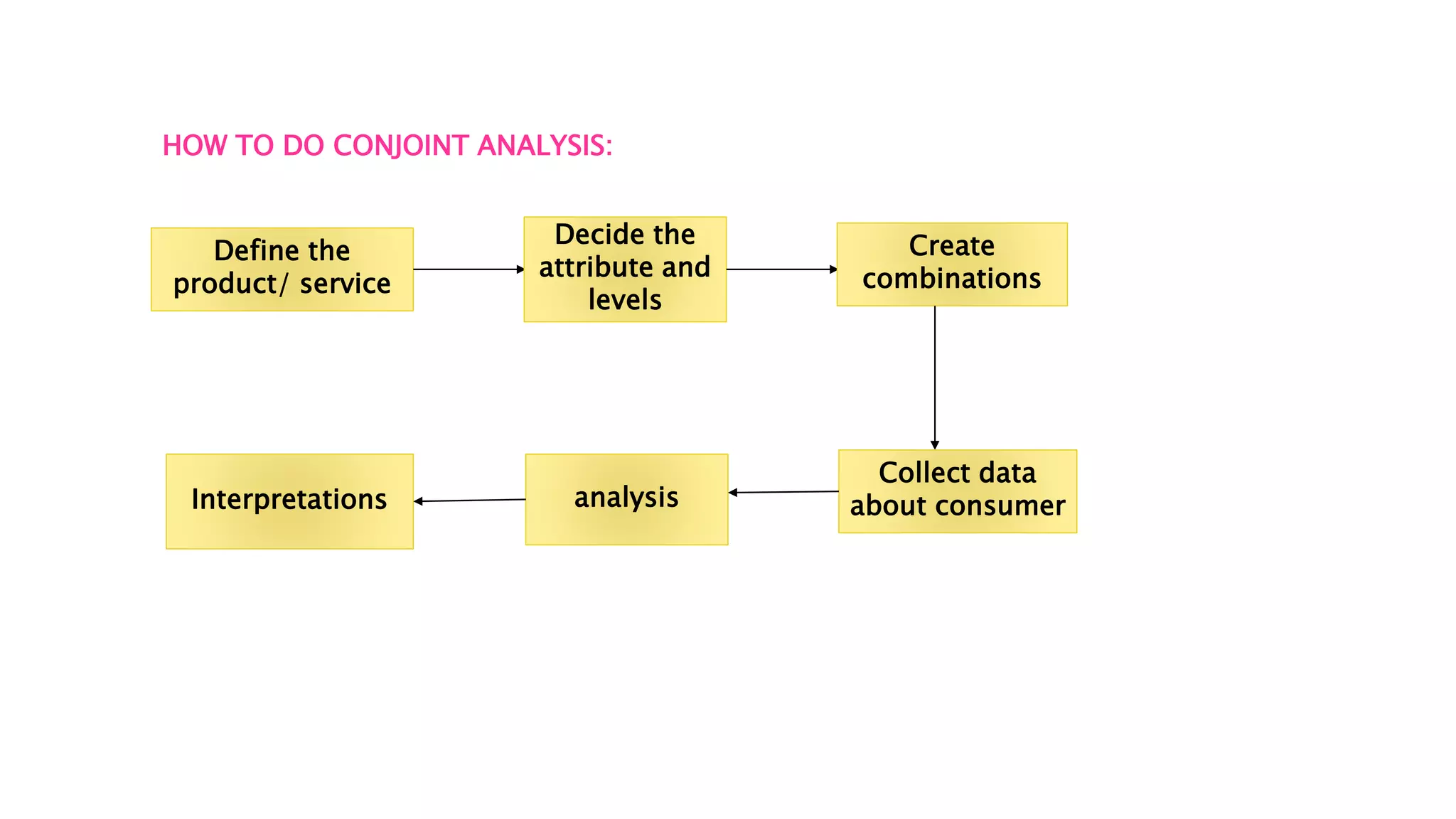
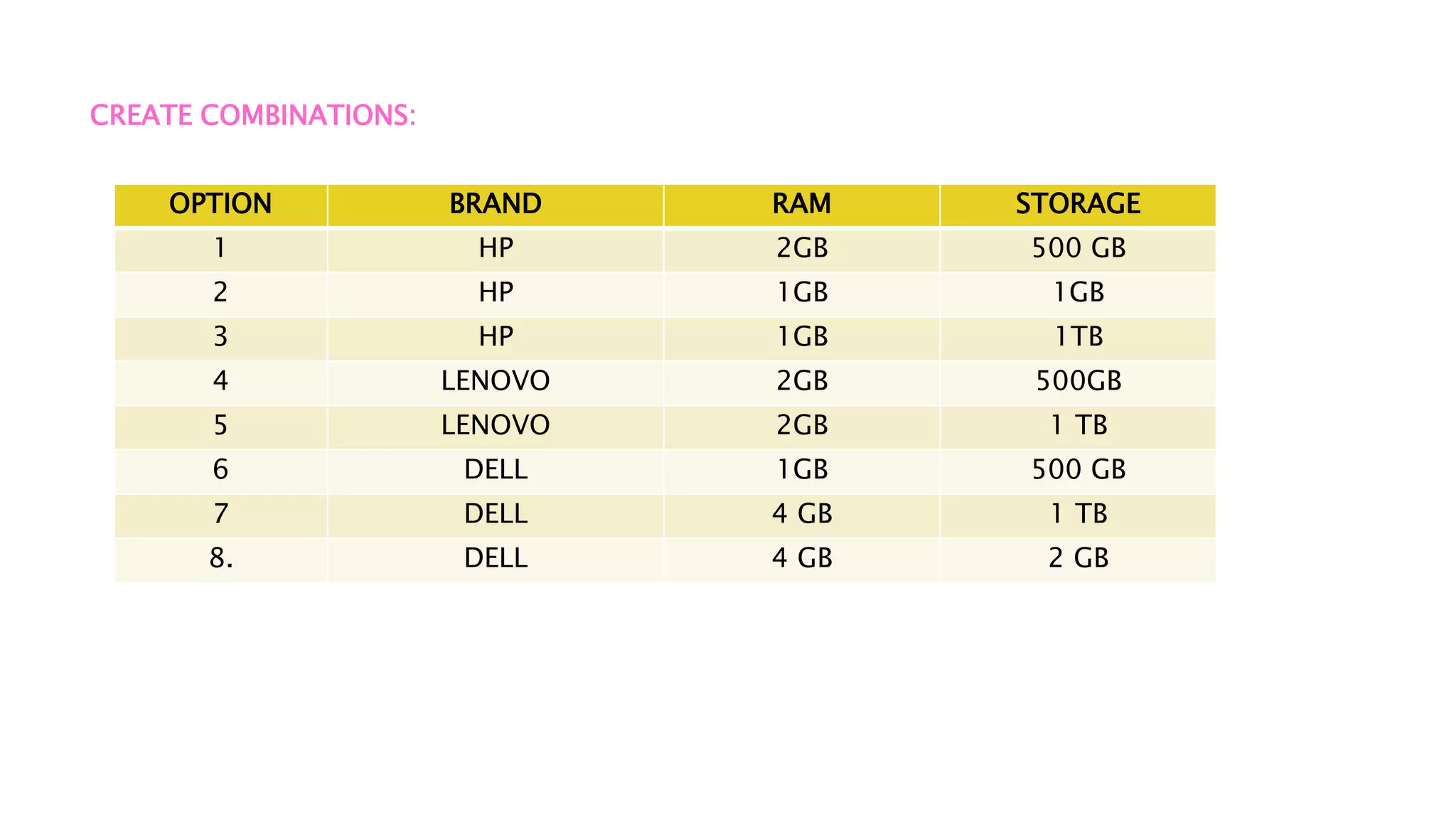
This document discusses marketing analytics and conjoint analysis. It defines marketing analytics as combining concepts of marketing and business analytics to solve broader marketing problems by breaking them into smaller questions. Conjoint analysis is introduced as a way to identify what attributes of a product or service consumers value most by having them evaluate combinations of attributes. The document provides examples of how conjoint analysis could be applied to new phone development by having consumers choose between combinations of phone brand, storage, RAM, etc. It outlines the steps of defining attributes and levels, creating combinations for consumers to evaluate, collecting their data, and interpreting the results.