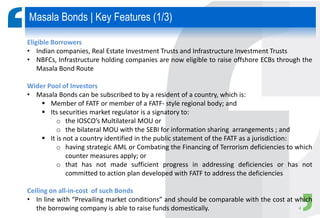
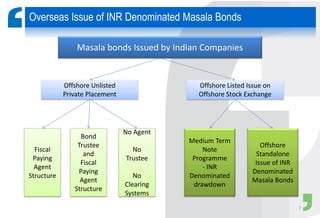
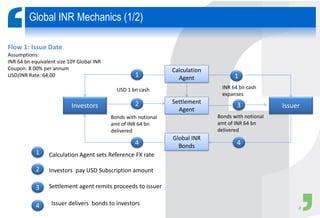
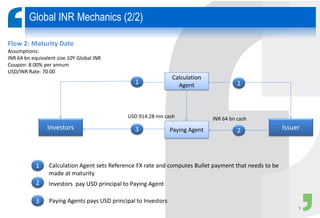
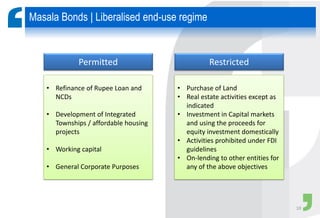
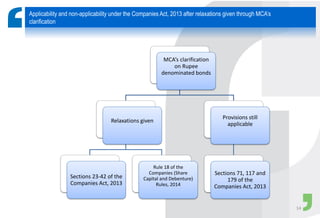
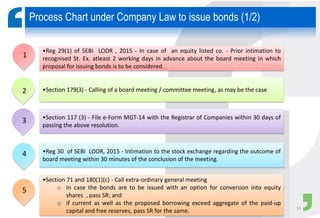
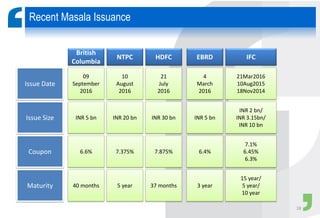
Masala bonds allow Indian entities to raise money from overseas markets denominated in Indian rupees rather than foreign currency. This shields issuers from currency risk while transferring that risk to offshore investors. Eligible issuers include Indian companies, REITs, InvITs, and NBFCs. Investors must be from jurisdictions meeting certain FATF criteria. Minimum bond maturity is 3 years. Individual issuers are limited to raising $750 million equivalent per year through masala bonds. Indian regulators provide certain exemptions from prospectus requirements and other regulations for masala bond issuances. Key considerations for offshore investors include access limitations, settlement risk, potential arbitrage opportunities from currency movements, and liquidity concerns.