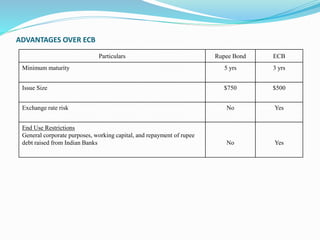
Rupee bonds allow Indian entities to raise money from overseas markets in rupees rather than foreign currency. The Reserve Bank of India introduced rupee bonds to liberalize debt raising options from overseas markets and relax restrictions on external commercial borrowings. Rupee bonds must have a minimum maturity of 5 years, can be used for general corporate purposes and repaying rupee debt, and do not expose issuers to exchange rate risk like external commercial borrowings. Eligible investors are from FATF-compliant jurisdictions and issuers can raise up to $750 million annually under automatic approval.