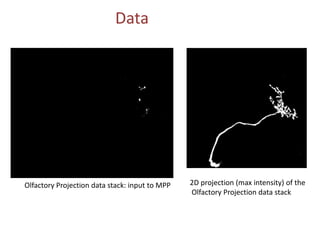
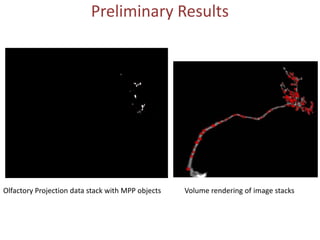
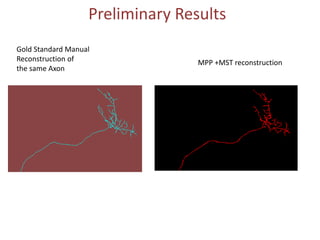
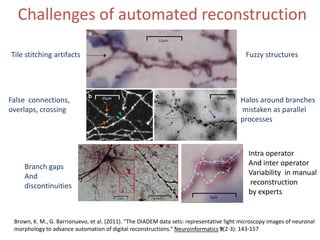
The document presents a detailed examination of neurite tracing using a marked point process (MPP) model, supervised by Prof. Ooi Wei Tsang and Prof. Daniel Racoceanu. It discusses the challenges and results of automated digital reconstruction and quantification of neuronal morphology, highlighting the unsupervised extraction of 3D neuronal networks while addressing issues like tile stitching artifacts and false connections. Key methodologies include energy optimization techniques and the integration of geometric constraints for improved object detection in neuronal imagery.




![Marked Point Process
• Set of objects= realization of a MPP
K: point process whose realization is a
random number of points given by a
random variable
• Marked point process objects defined in S= K x M
M: mark space
of the object
• Example: M= [Rmin,Rmax]
• And (x,y, R) defines a disc object
A K
B
centre radius C
D E
F](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markedpointprocessforneuritetracing-120509052657-phpapp01/85/Marked-Point-Process-For-Neurite-Tracing-8-320.jpg)


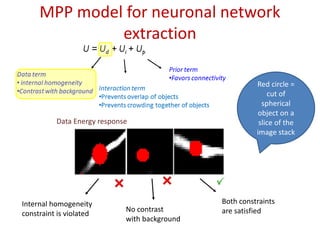
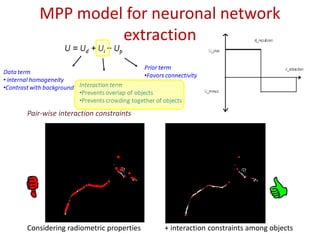
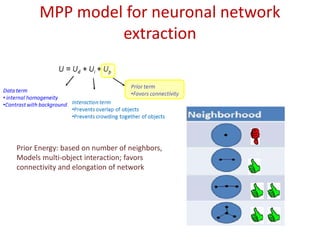
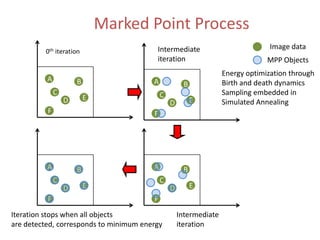
![MPP model for neuronal network
extraction
• Aim: unsupervised 3D neuronal network extraction
• Model: object process (objects: sphere ~ U ([rmin , rmax ])
specified by an Energy:
U = Ud + Ui + Up
Prior term
Data term
•Favors connectivity
• internal homogeneity
•Contrast with background Interaction term
•Prevents overlap of objects
•Prevents crowding together of objects
• Optimization: Multiple Birth and Death dynamics
embedded in Simulated annealing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markedpointprocessforneuritetracing-120509052657-phpapp01/85/Marked-Point-Process-For-Neurite-Tracing-11-320.jpg)