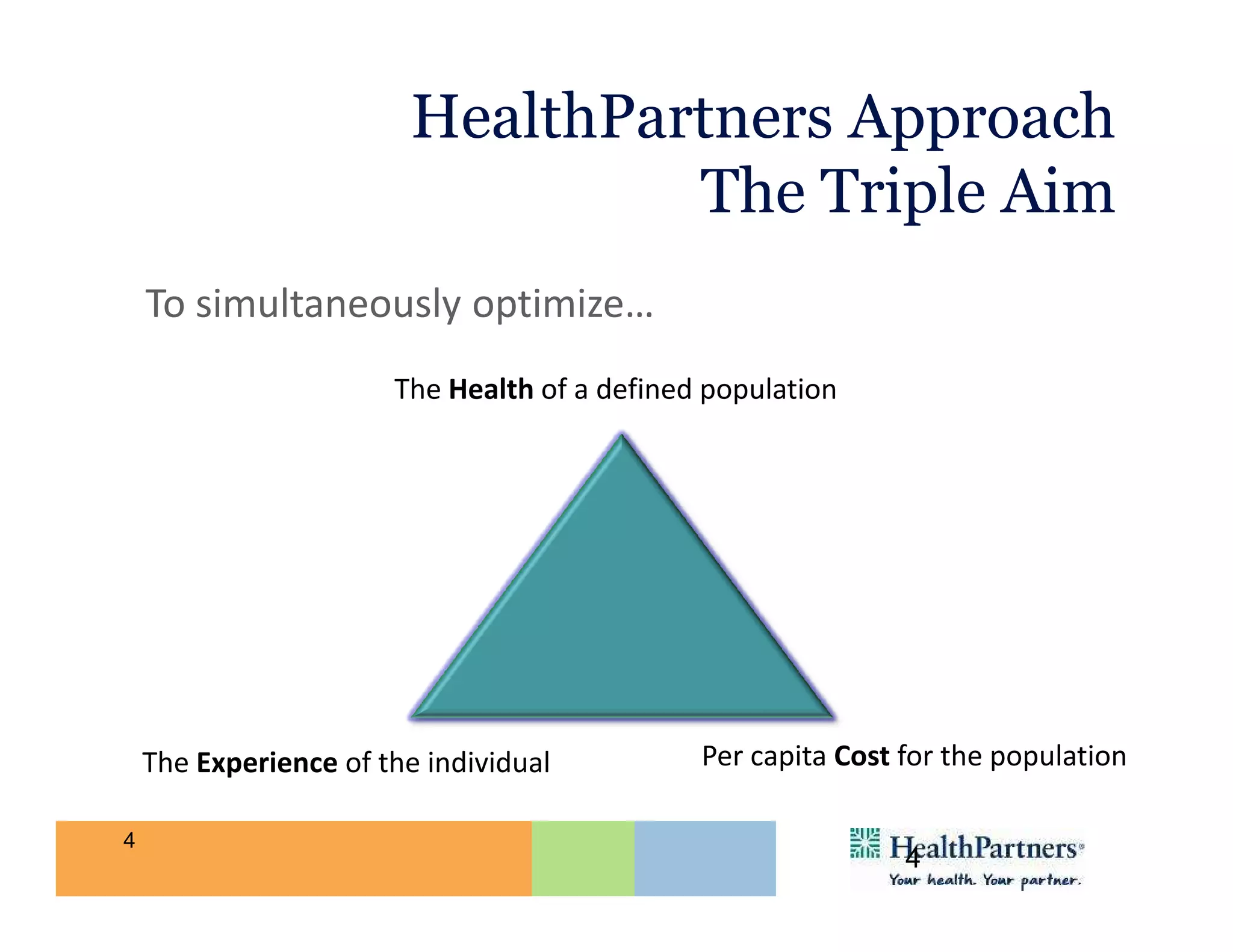
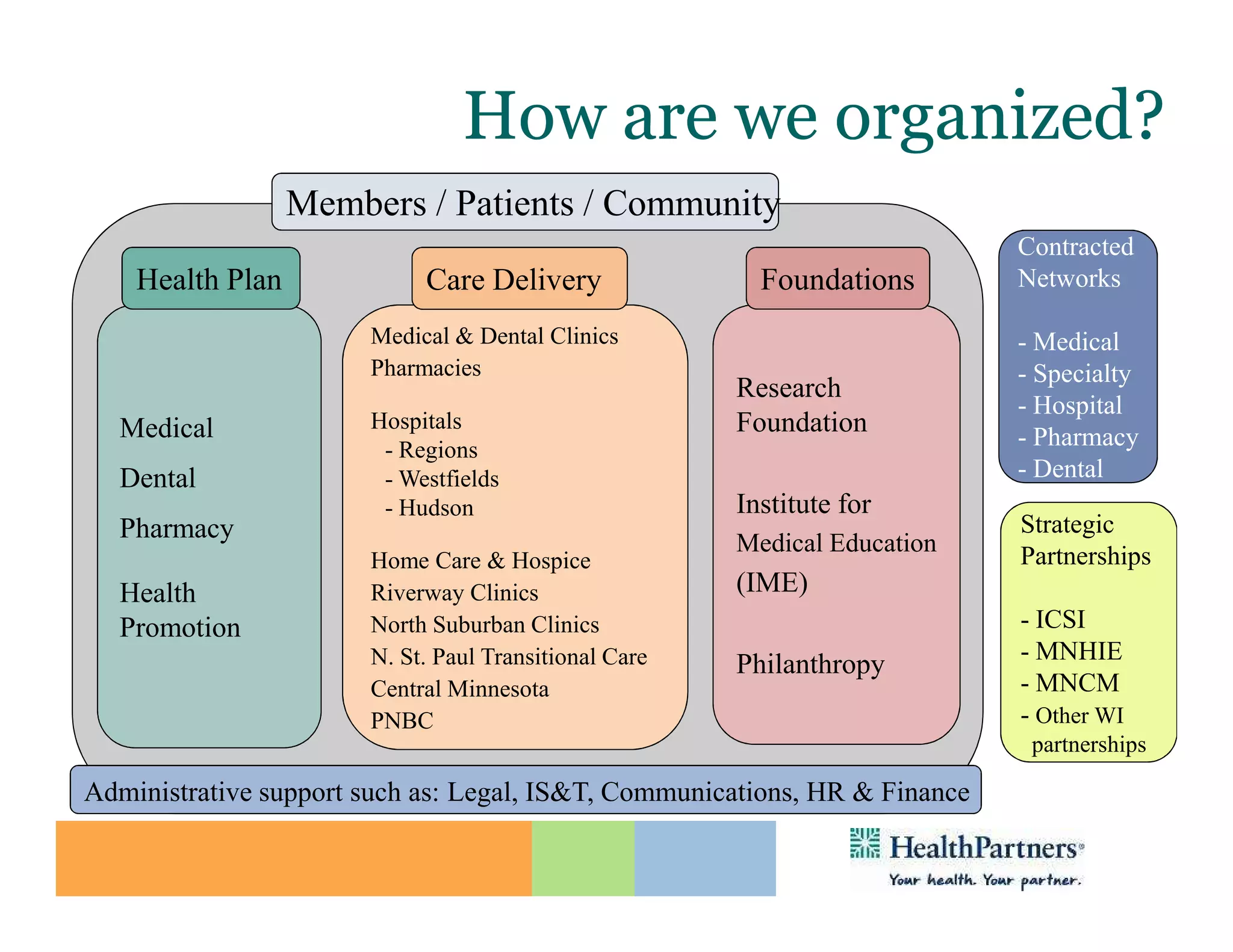
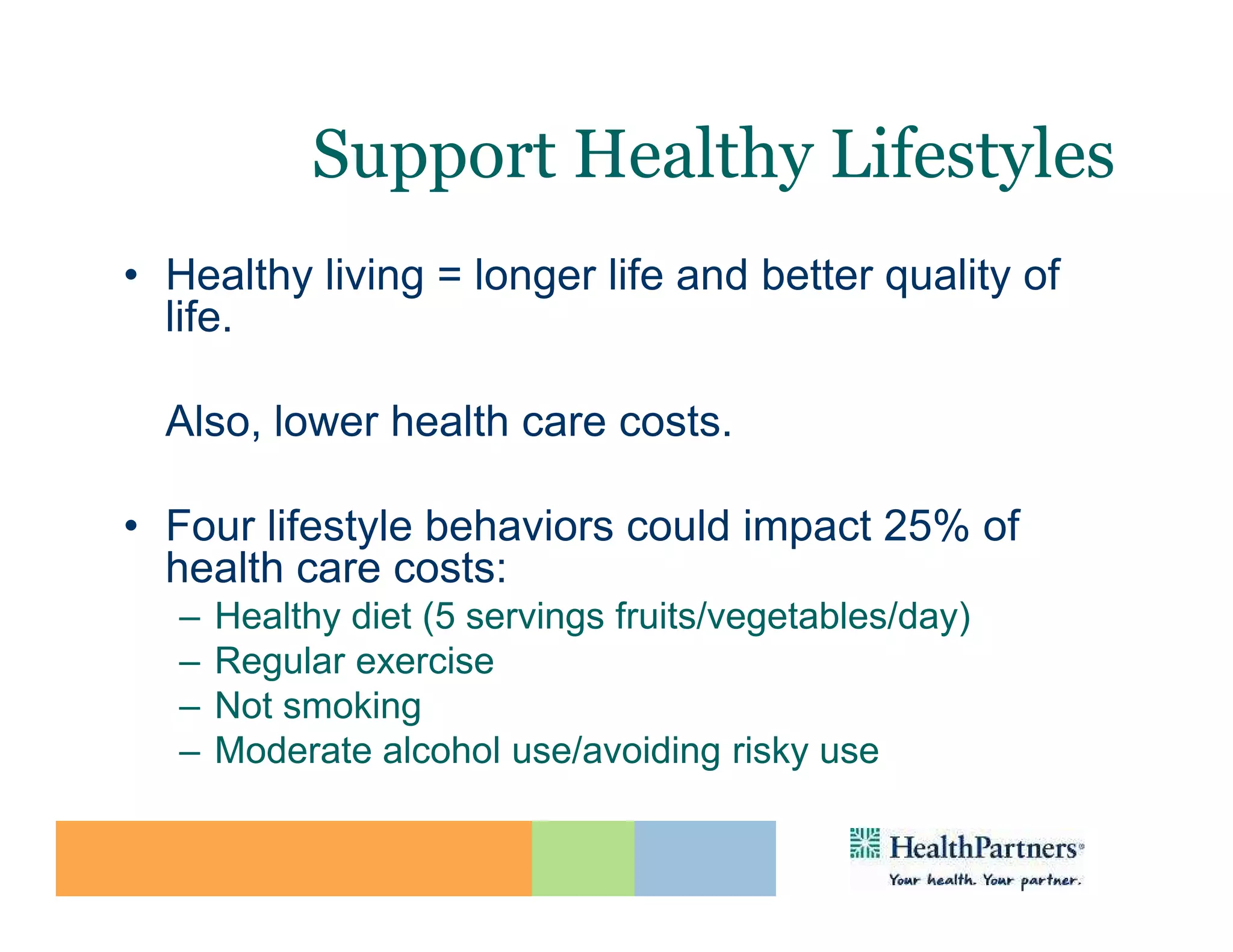
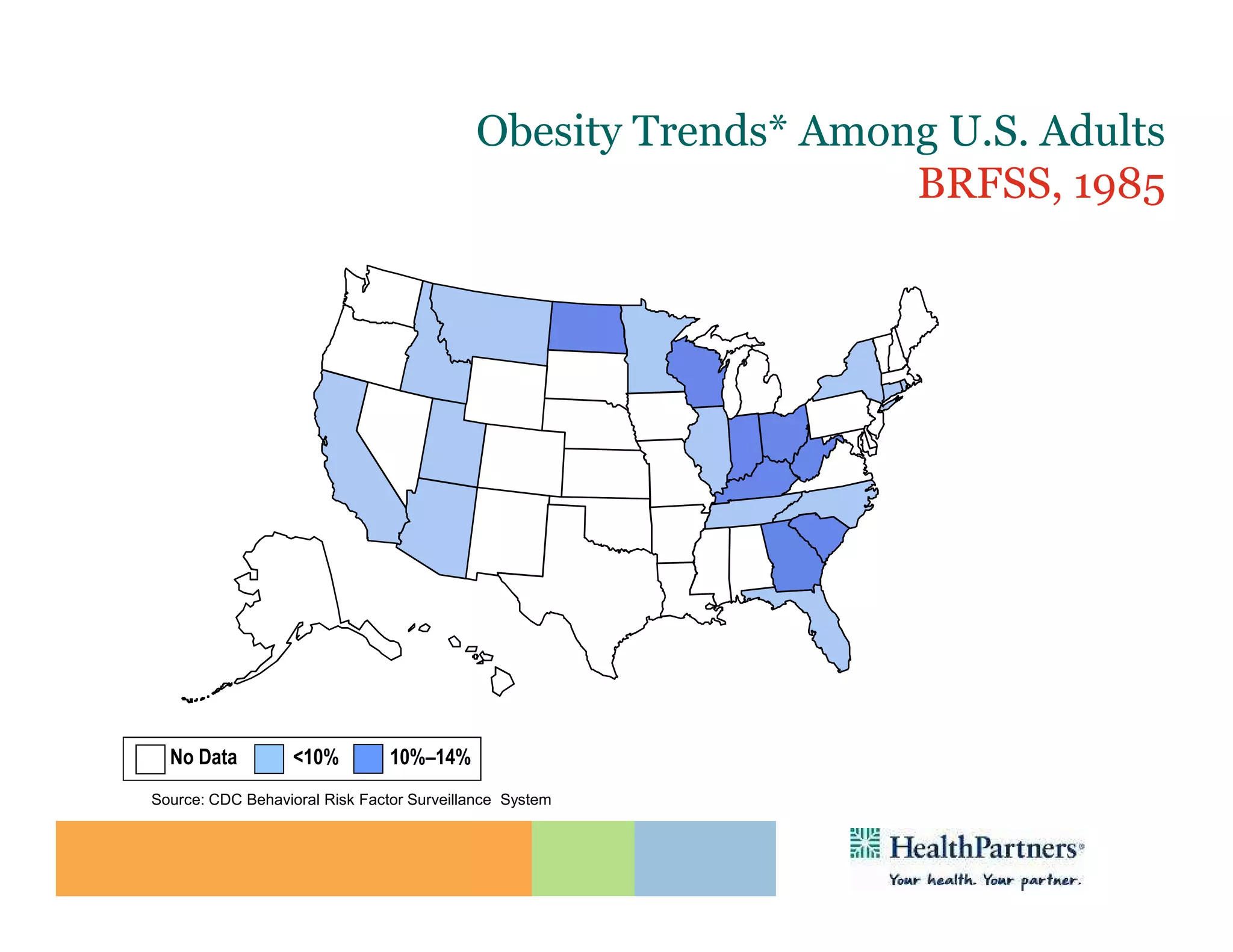
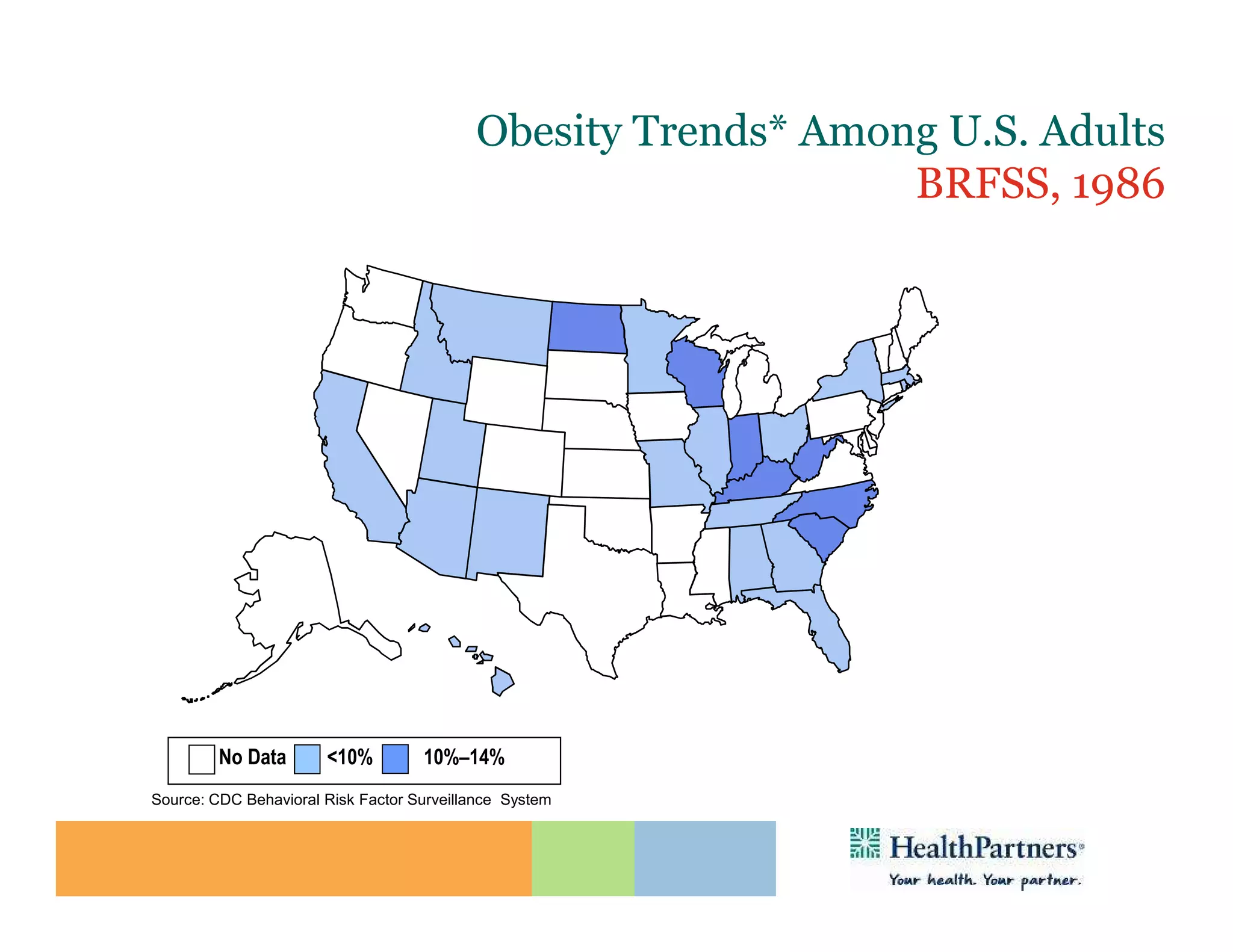
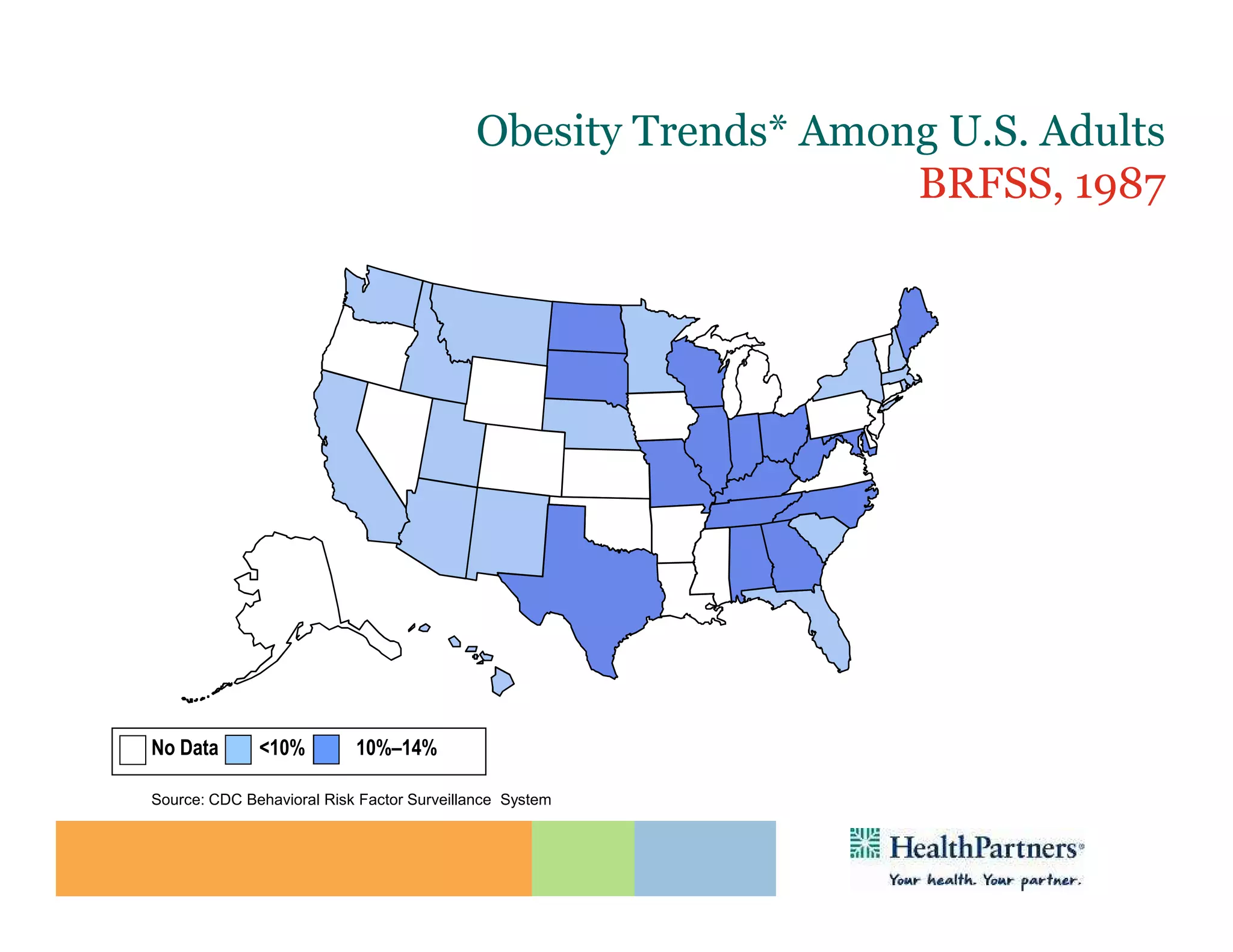
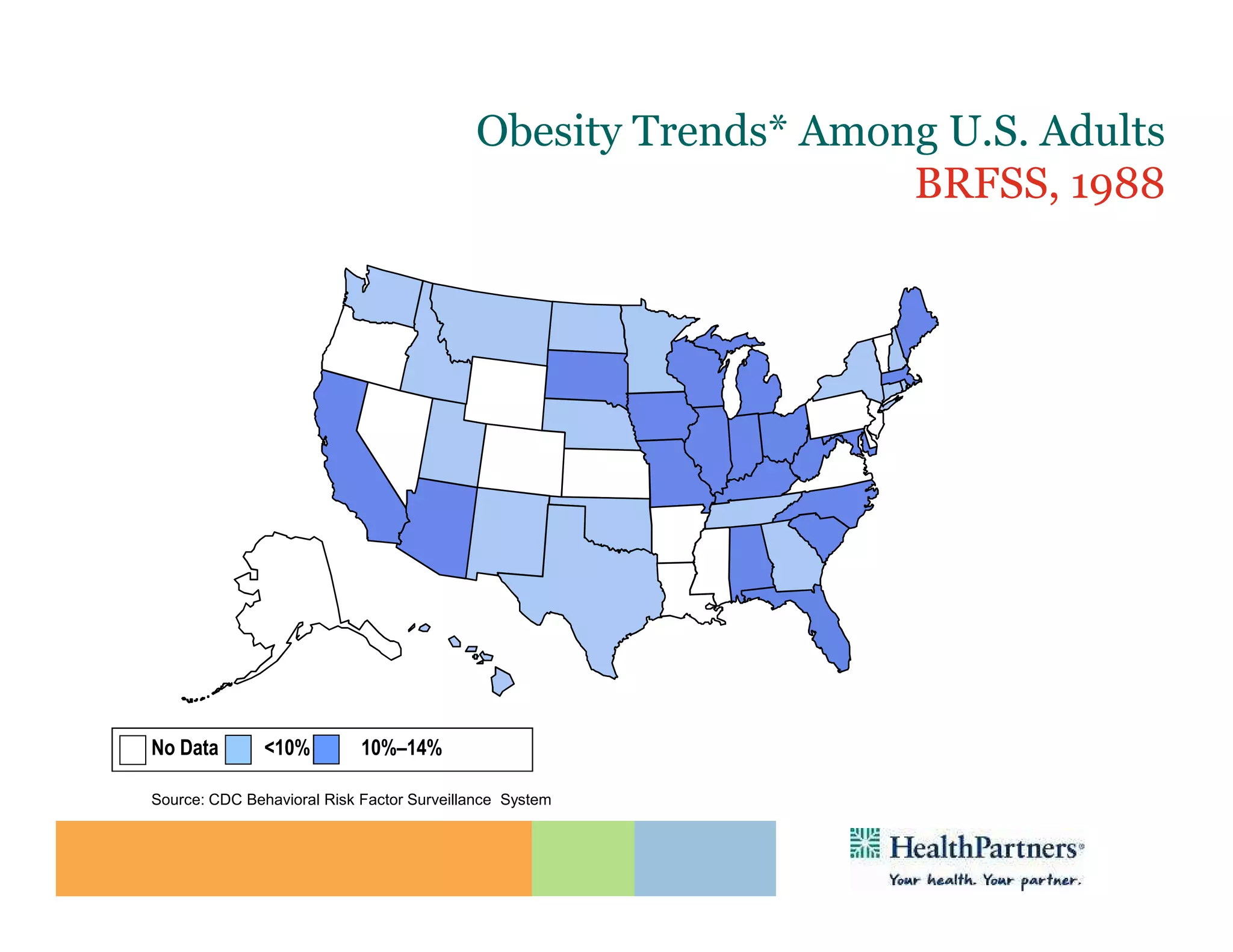
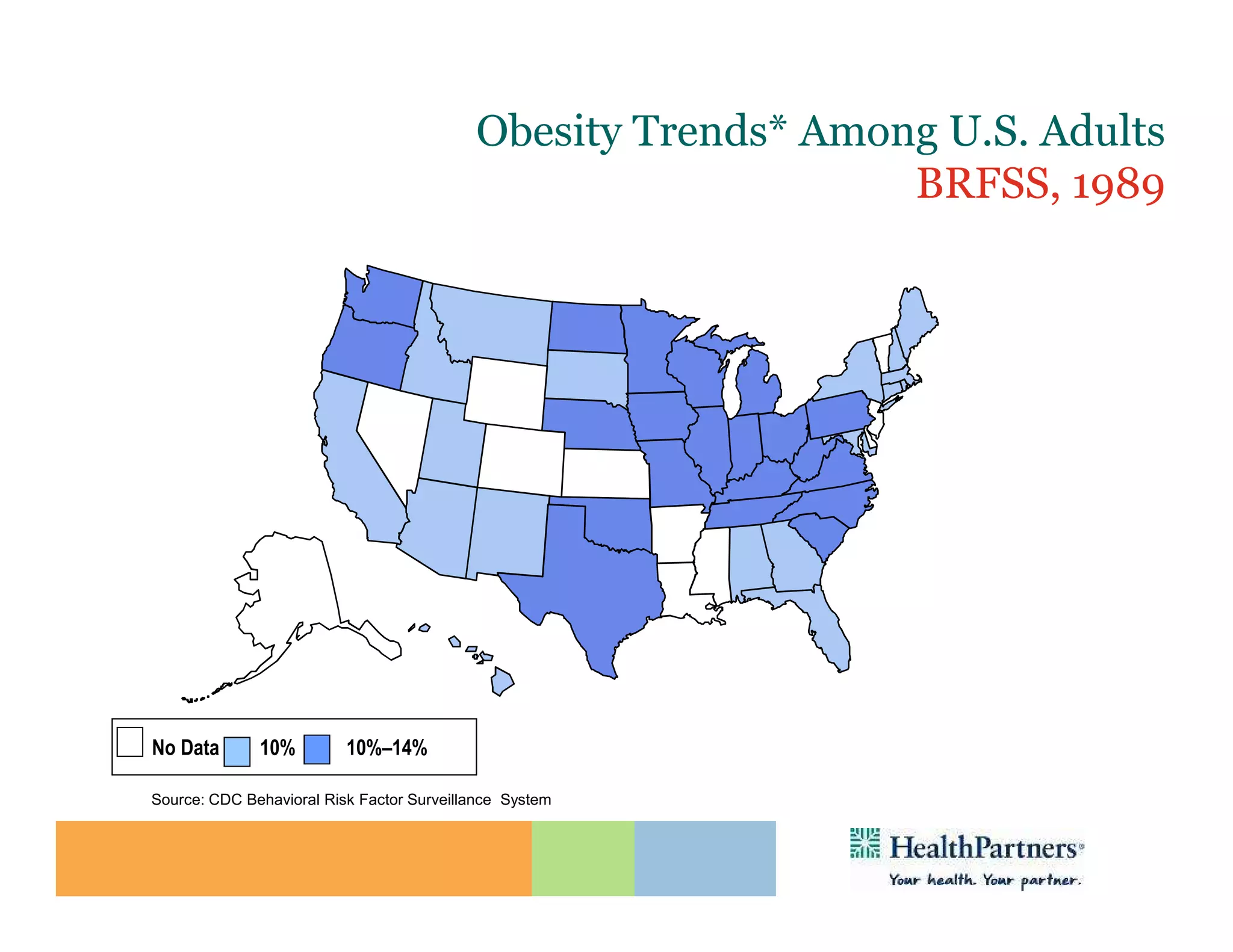
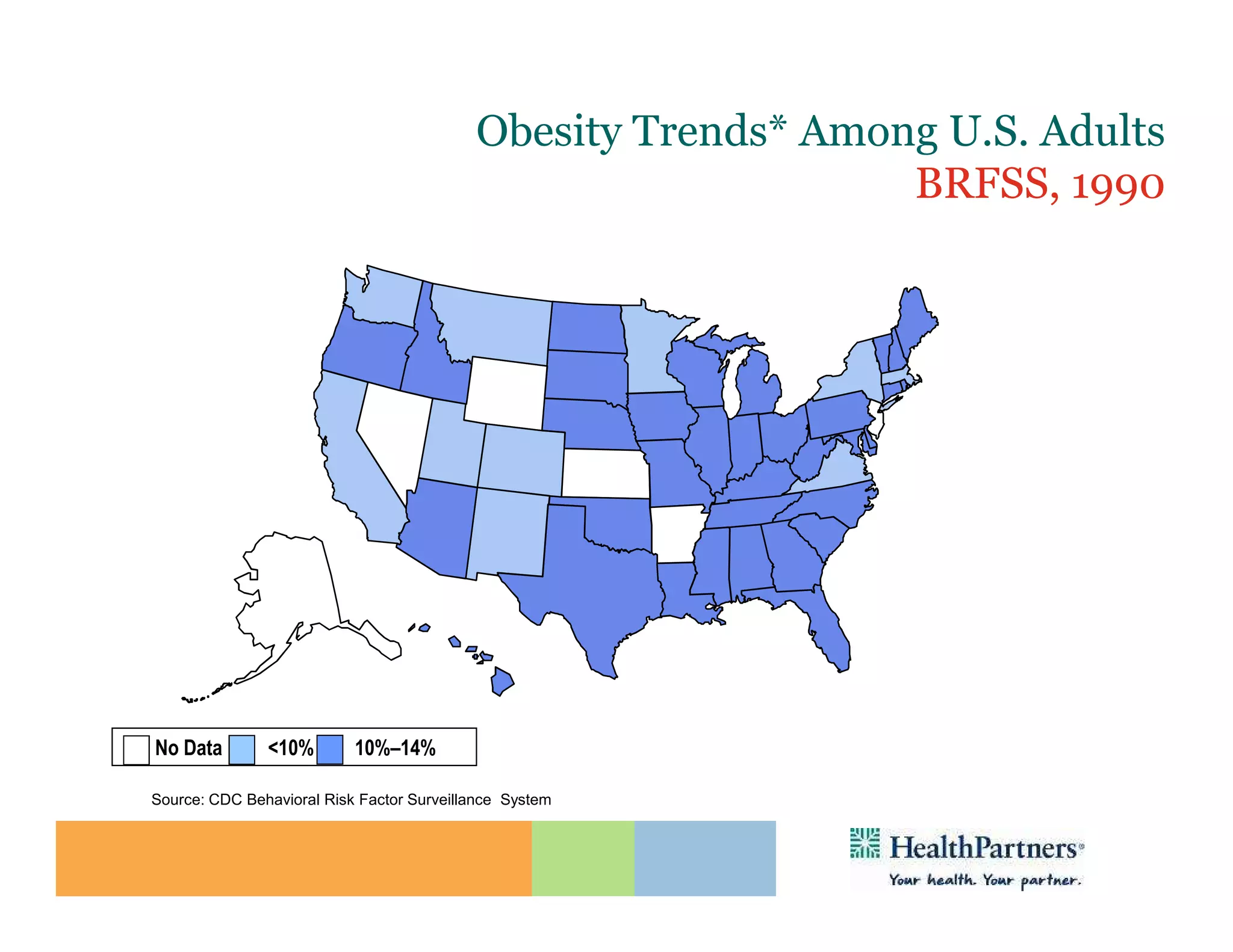
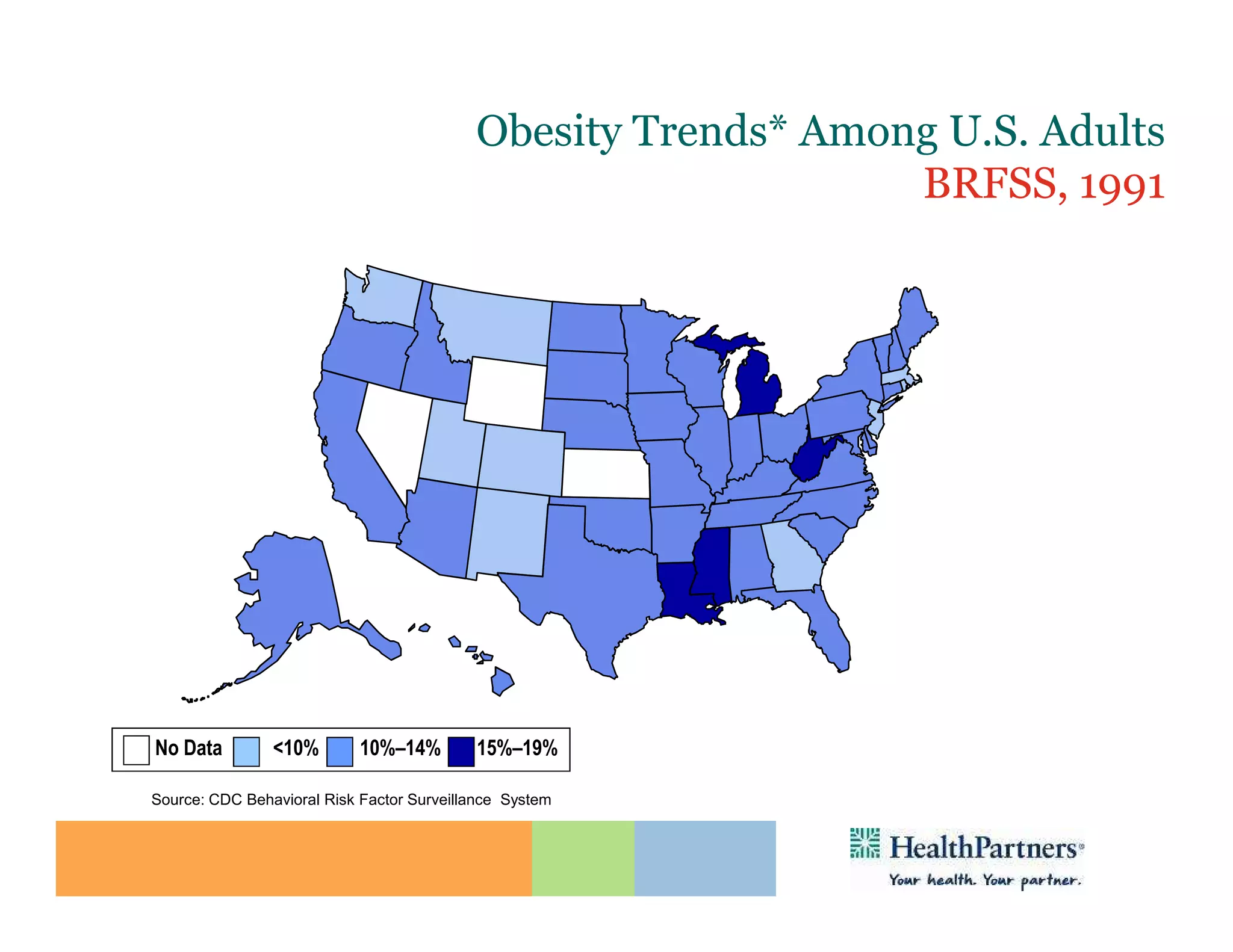
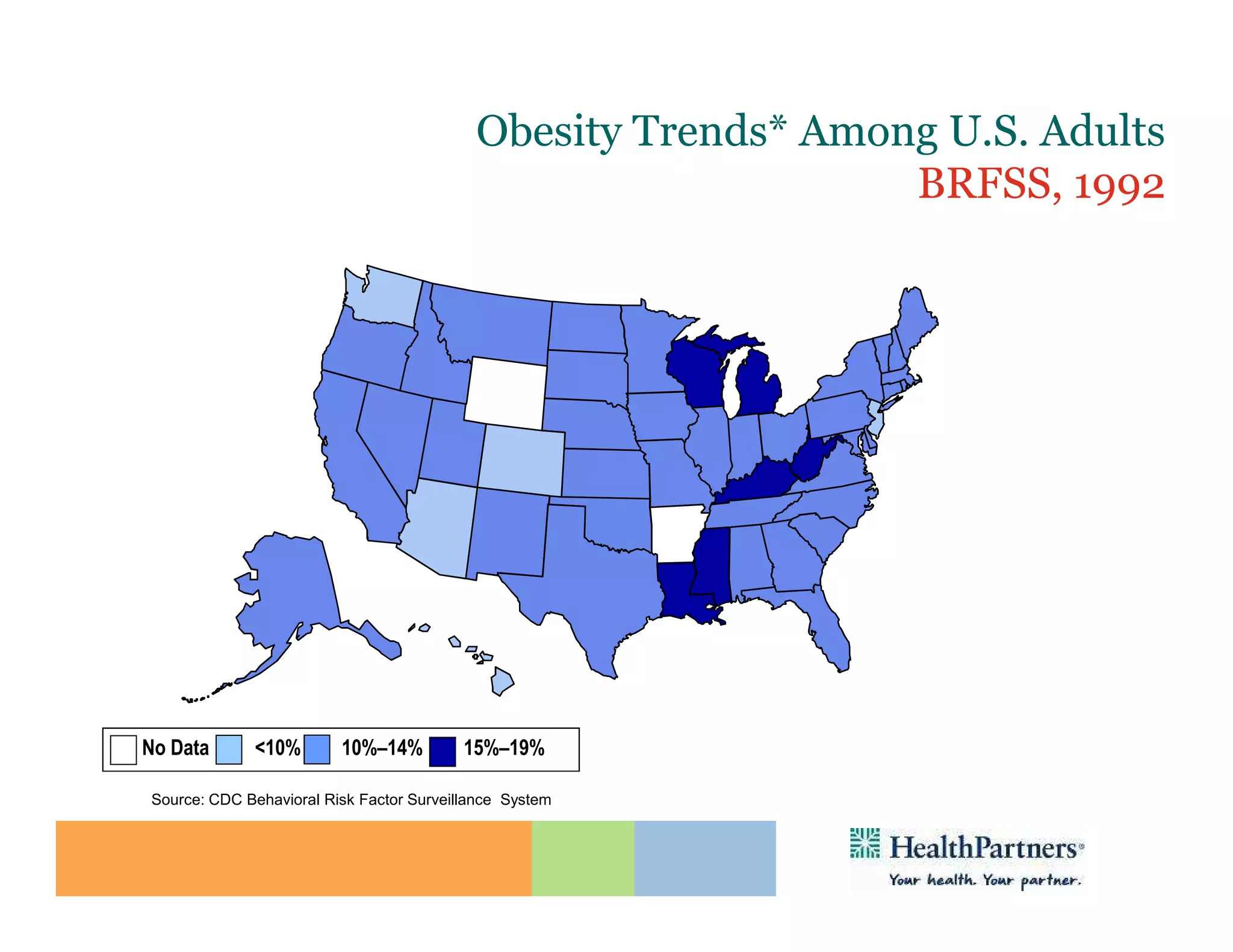
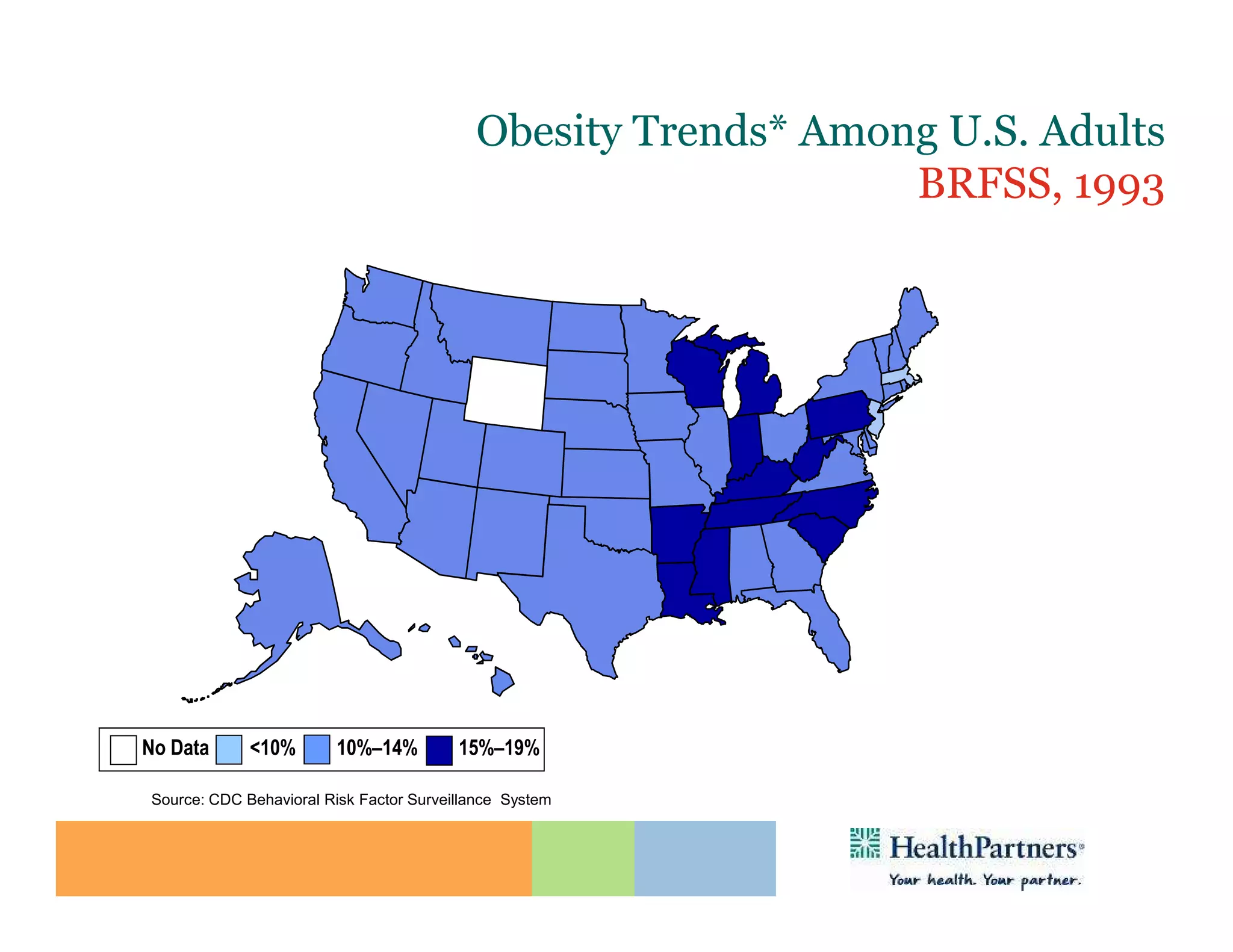
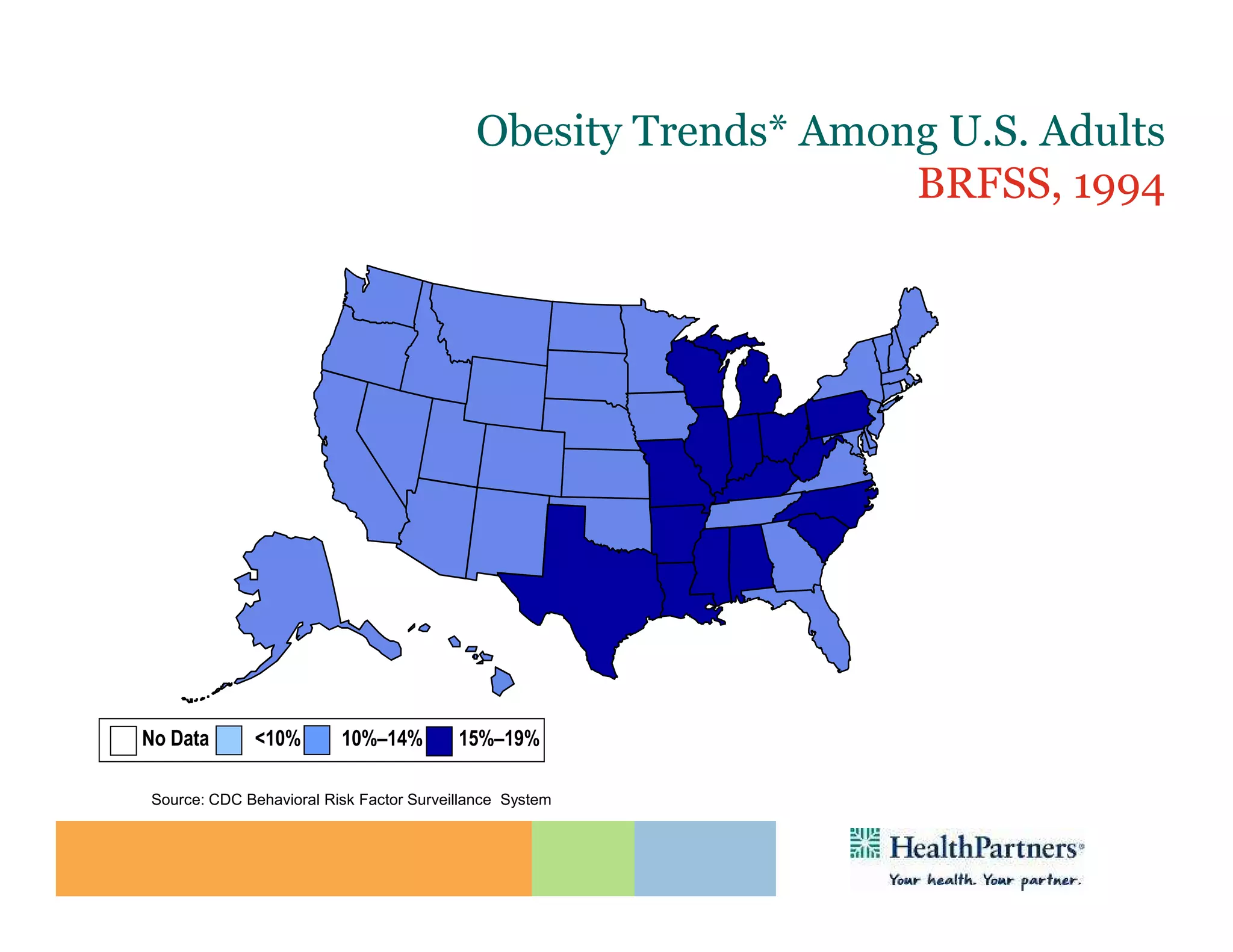
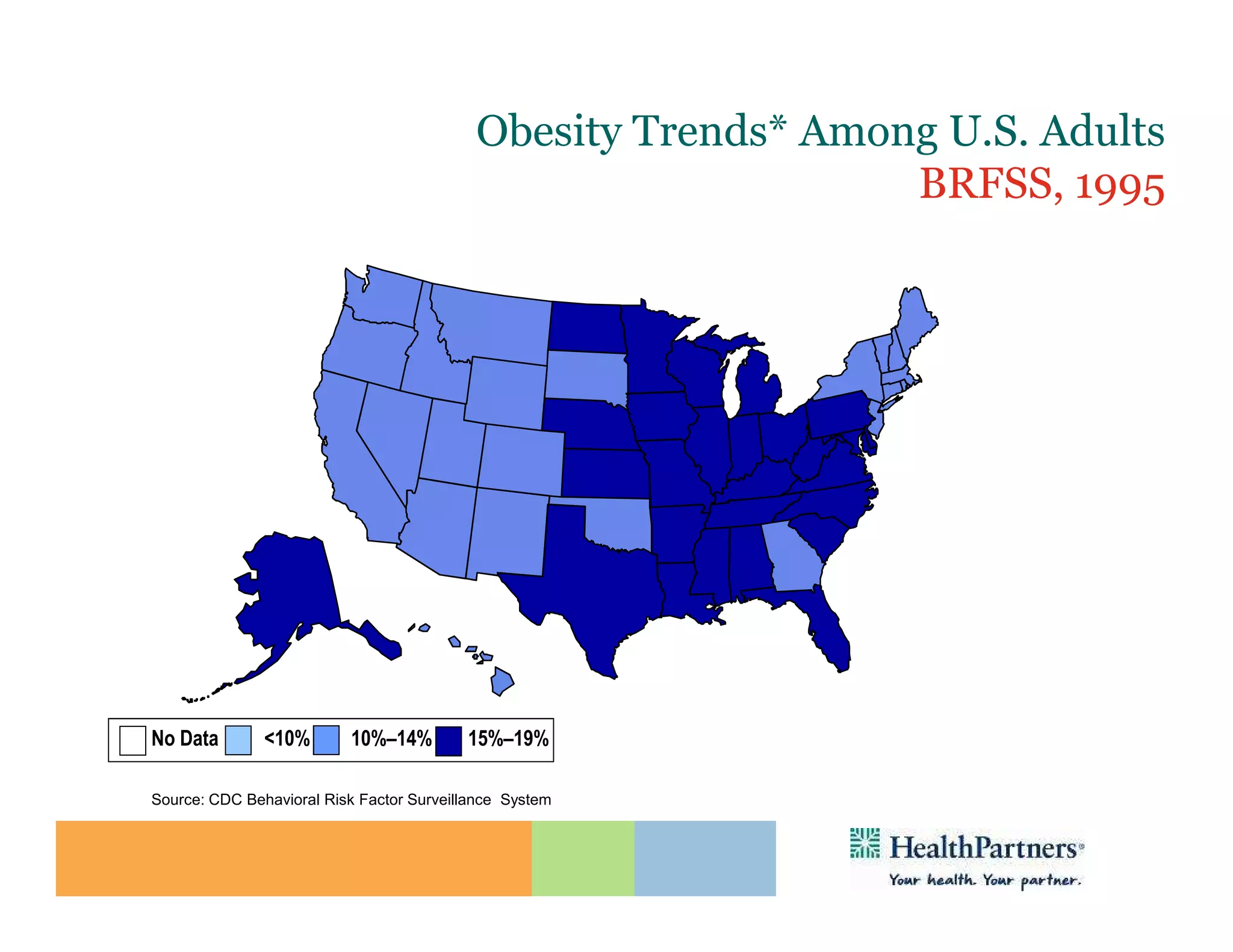
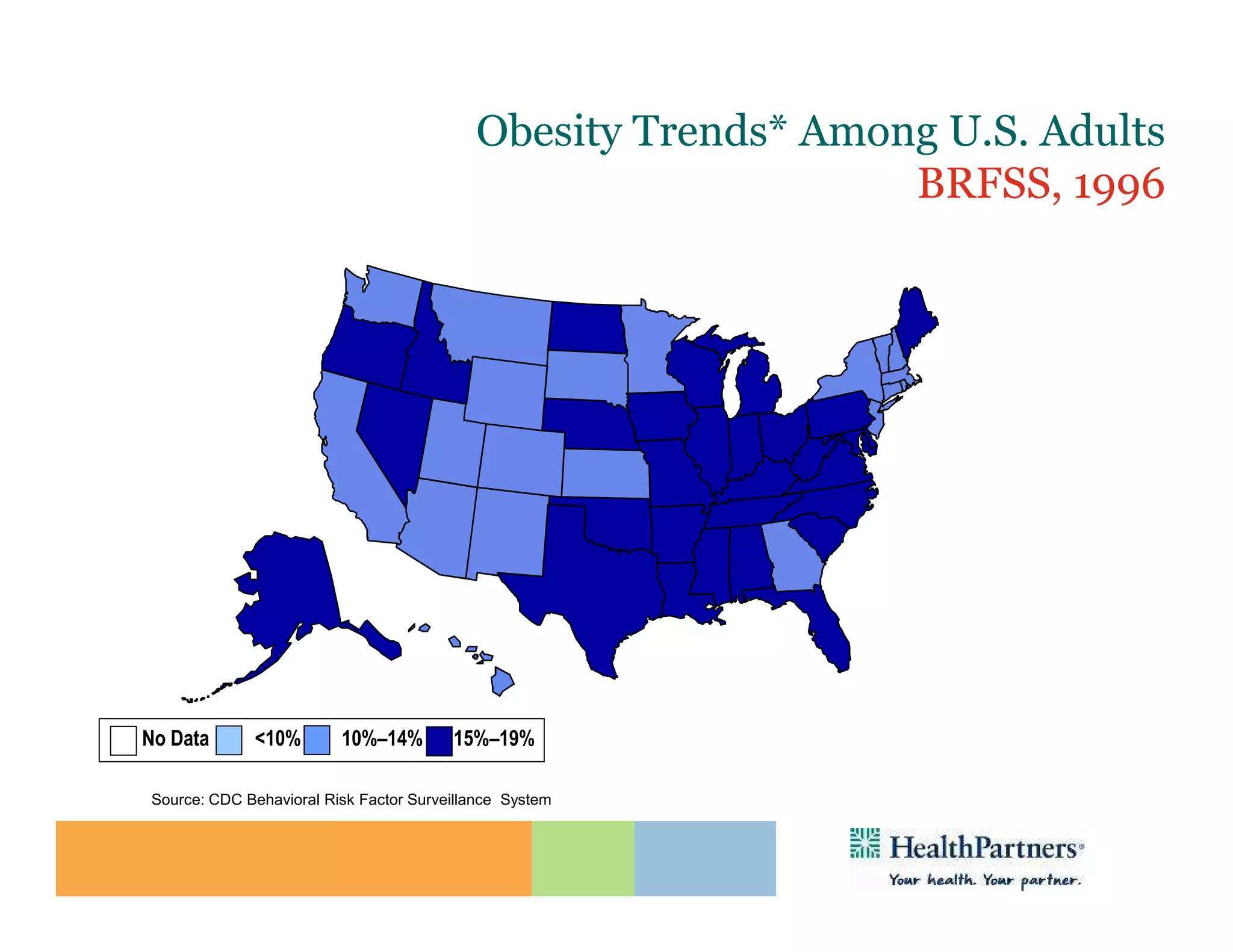
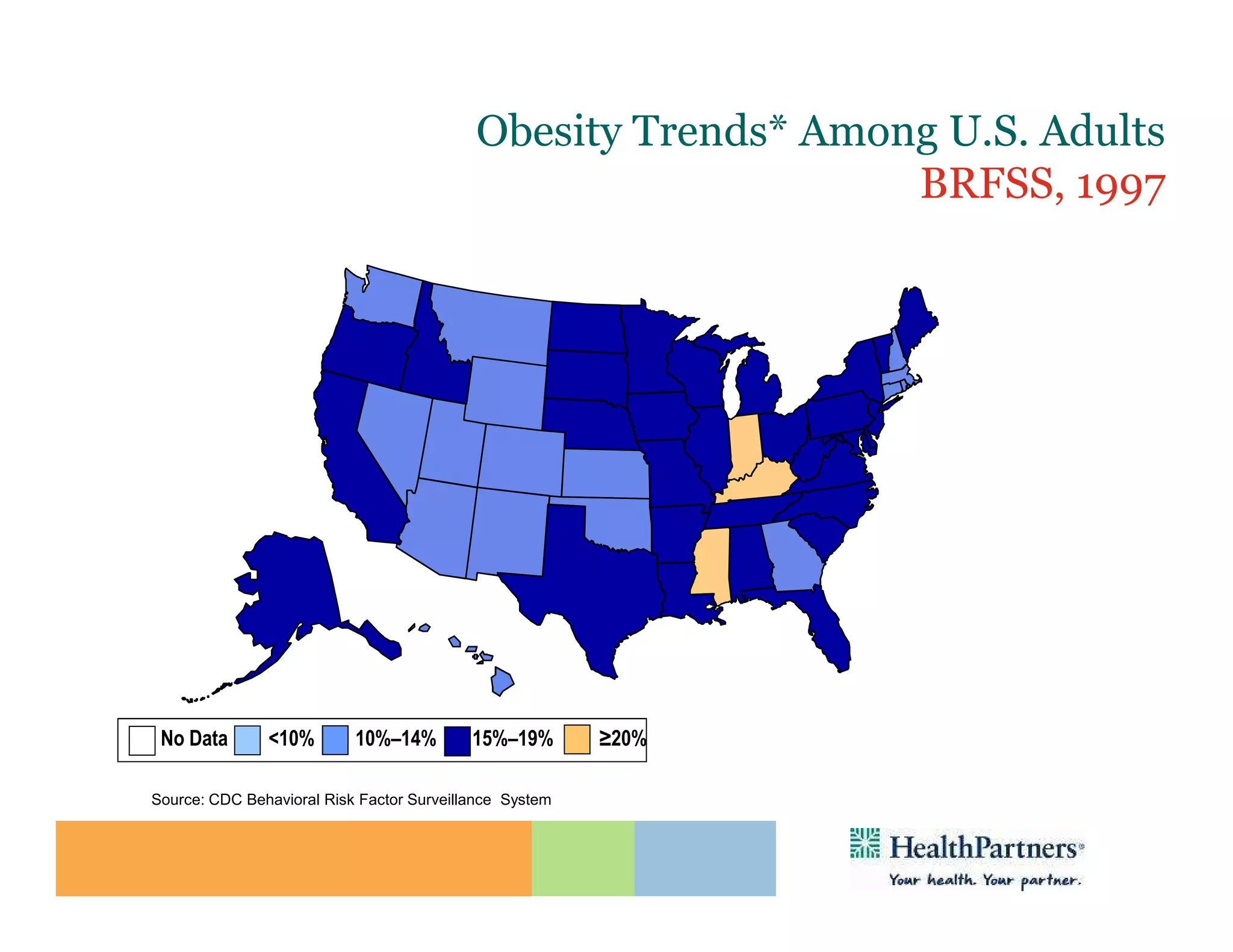
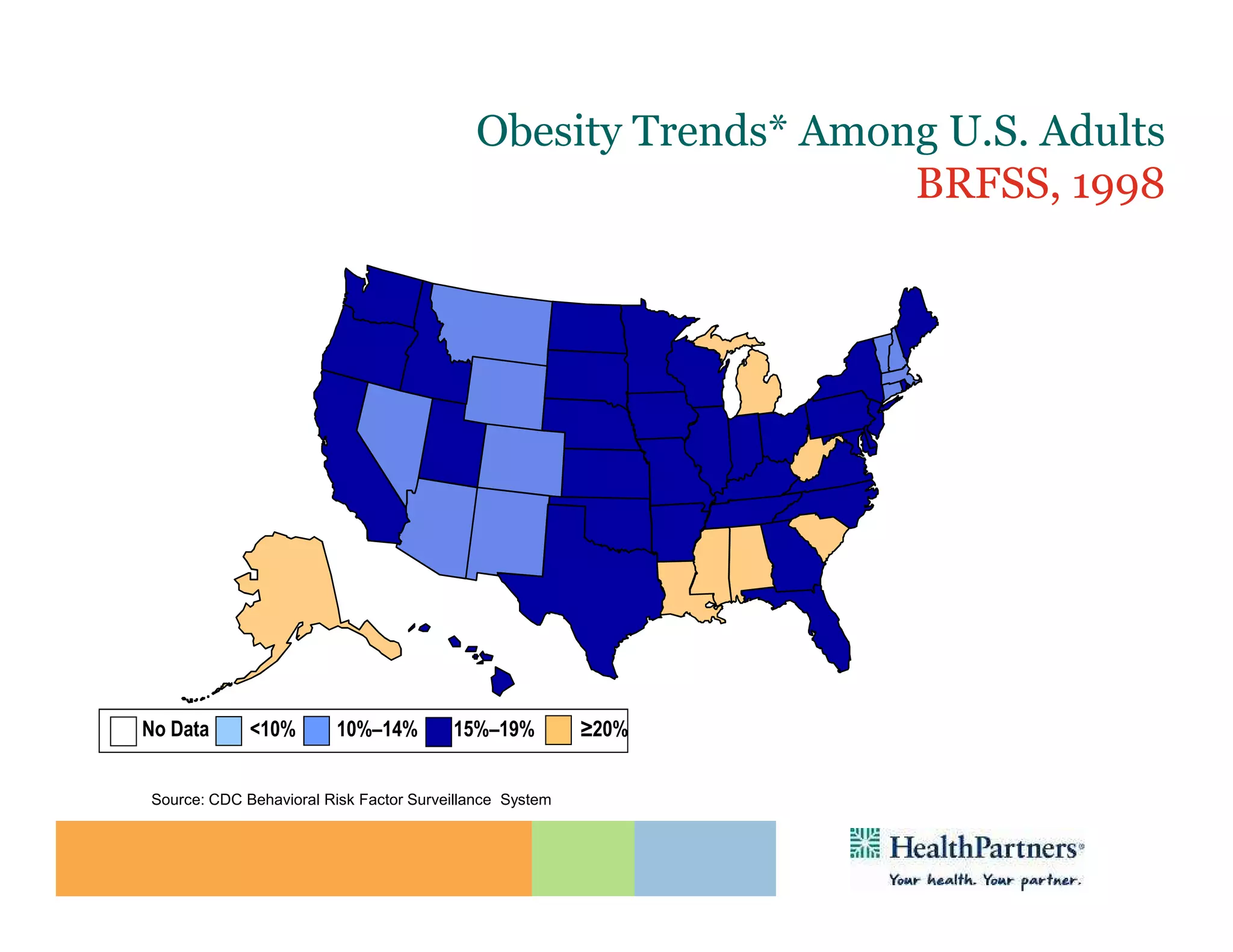
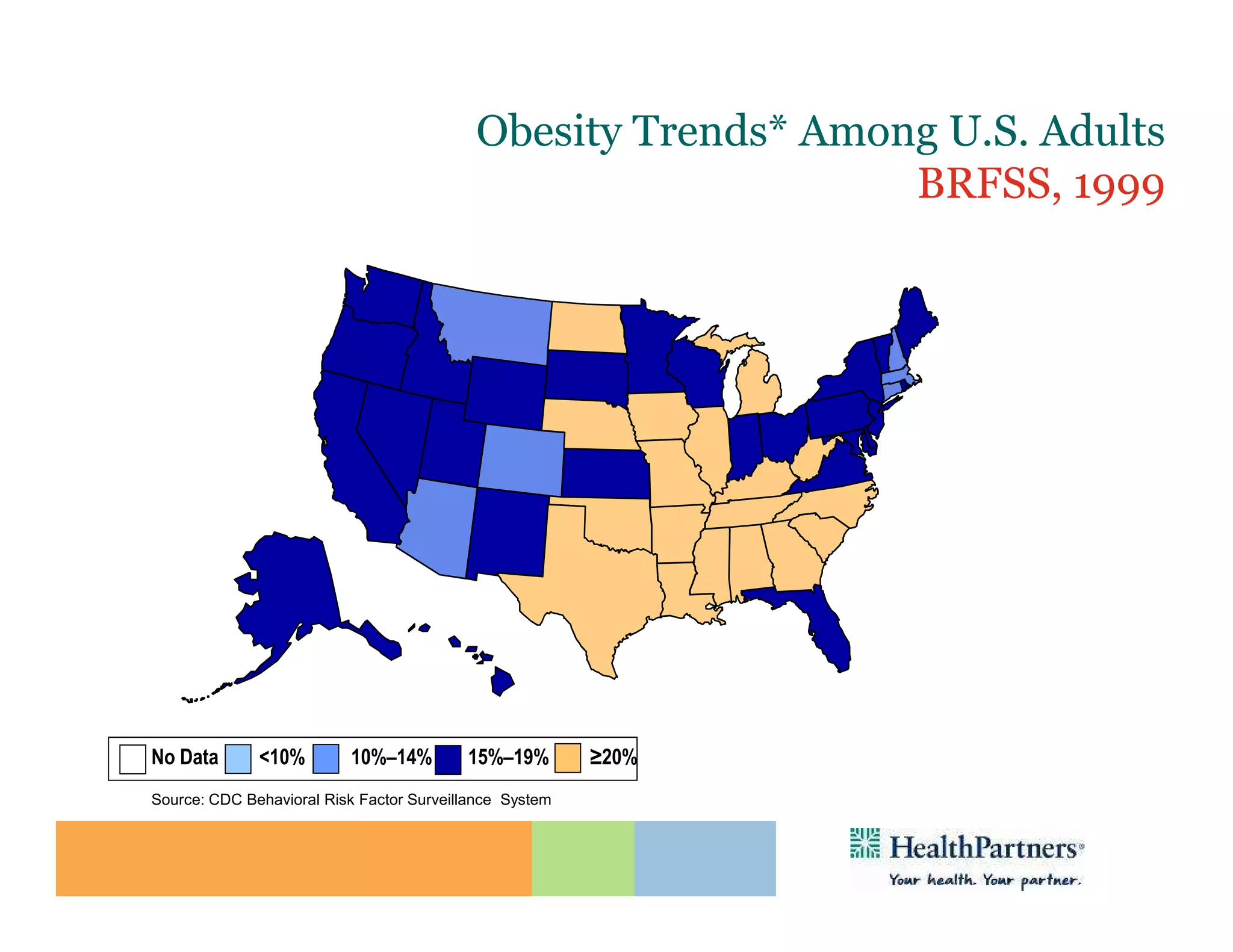
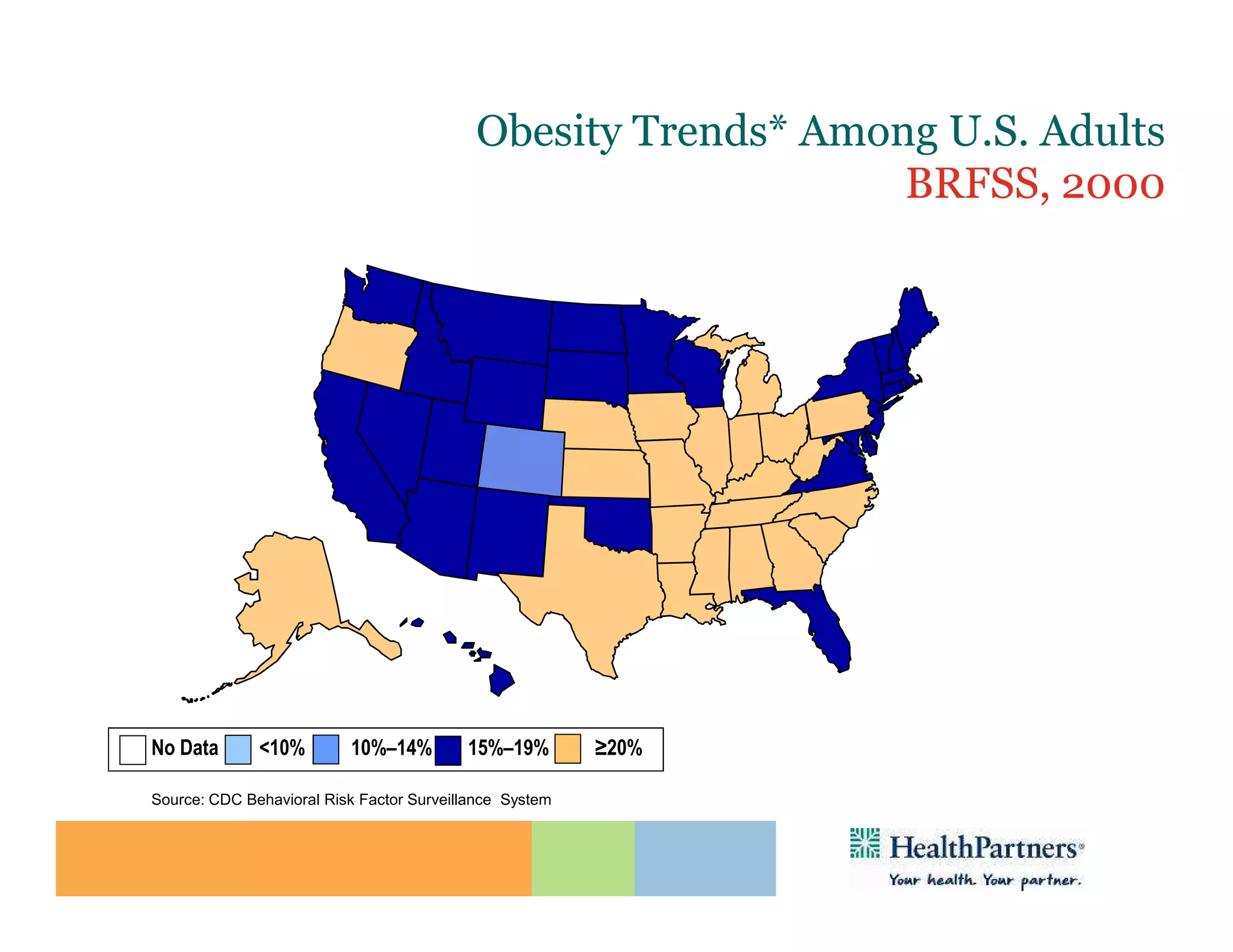
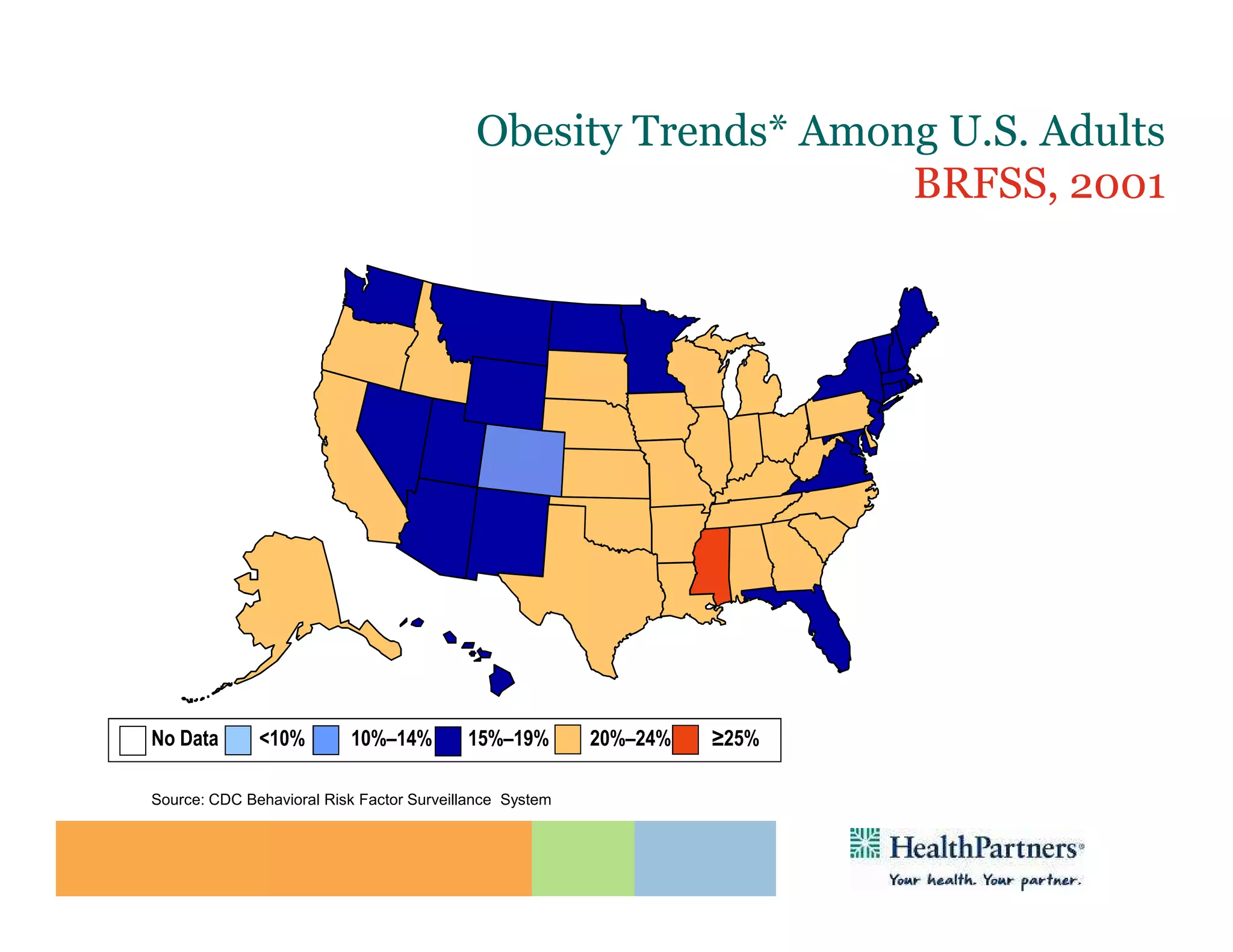
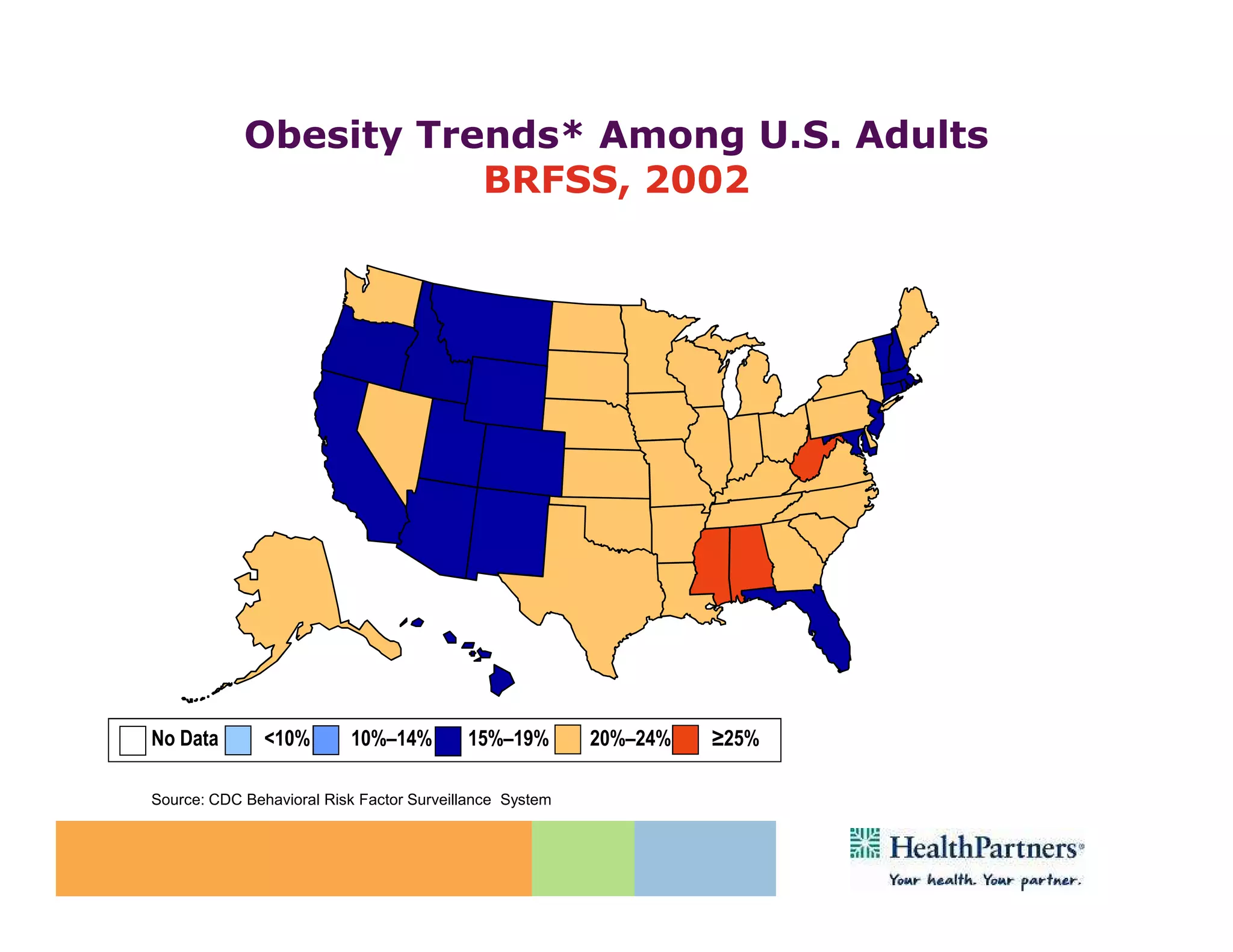
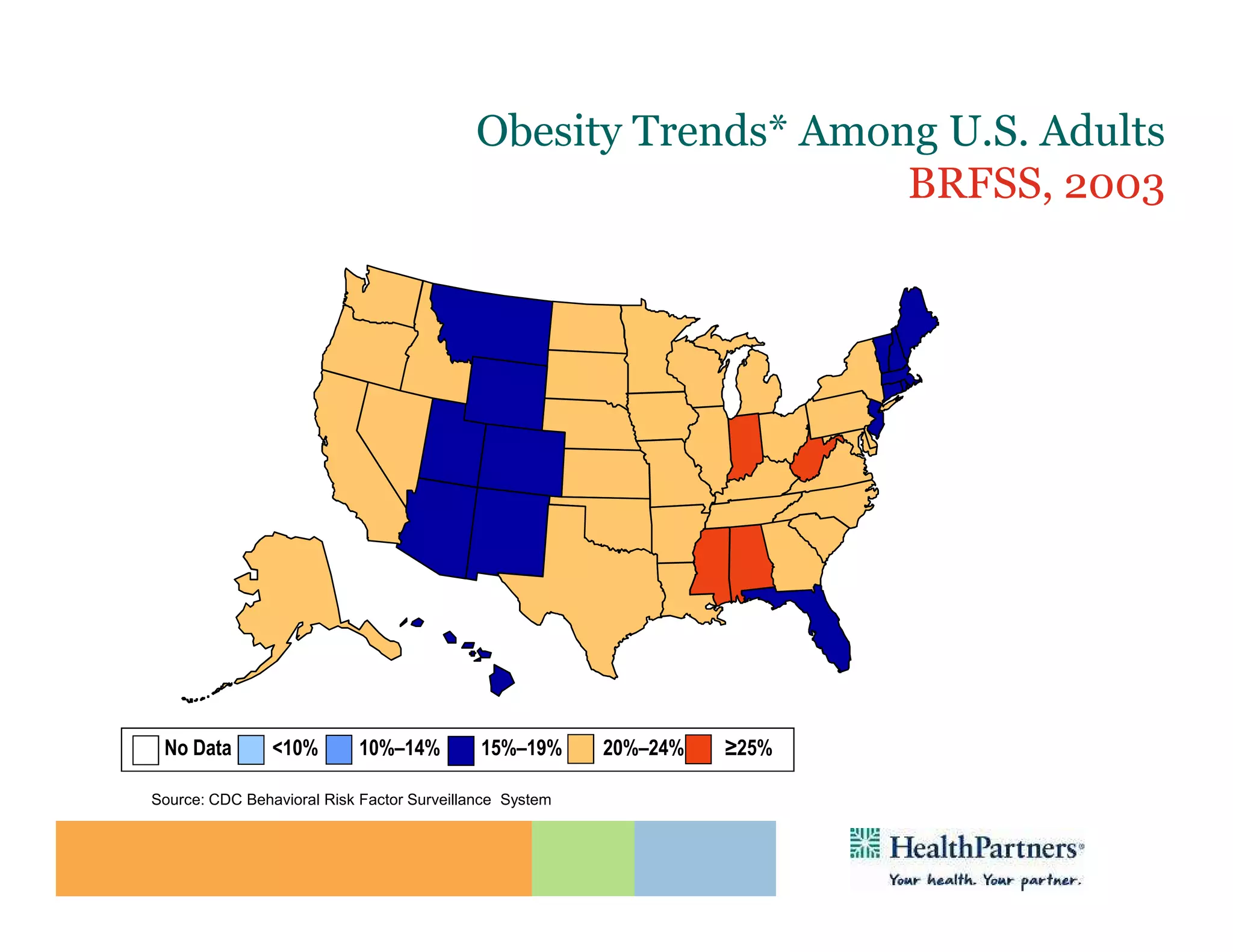
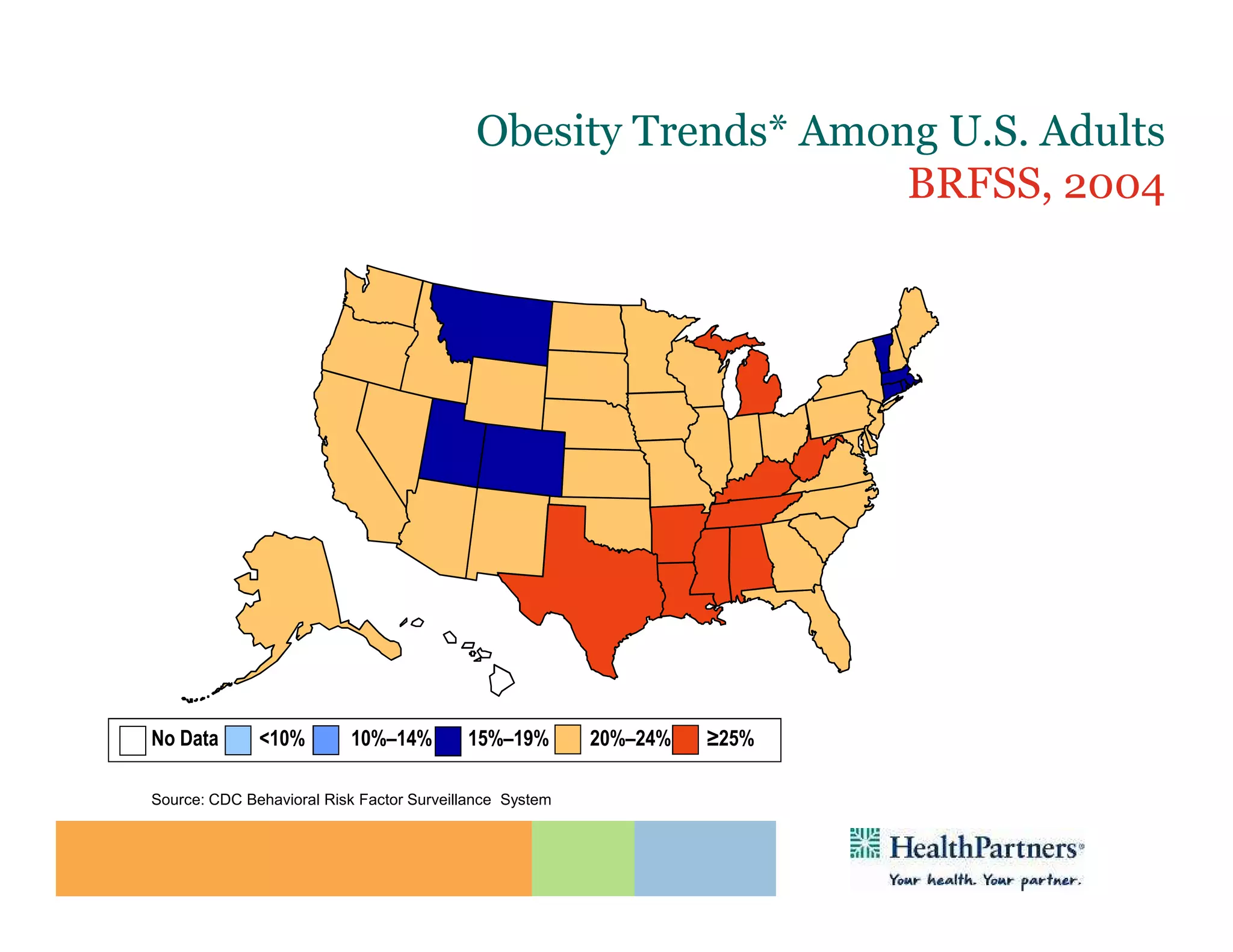
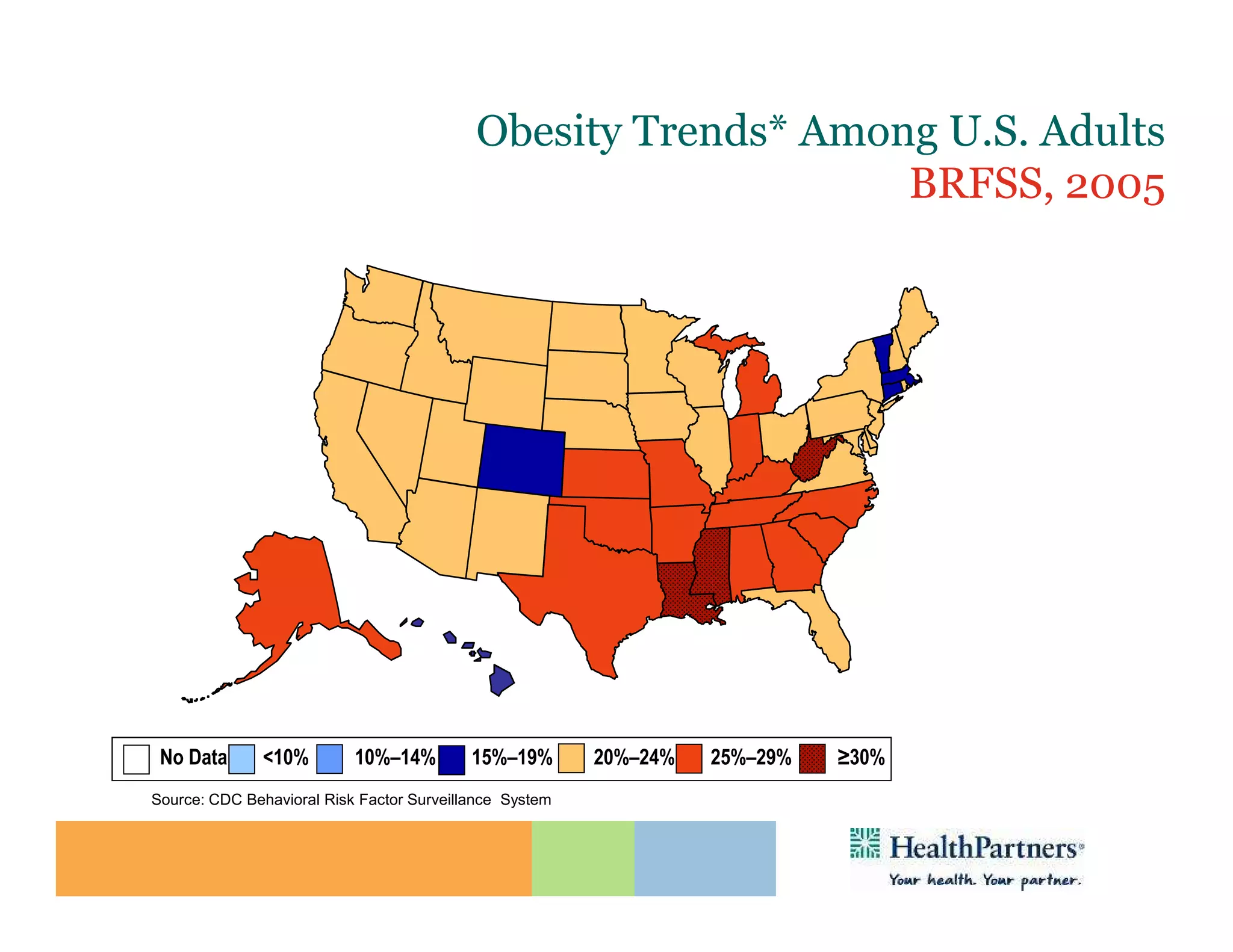
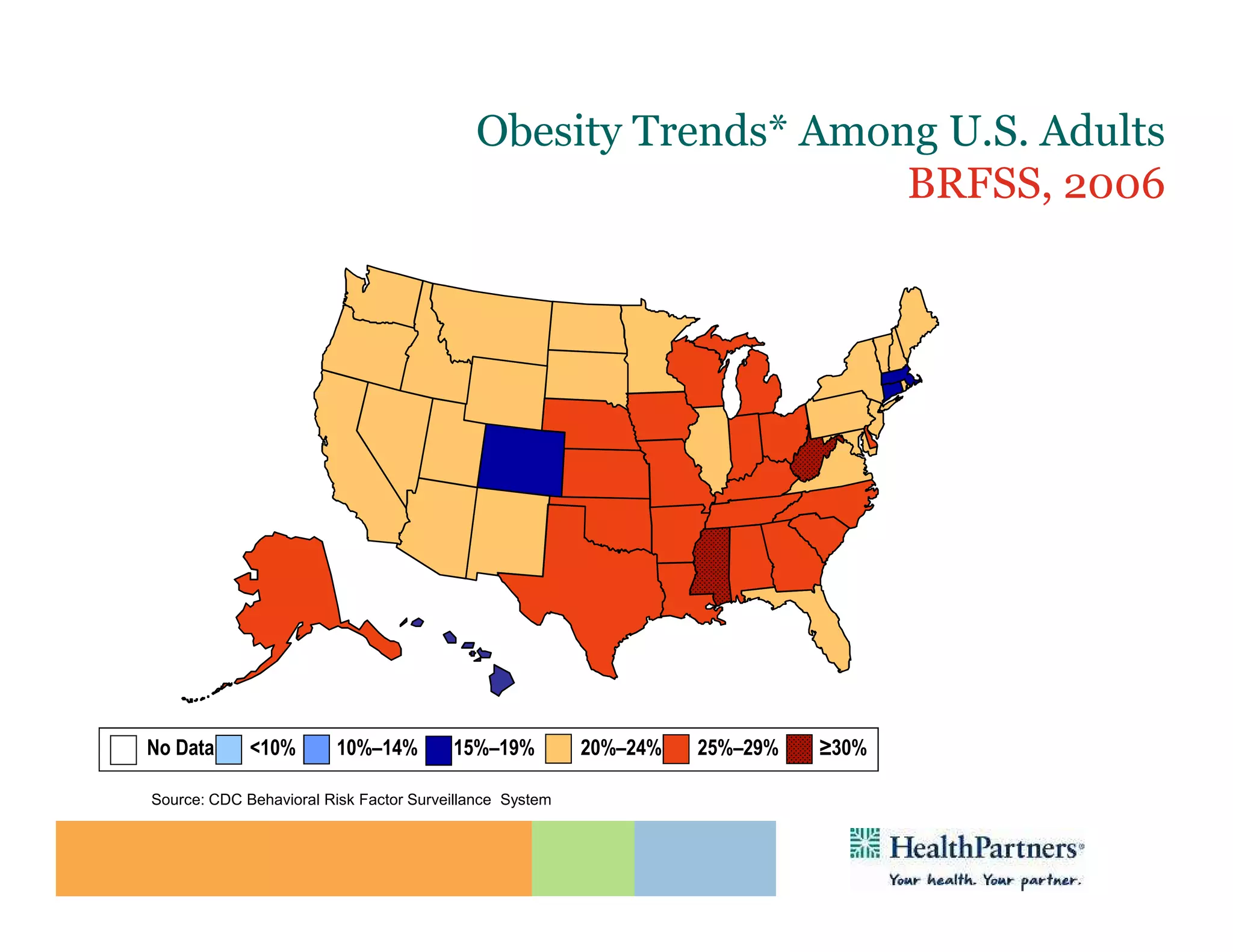
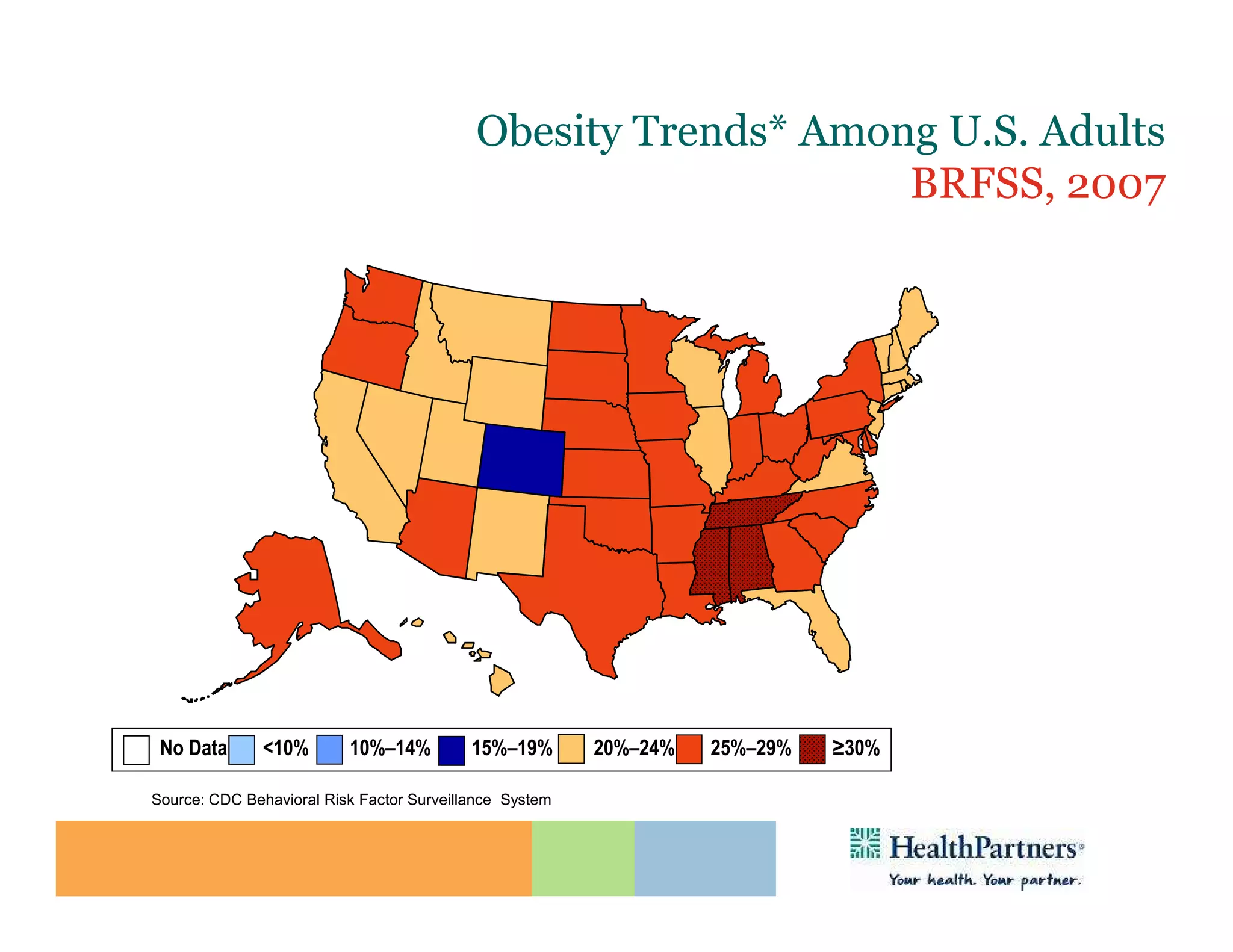
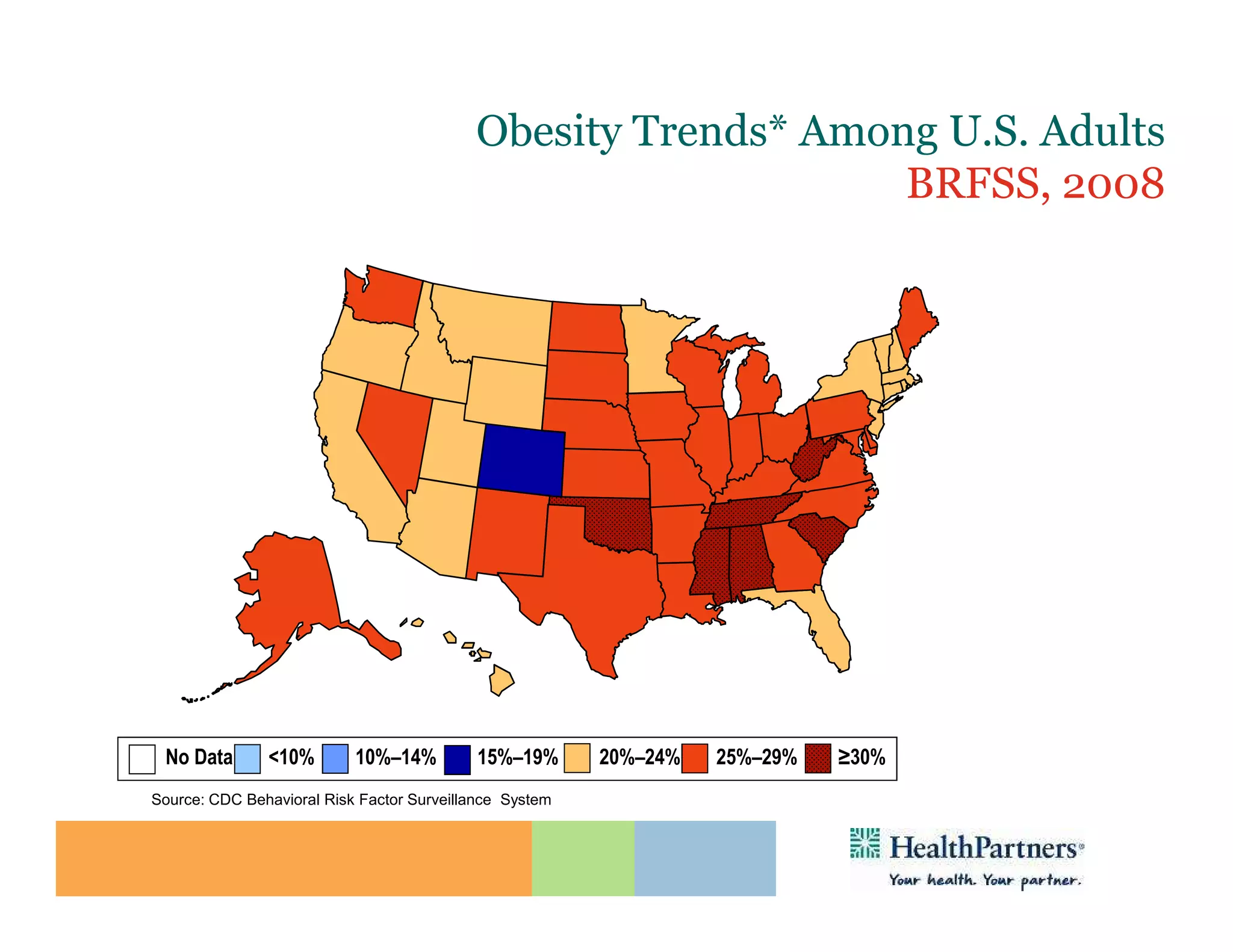
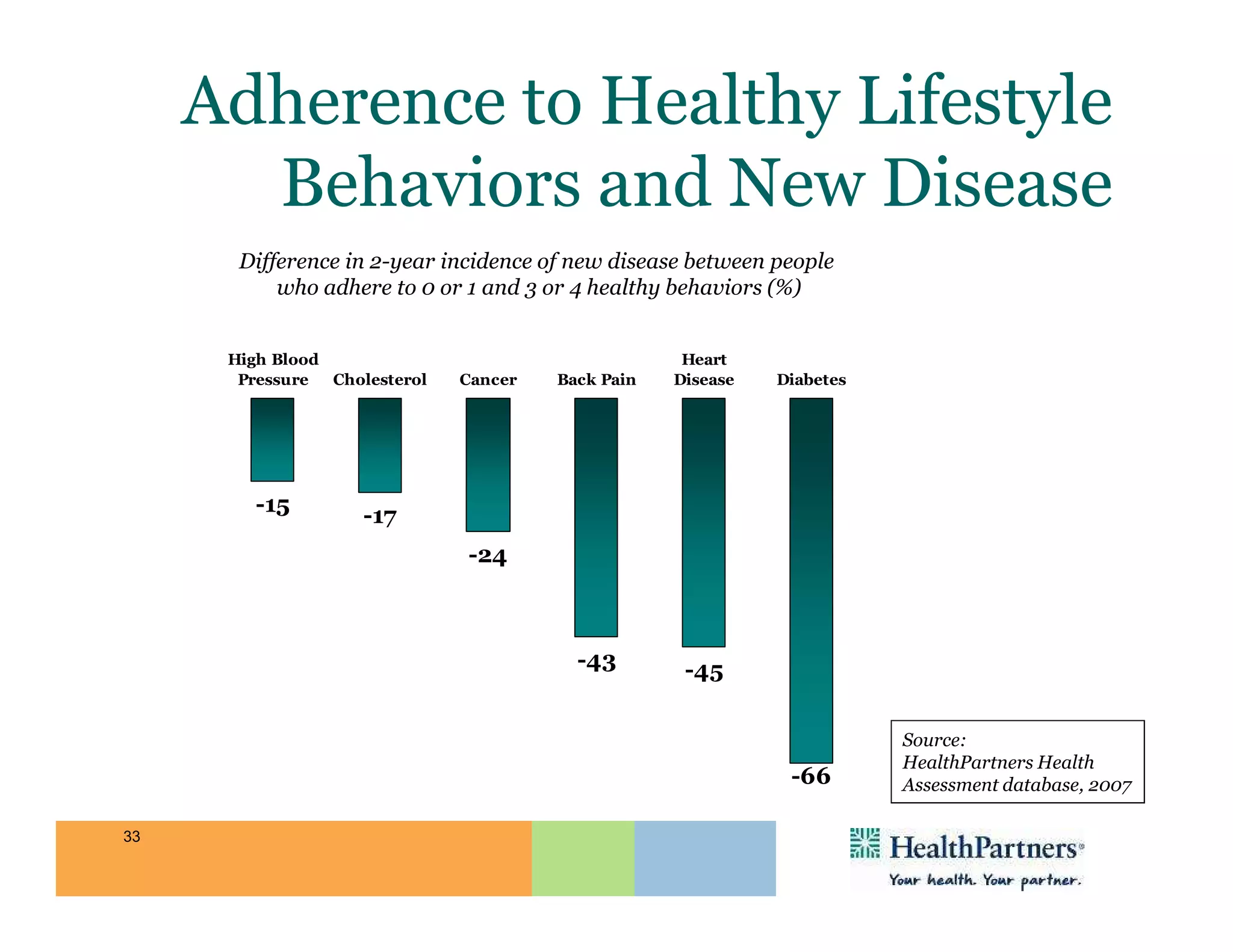
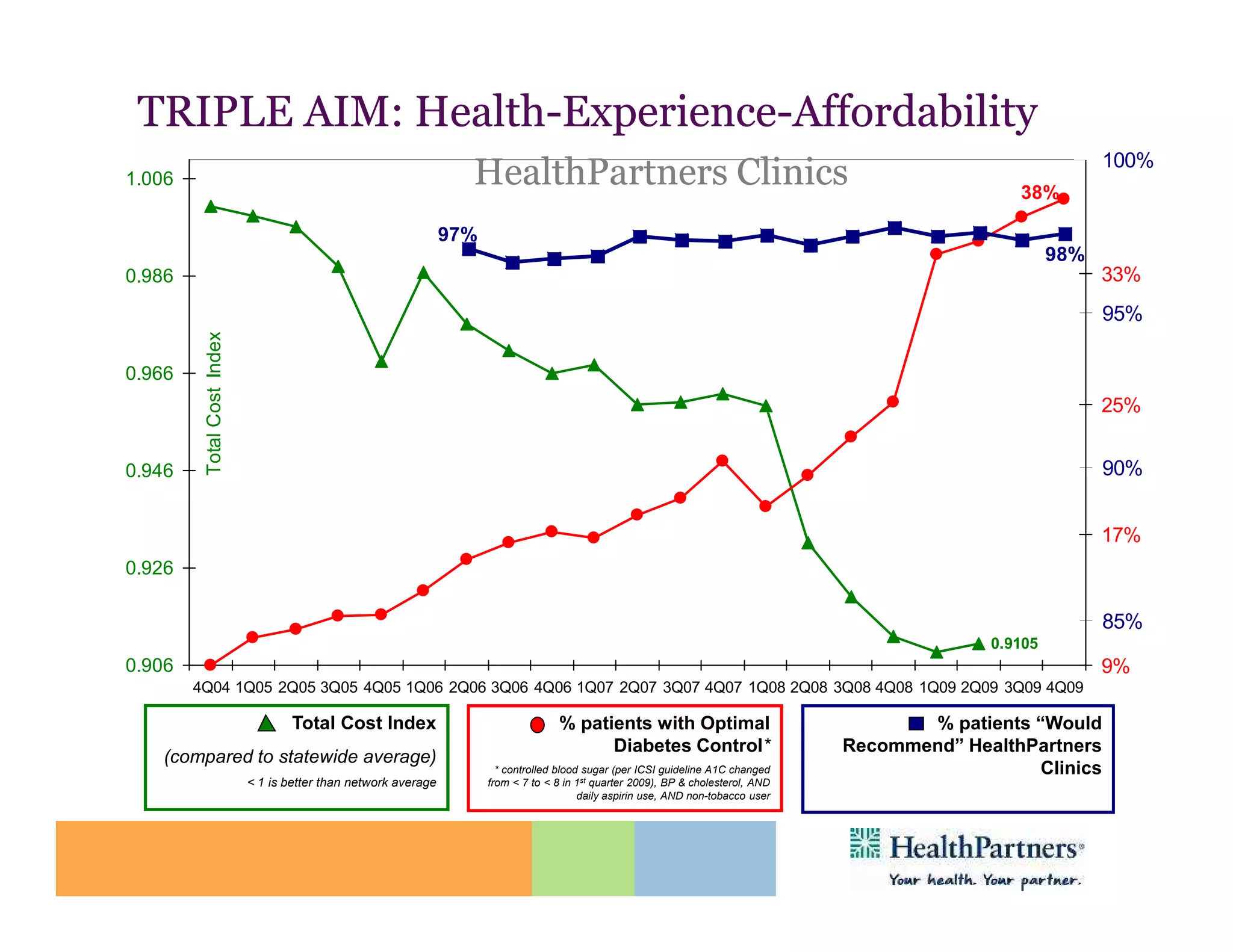
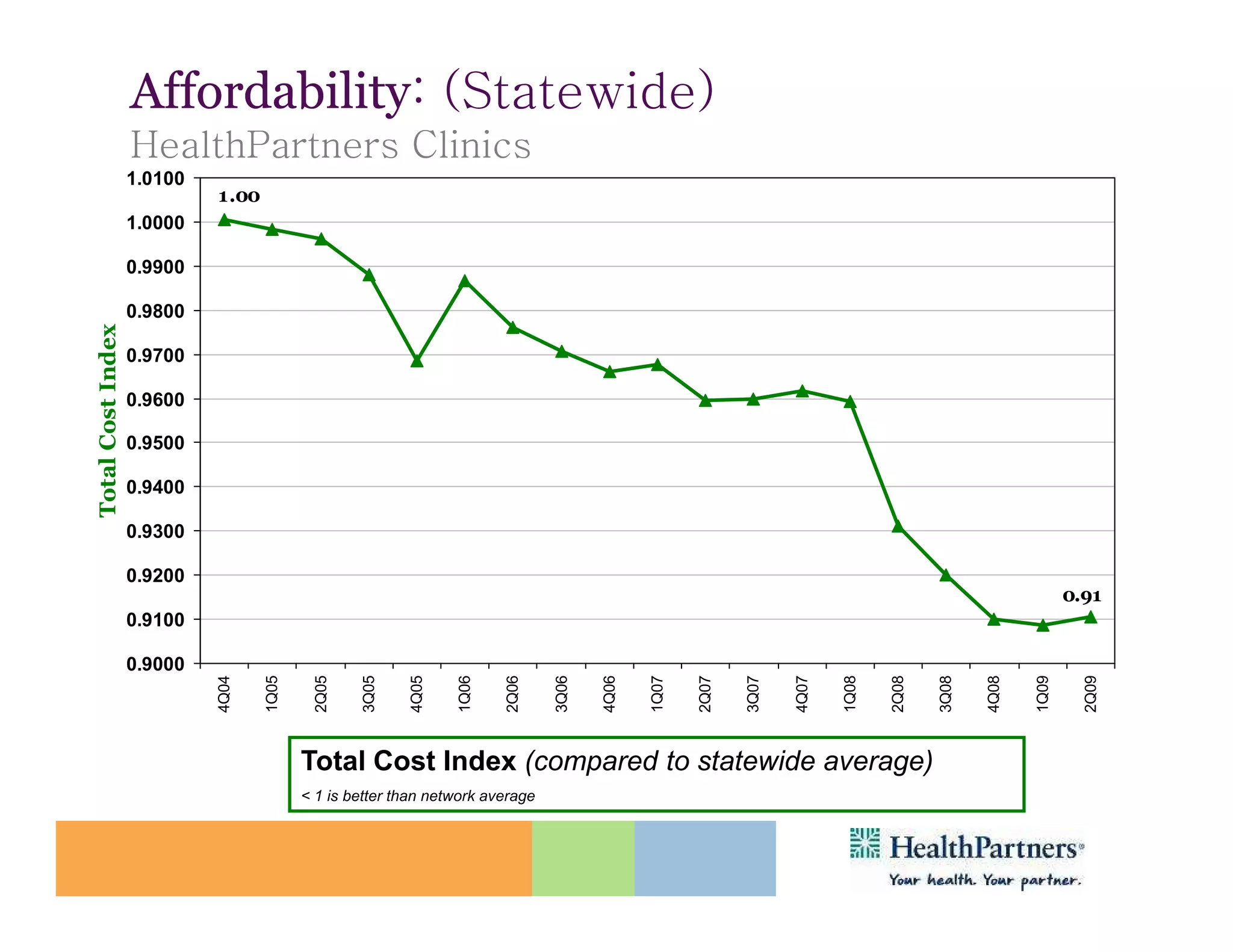
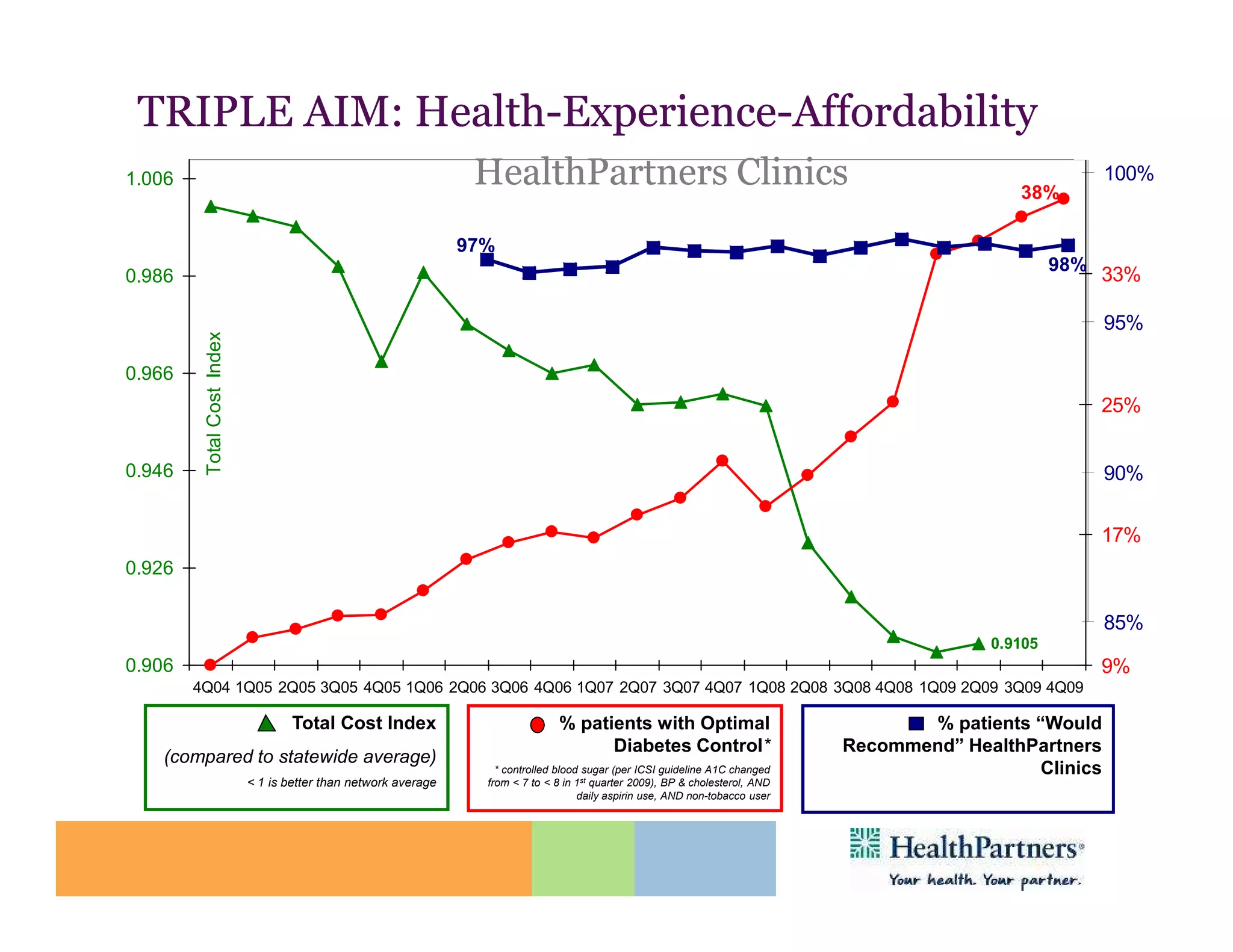
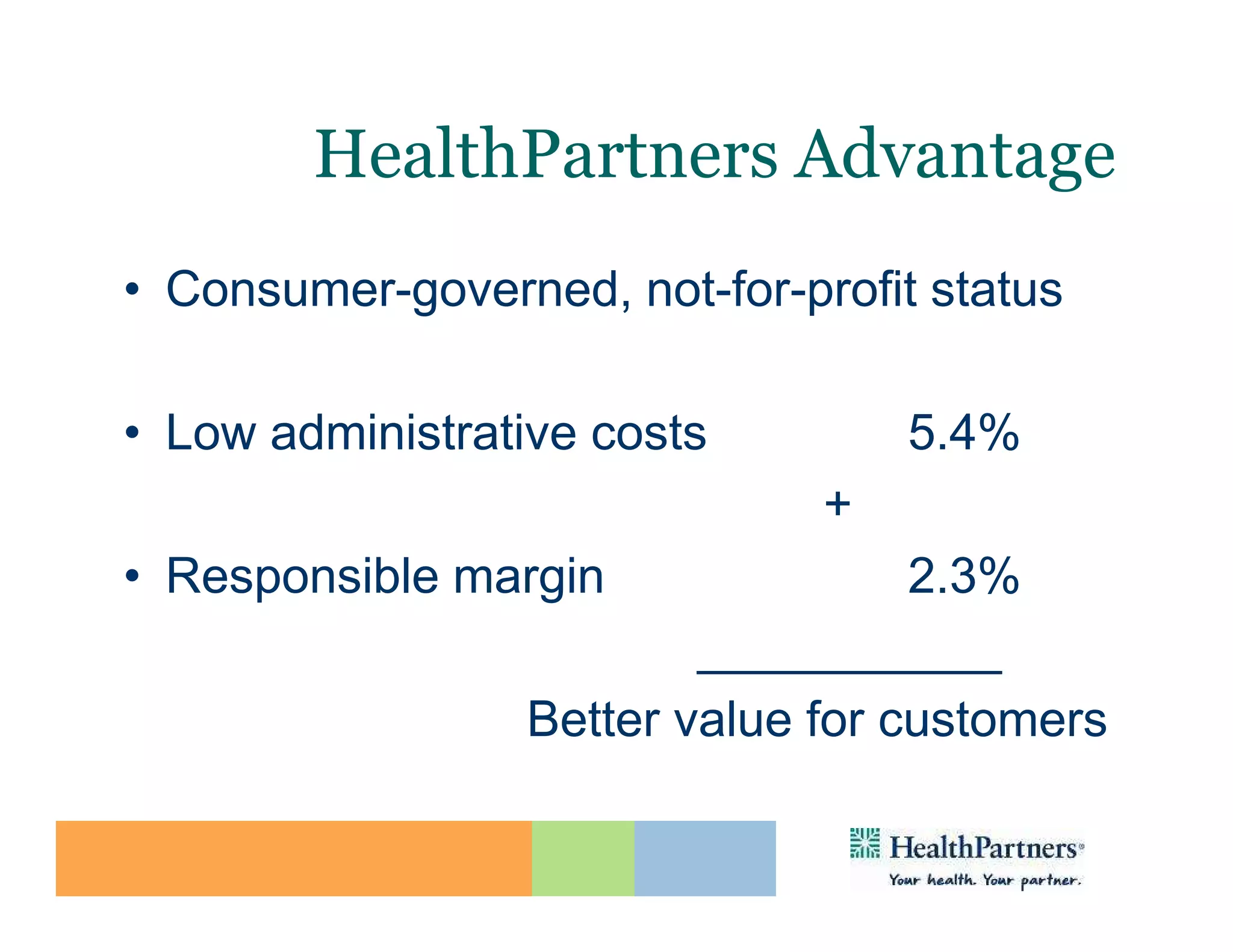
HealthPartners, a consumer-governed and not-for-profit organization, aims to improve the health of its members and the community through a focus on the triple aim of optimizing health, patient experience, and cost-effectiveness. The organization emphasizes coordinated care, healthy lifestyle support, and the use of technology to enhance healthcare delivery and affordability. HealthPartners advocates for real healthcare reform, including payment systems that prioritize value over service volume and active partnerships with consumers in health decisions.