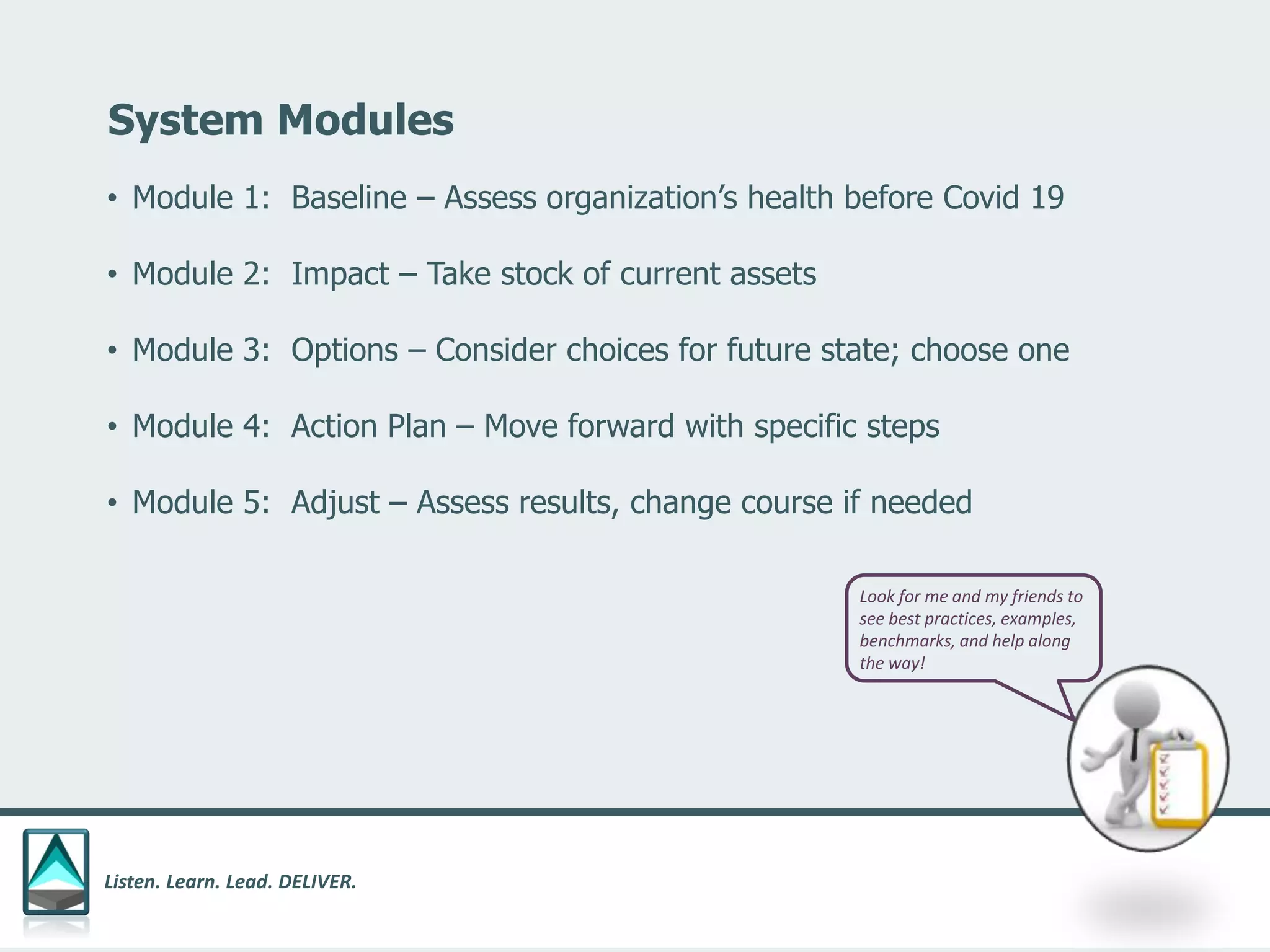
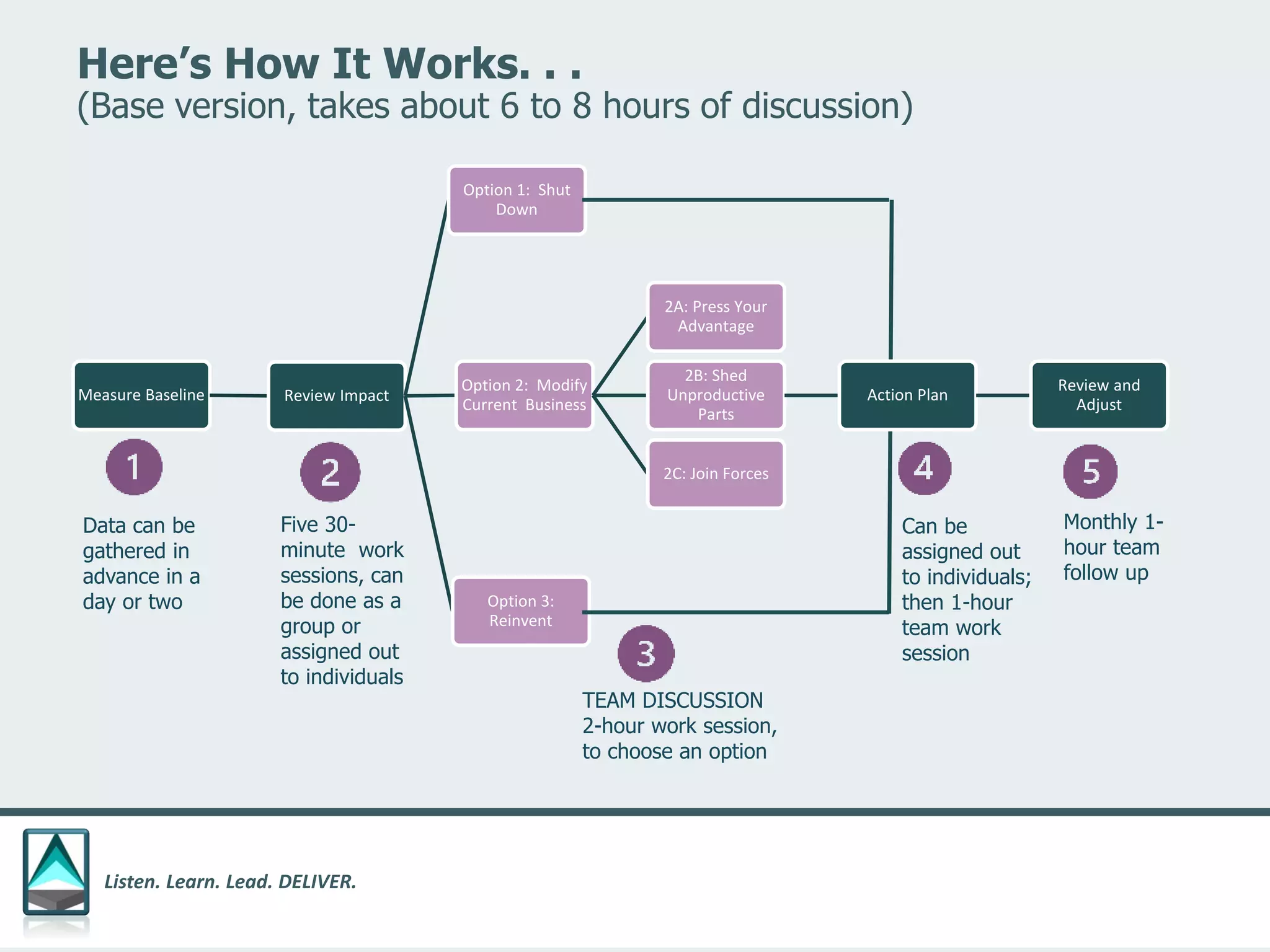
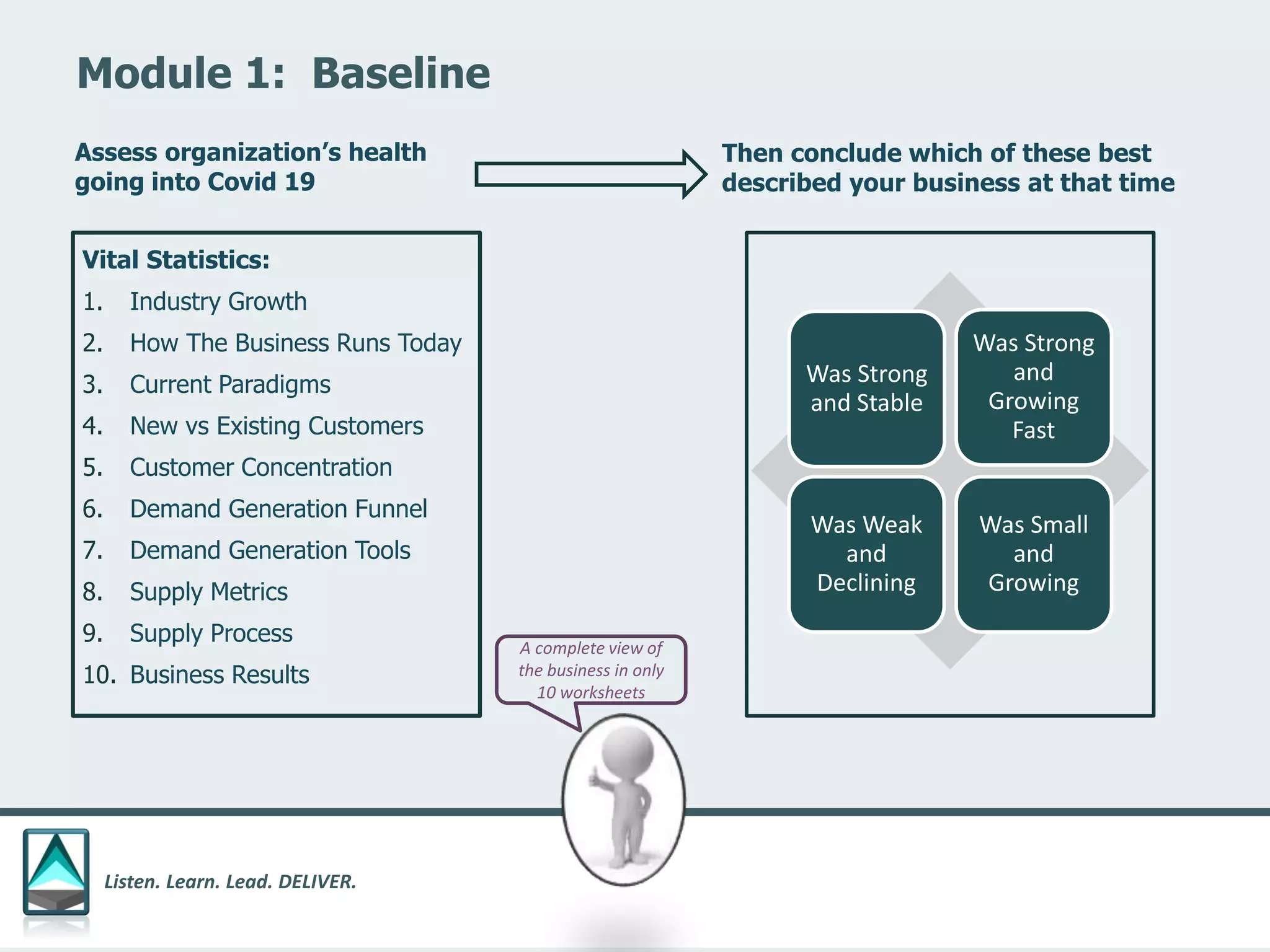
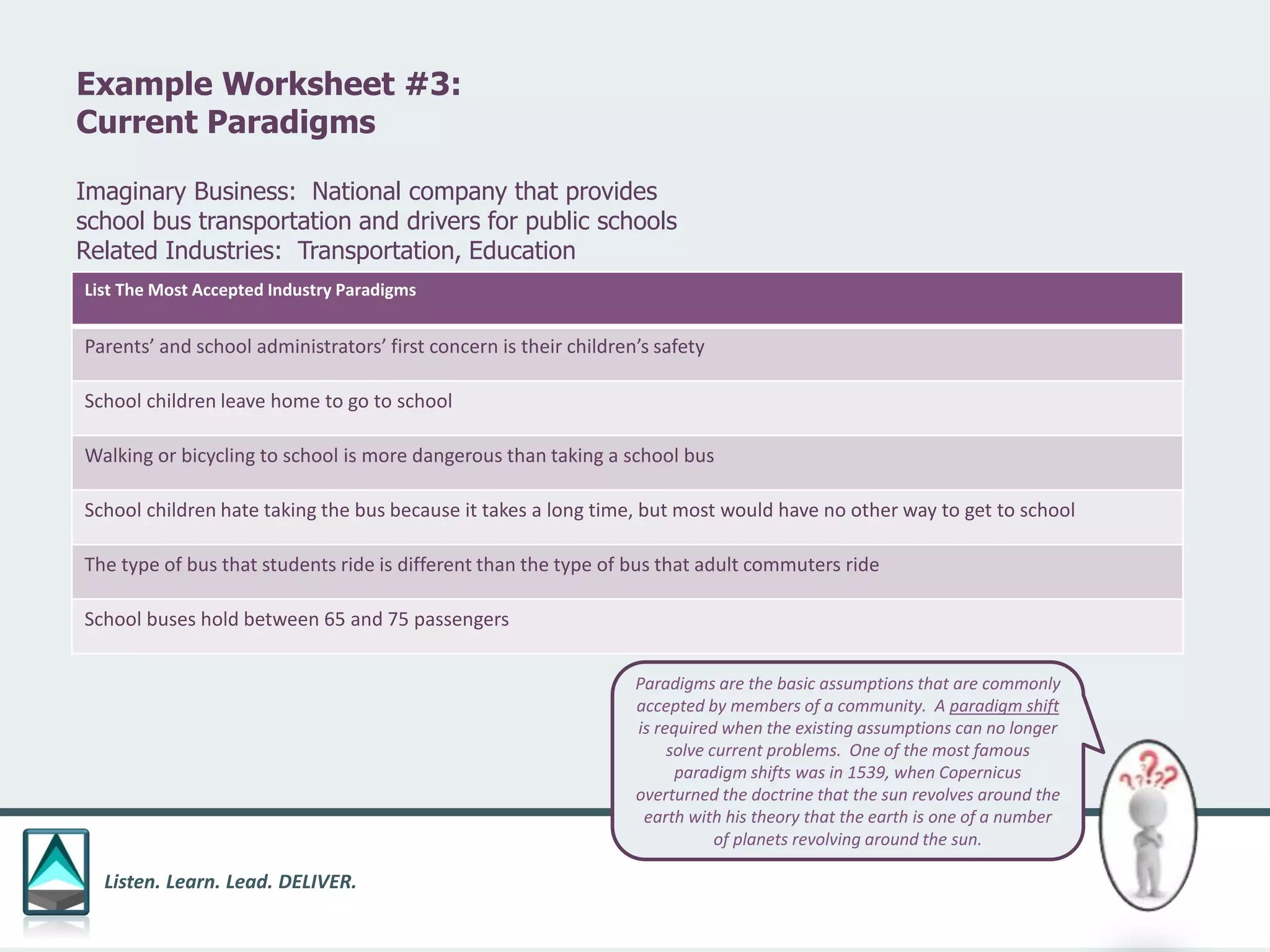
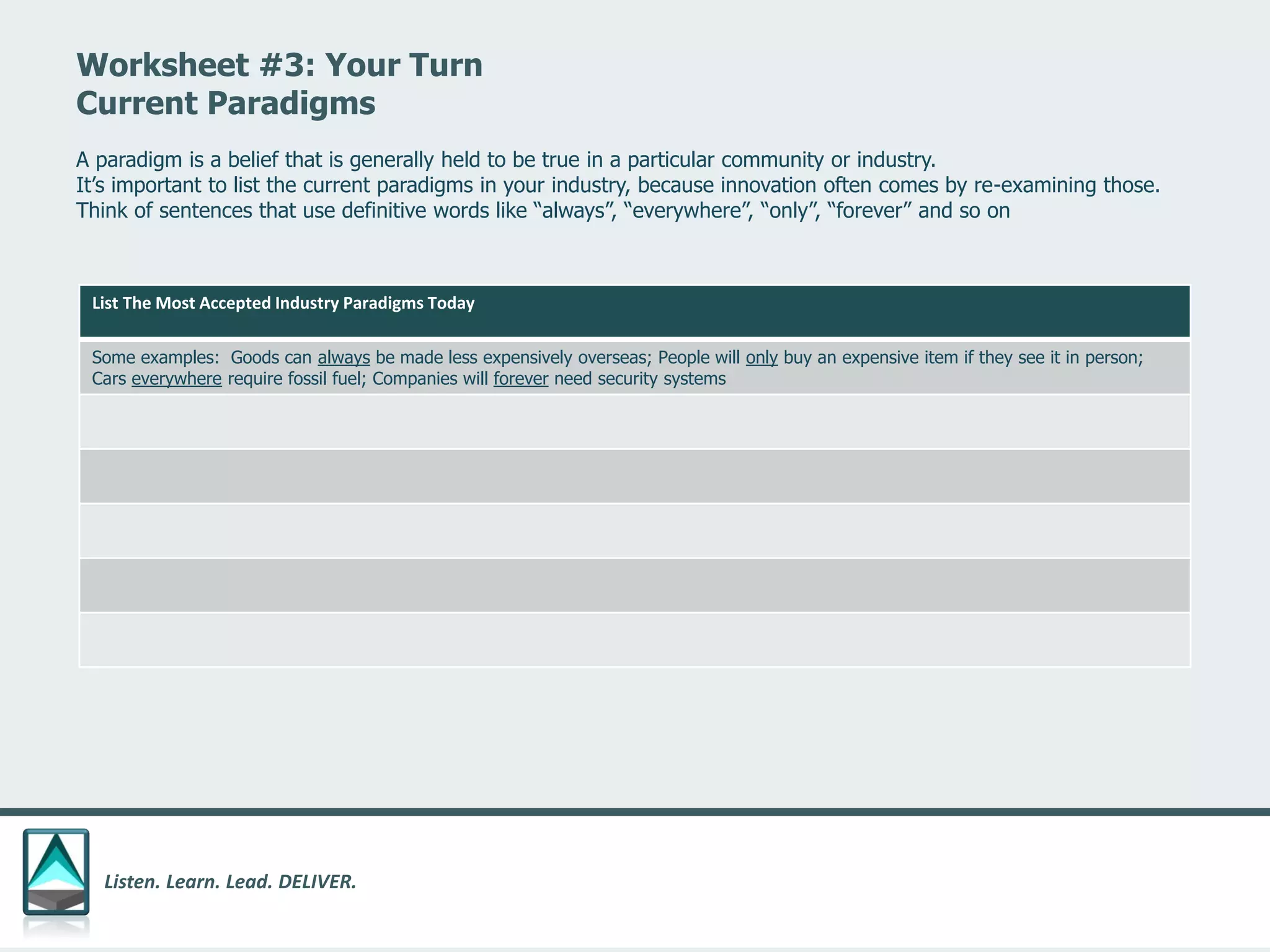
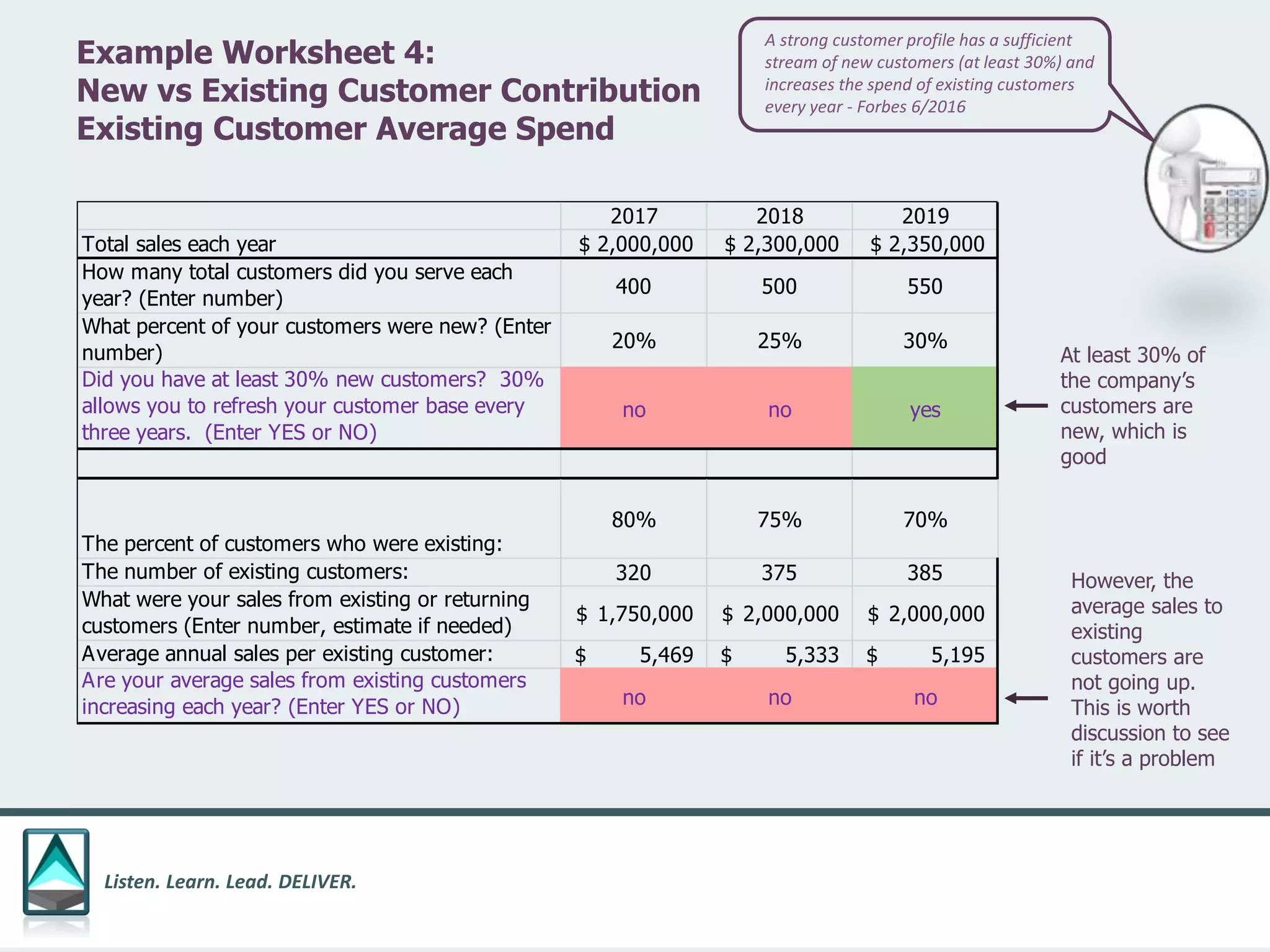
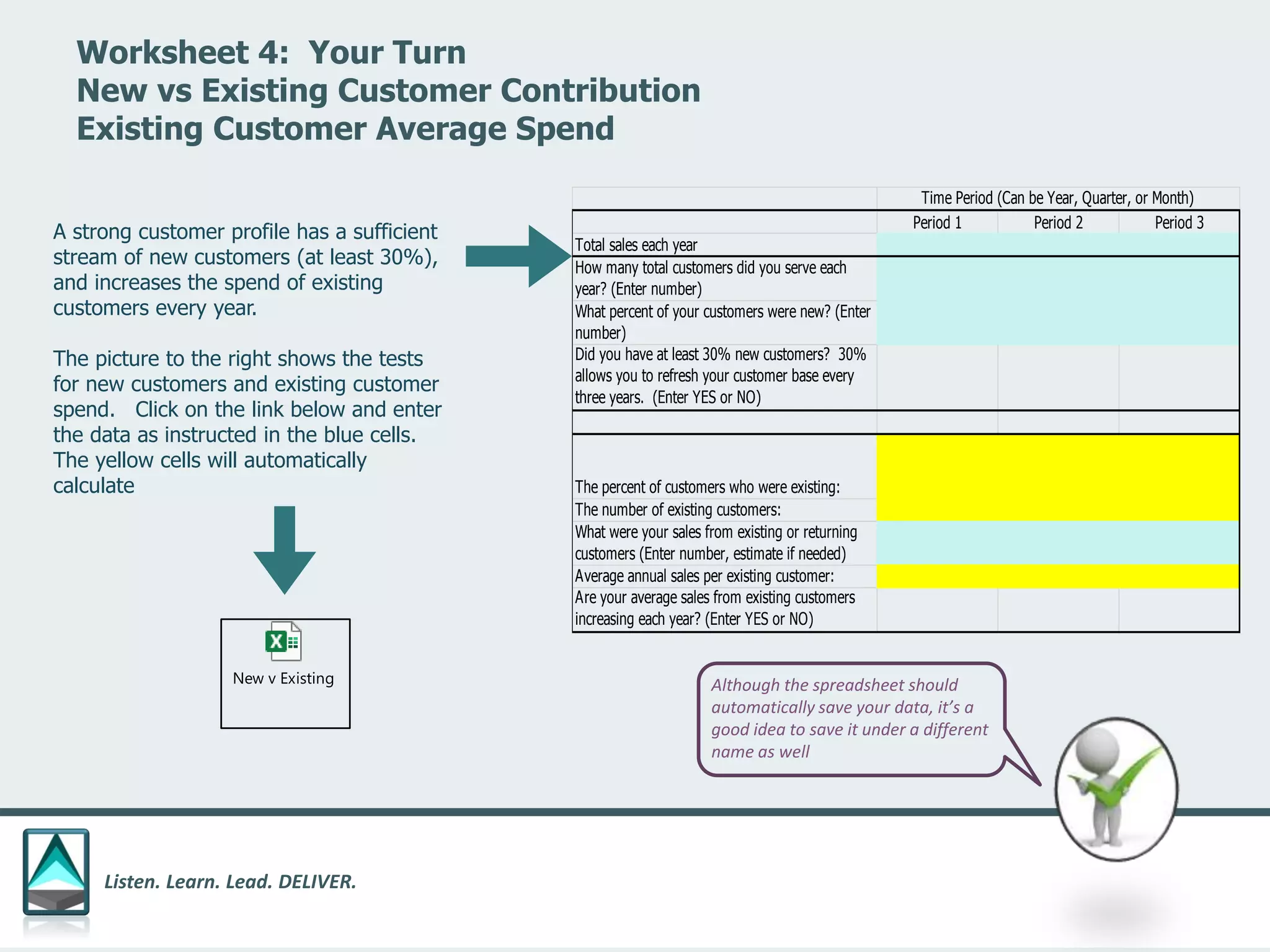
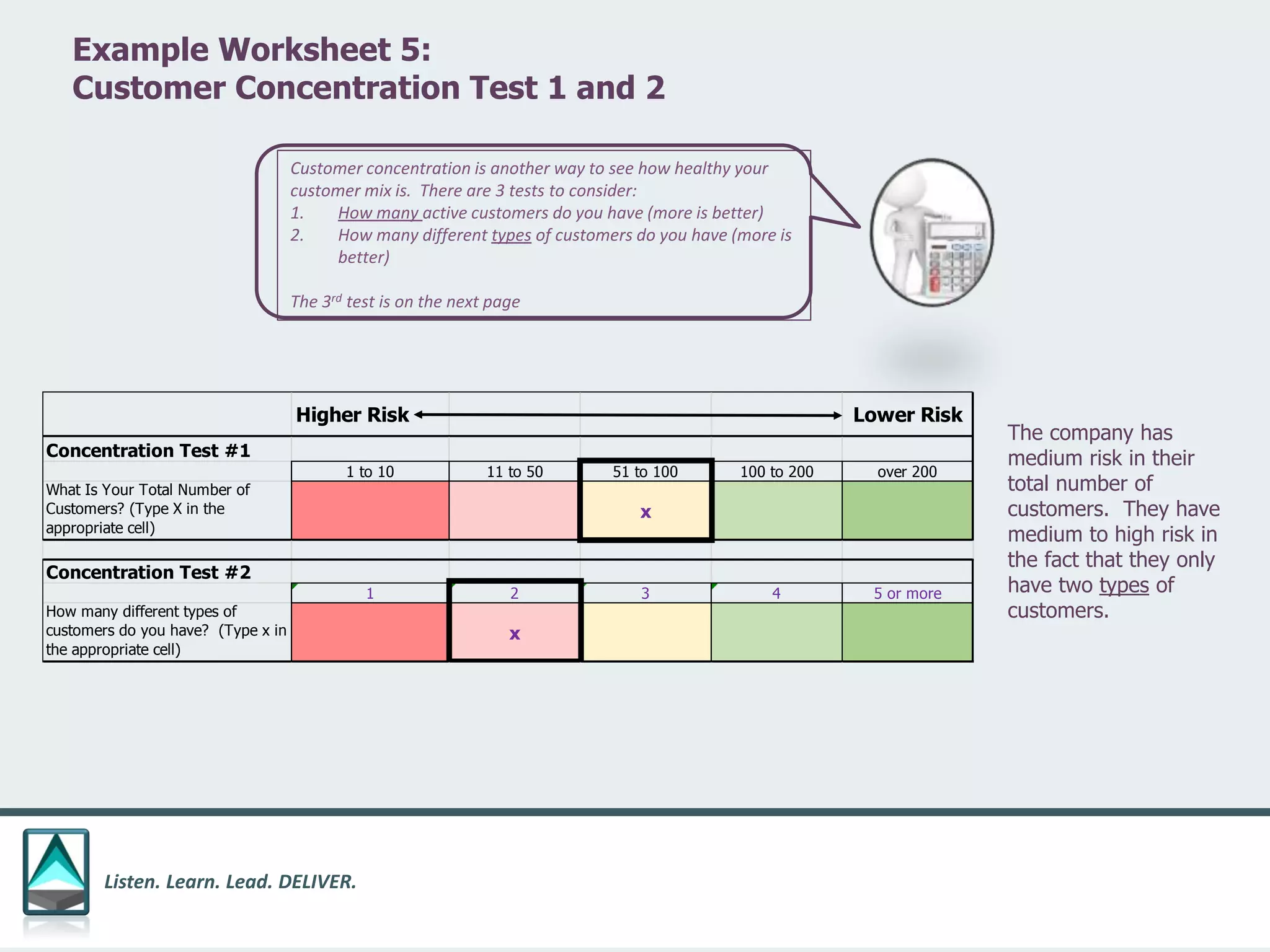
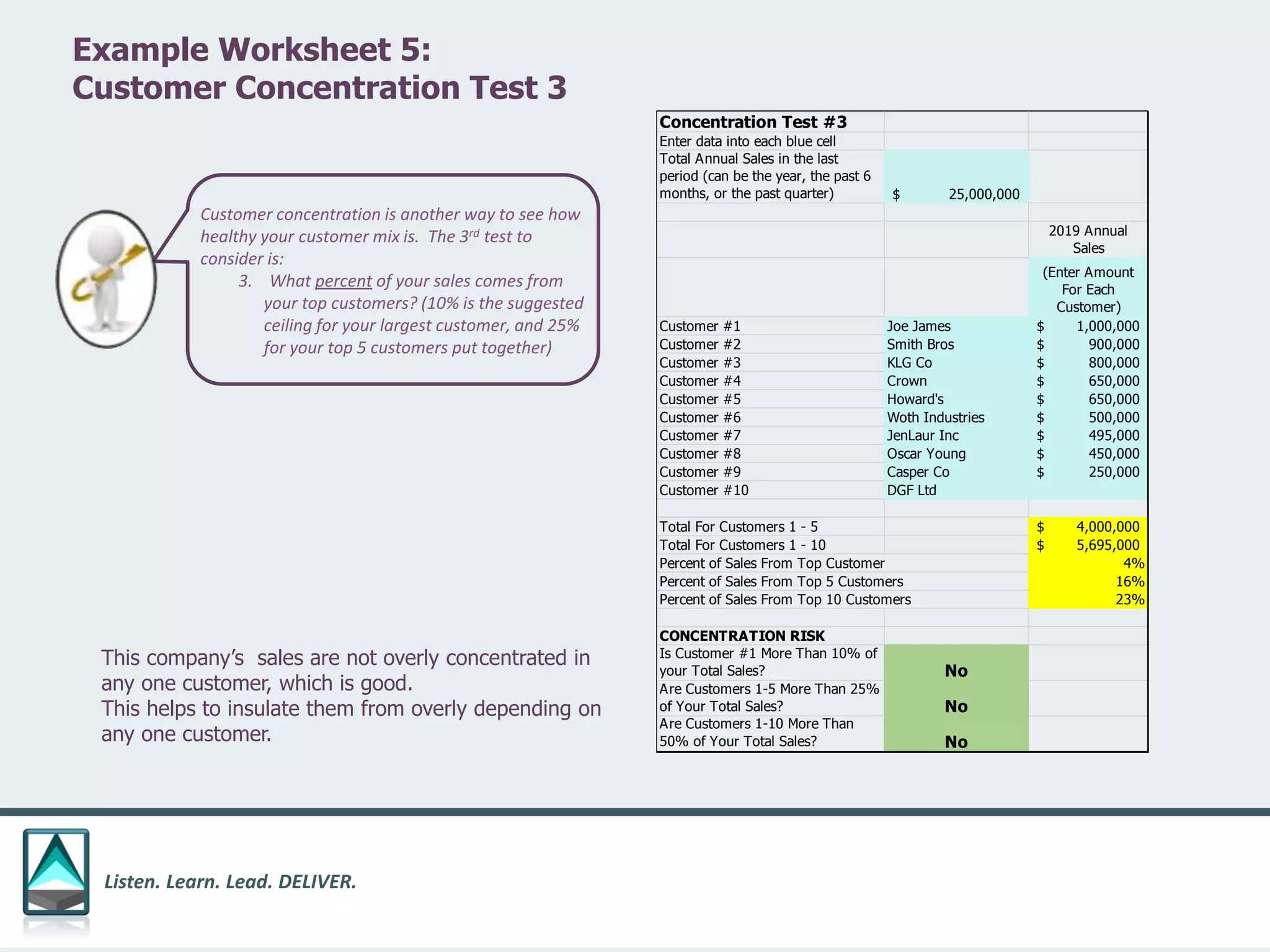
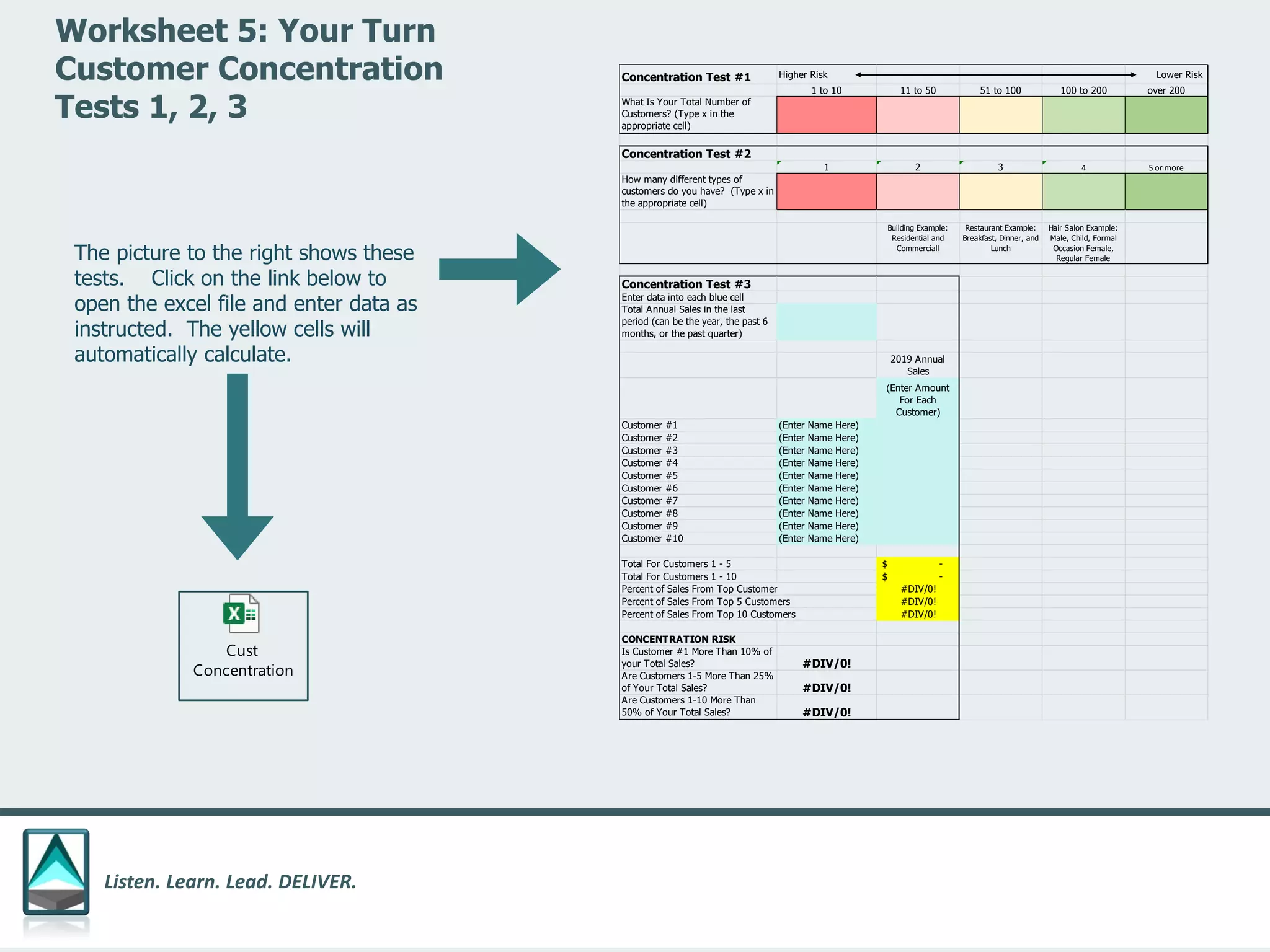
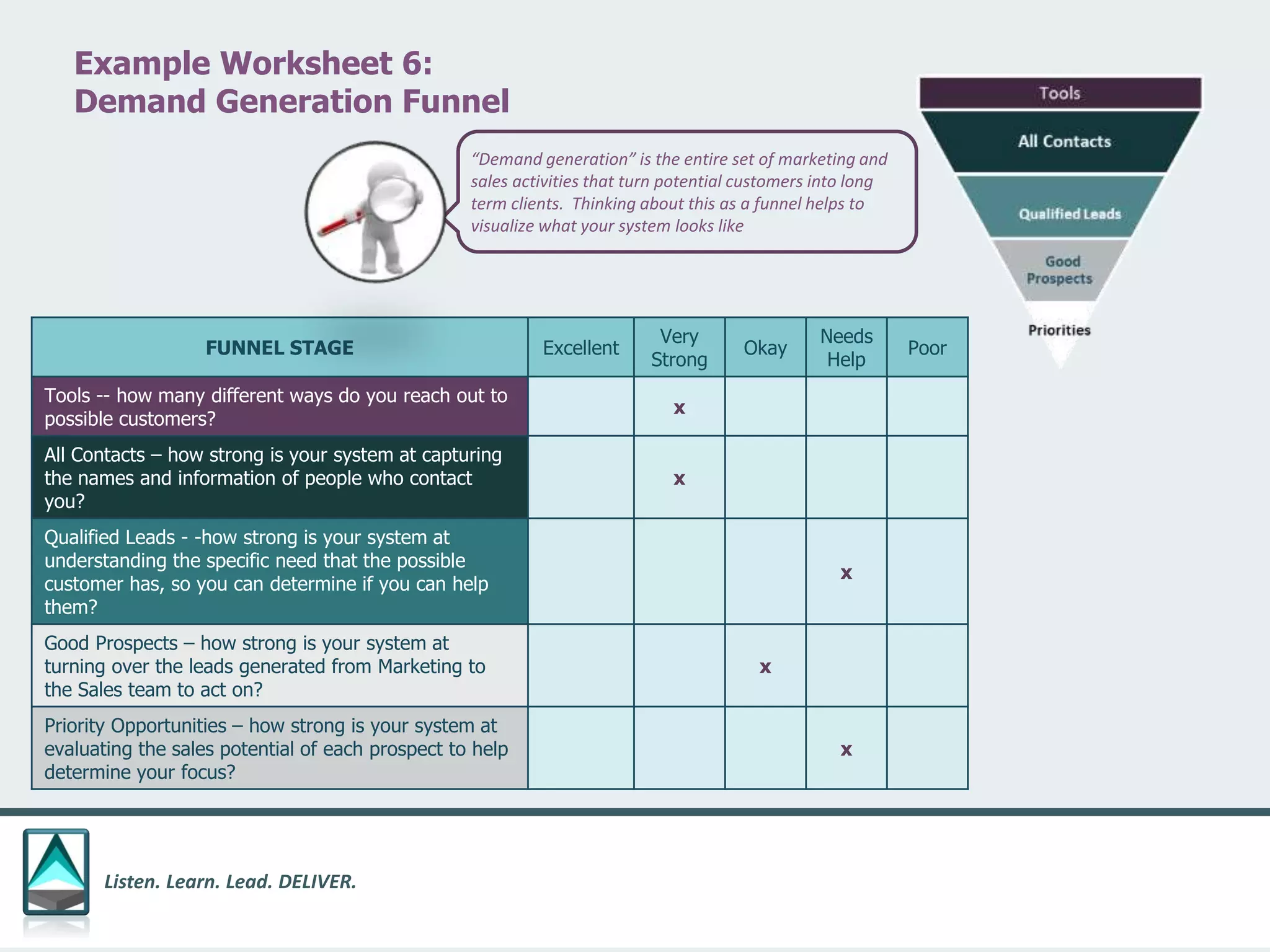
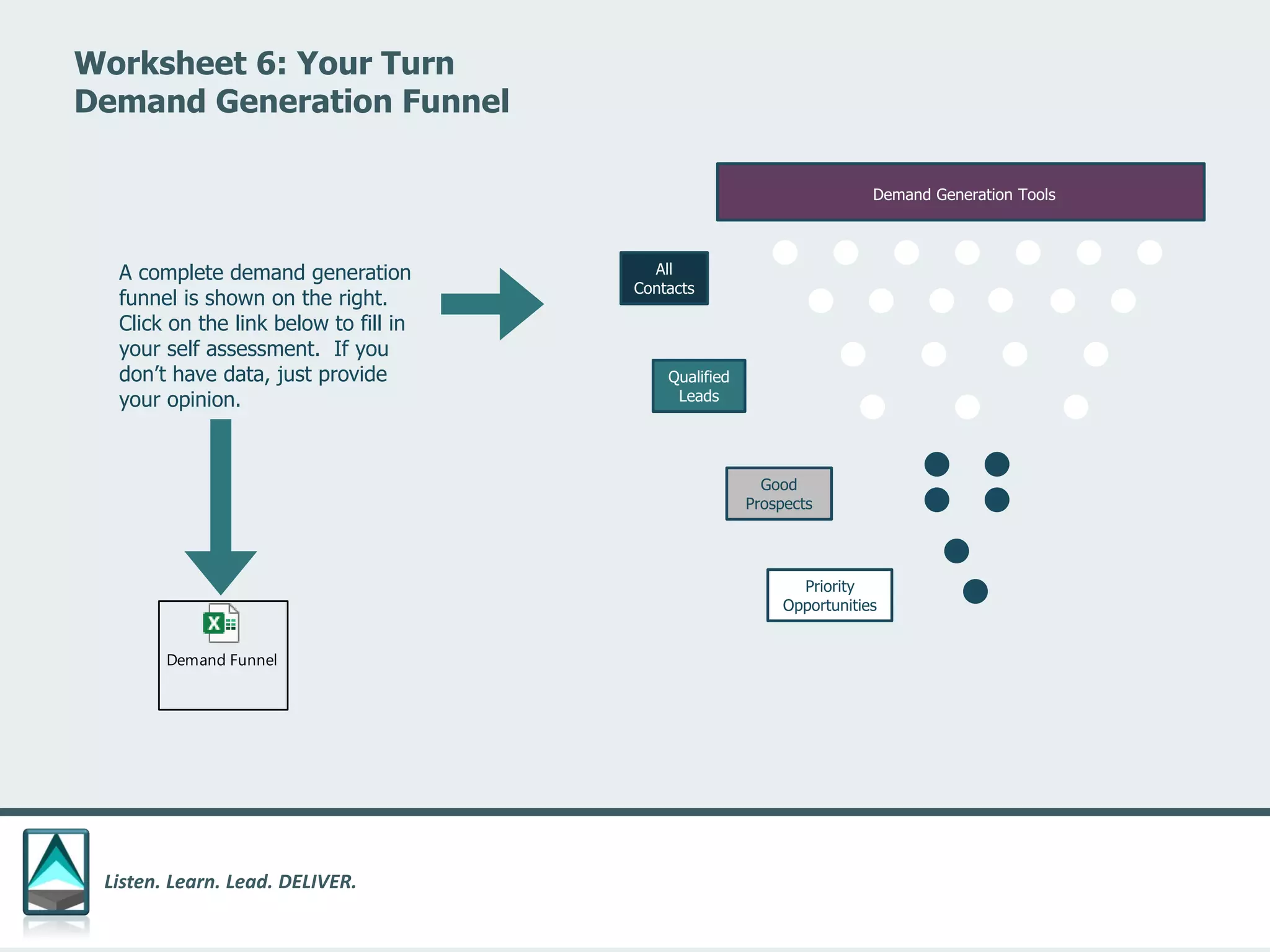
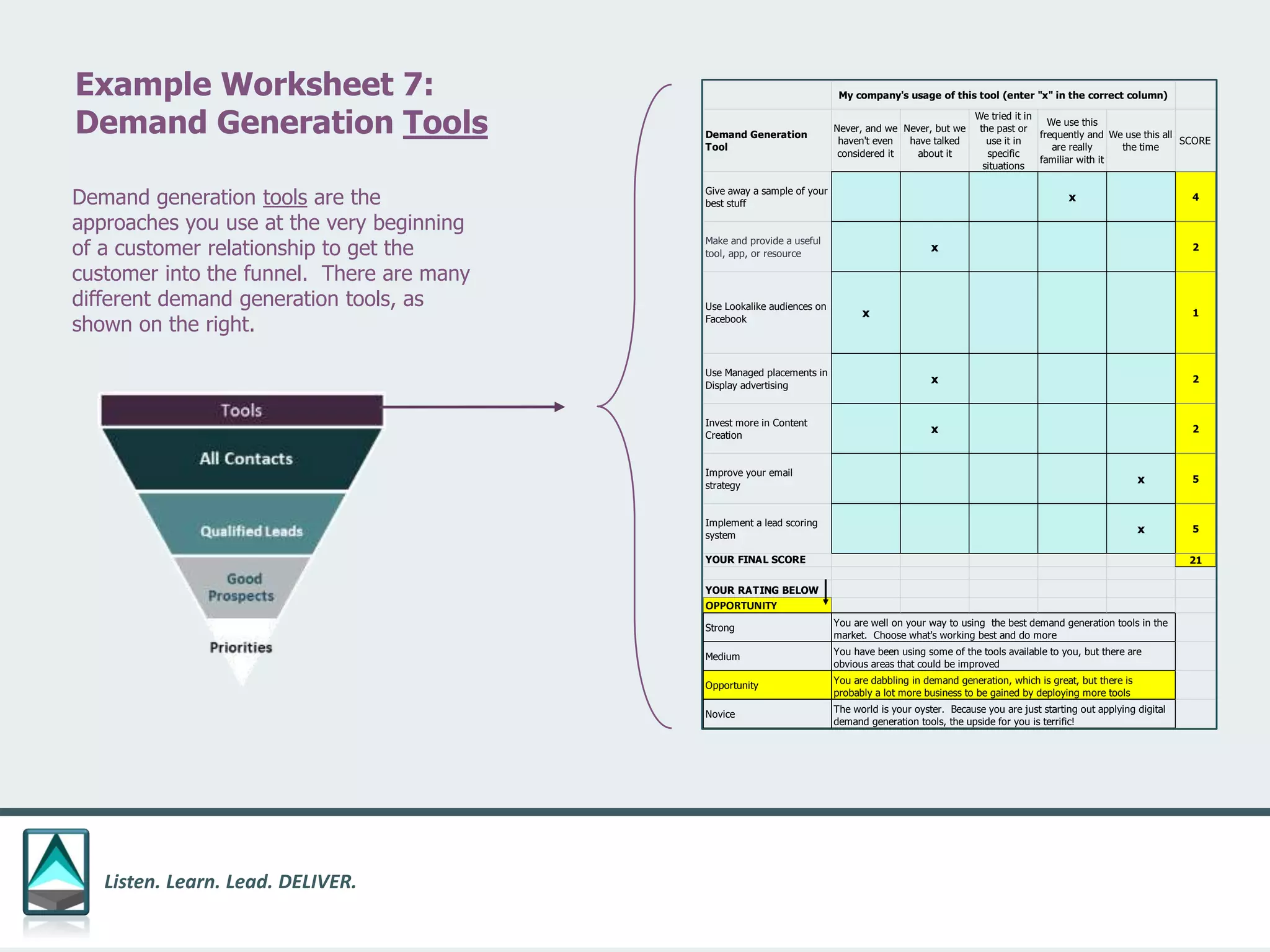
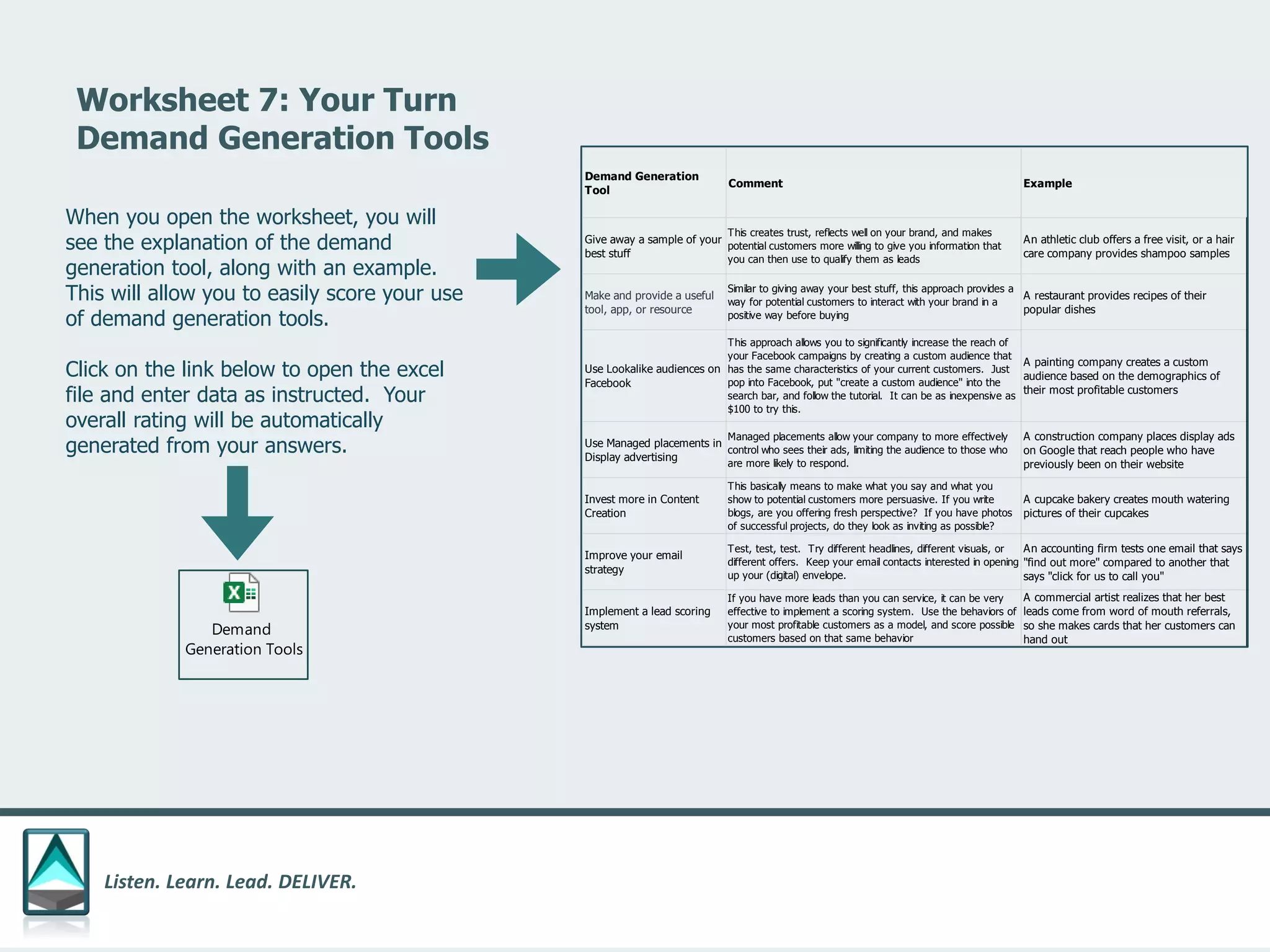
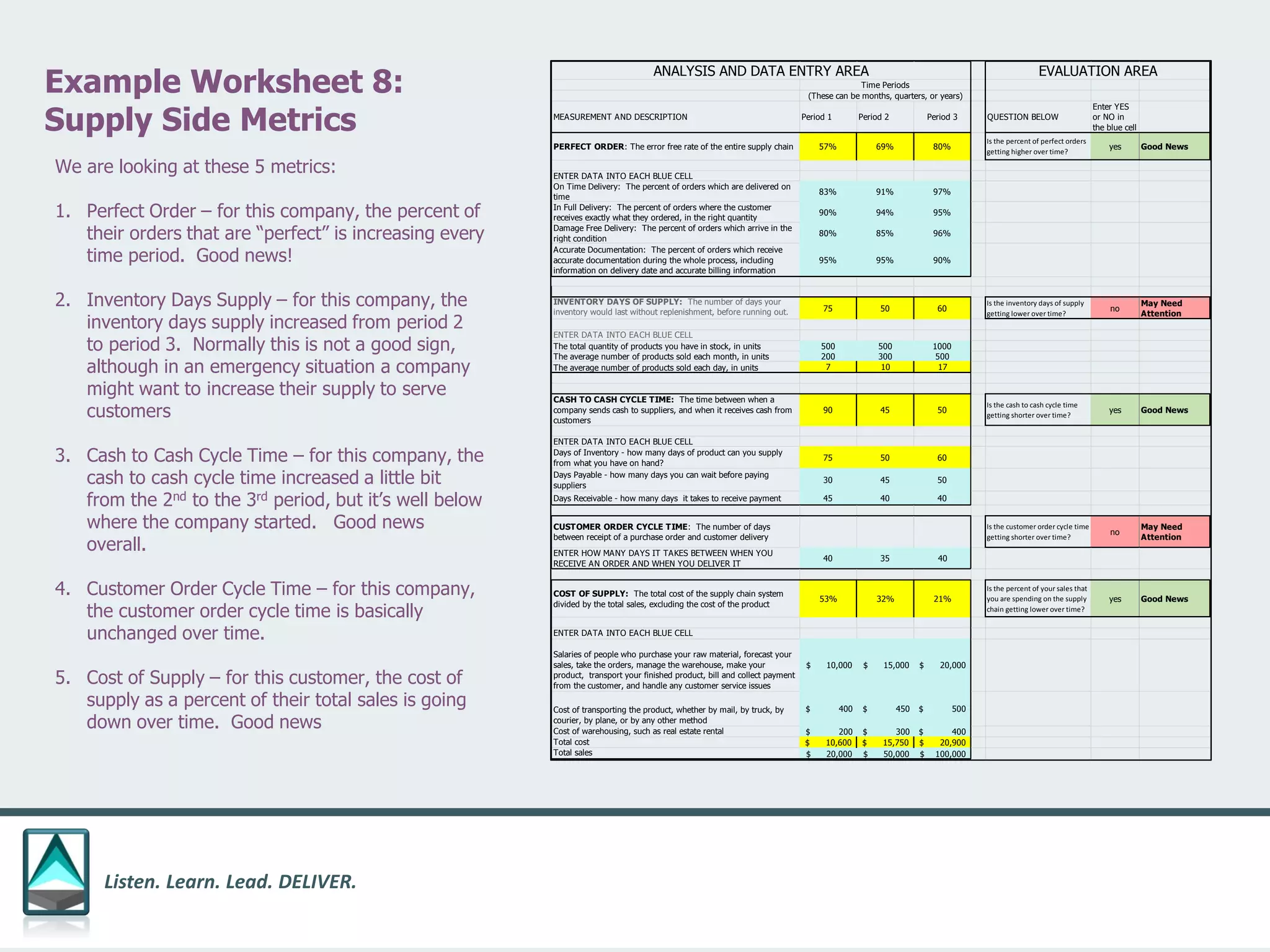
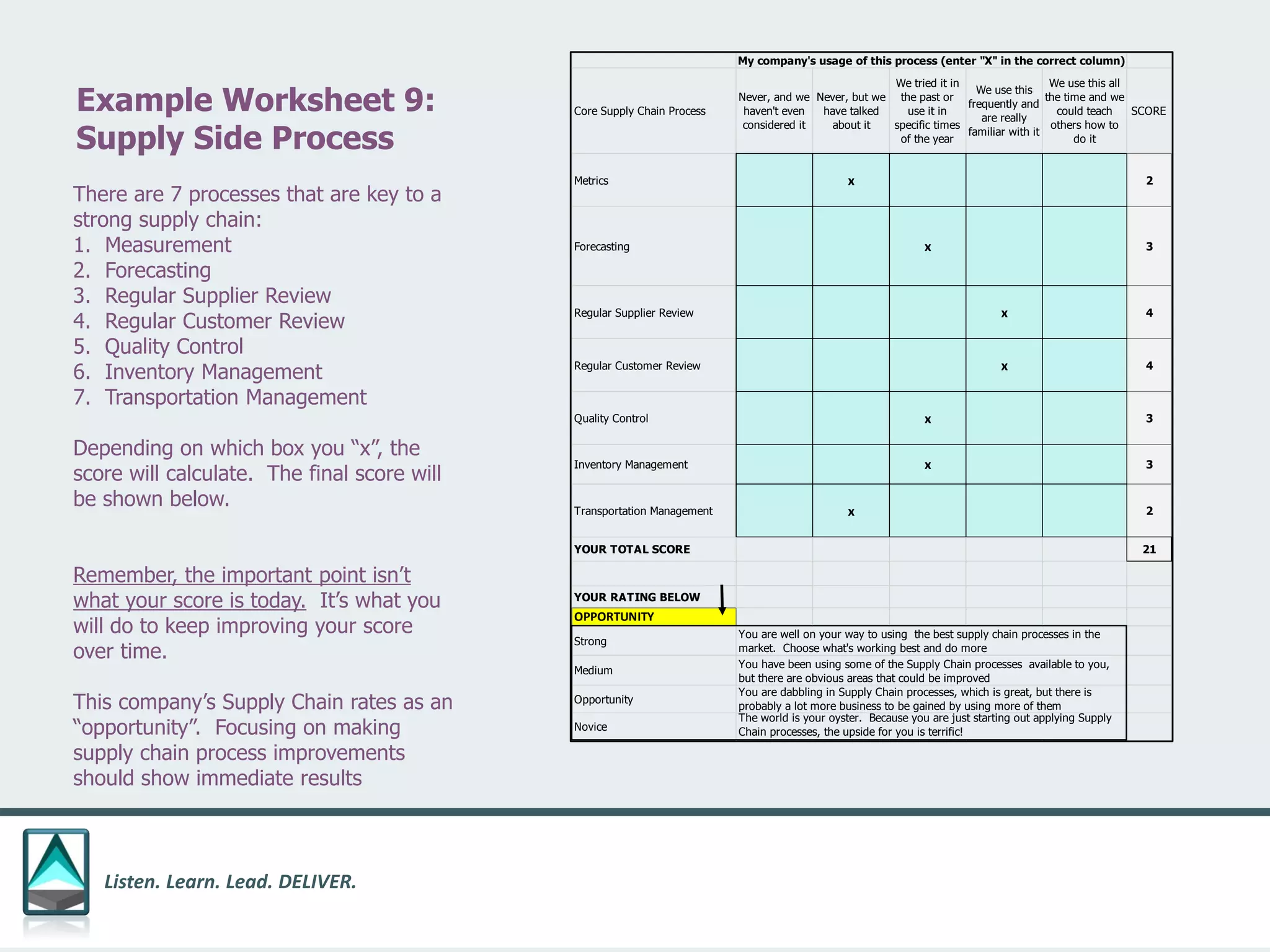
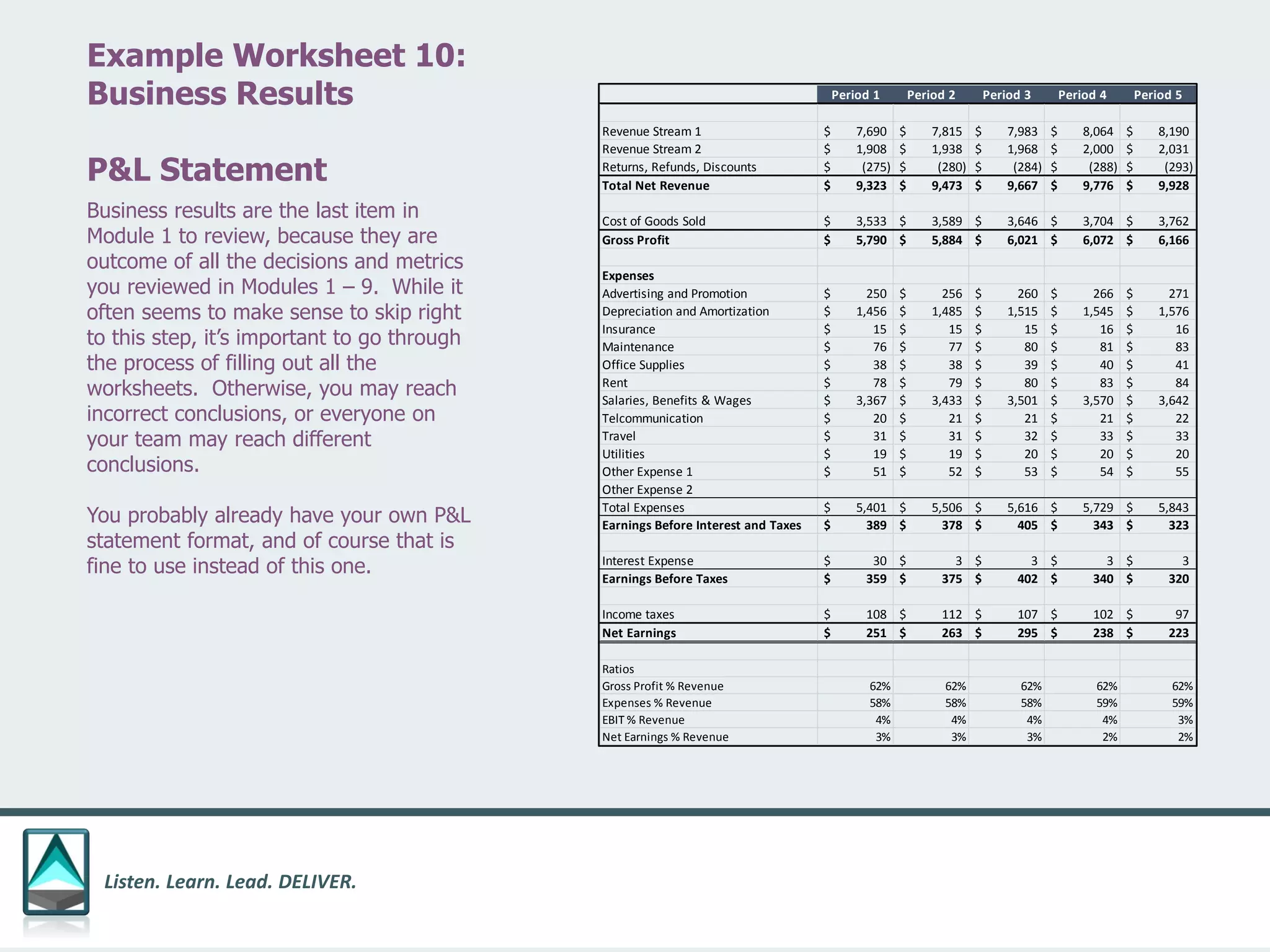
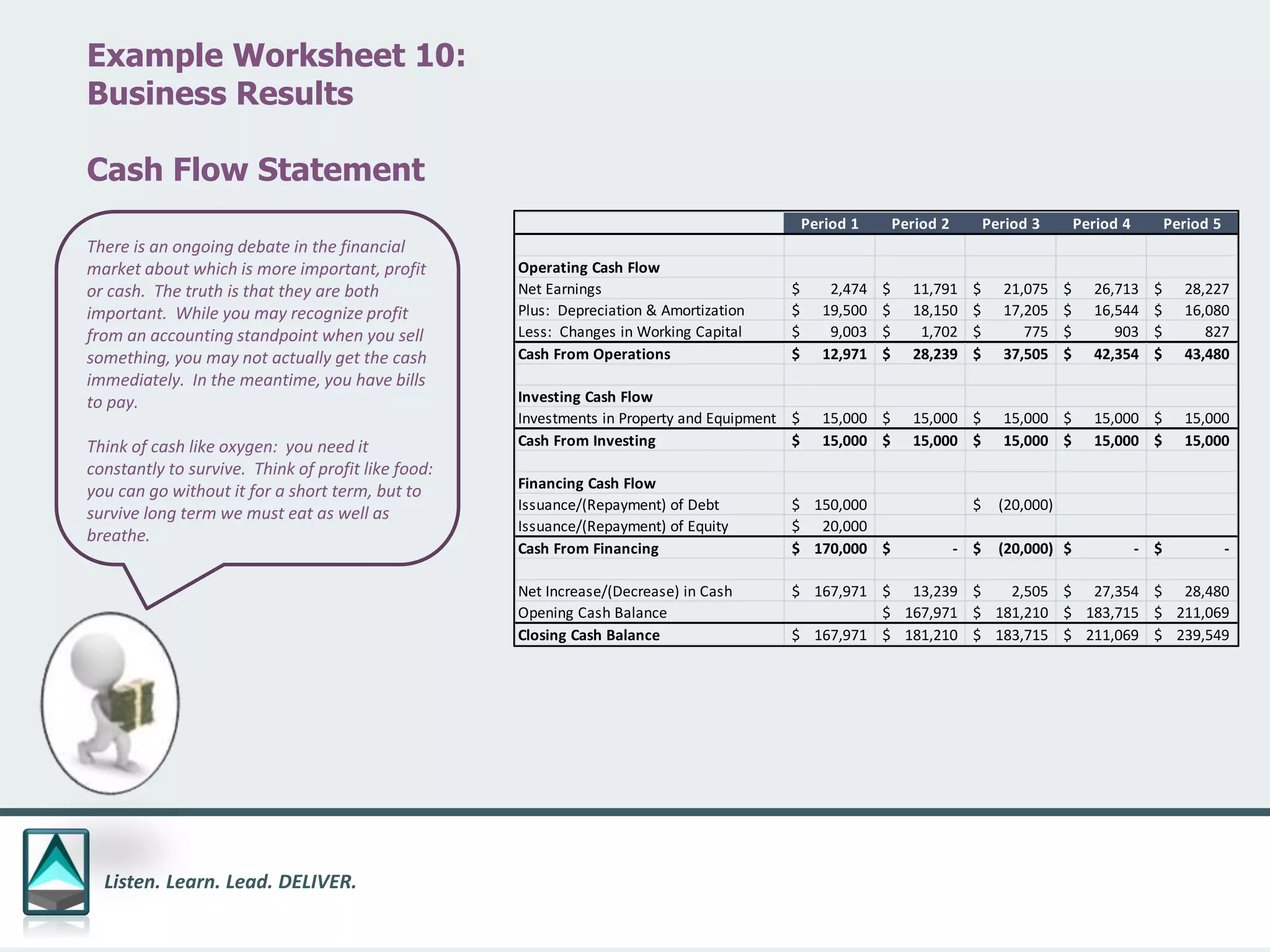
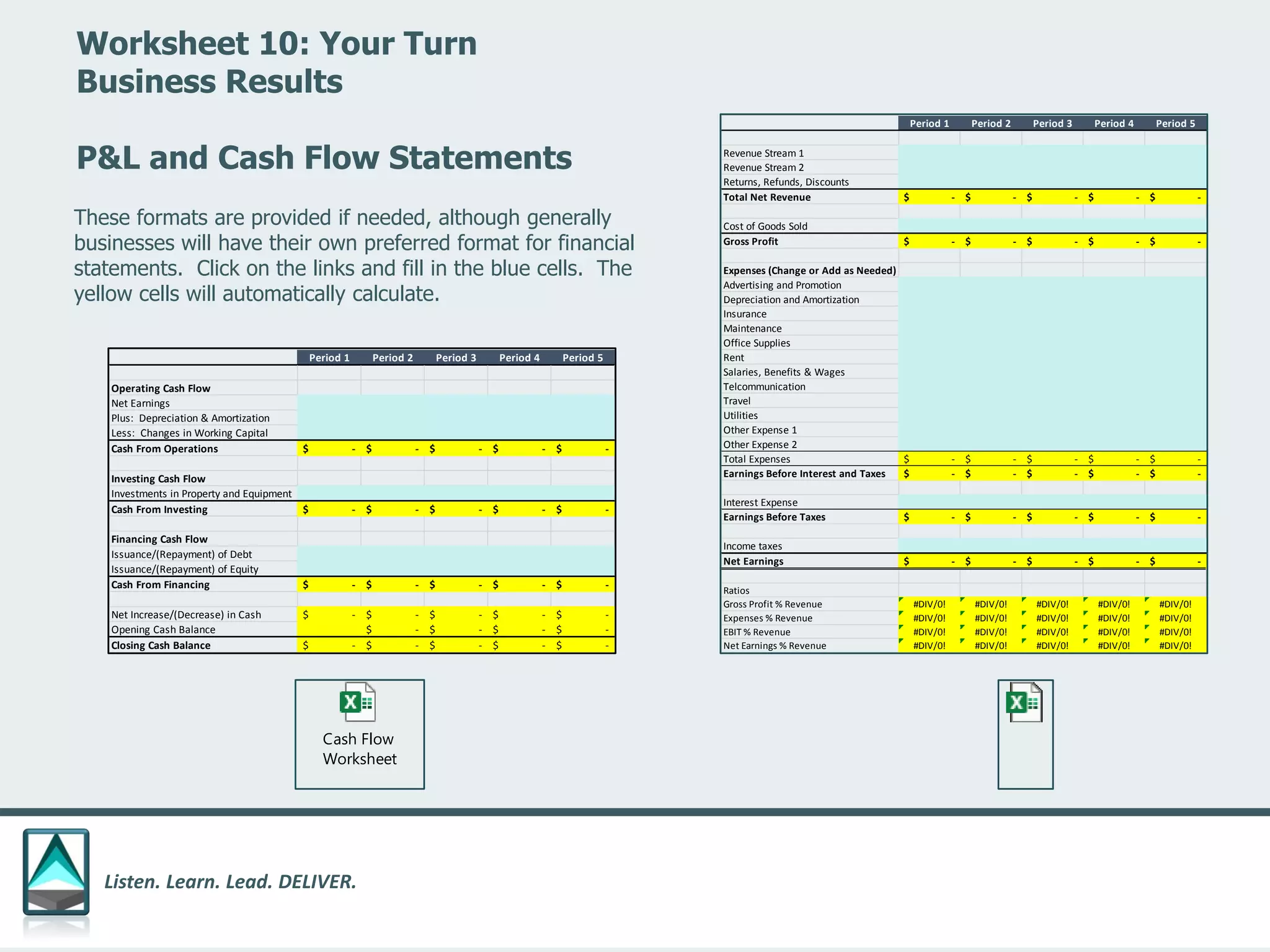
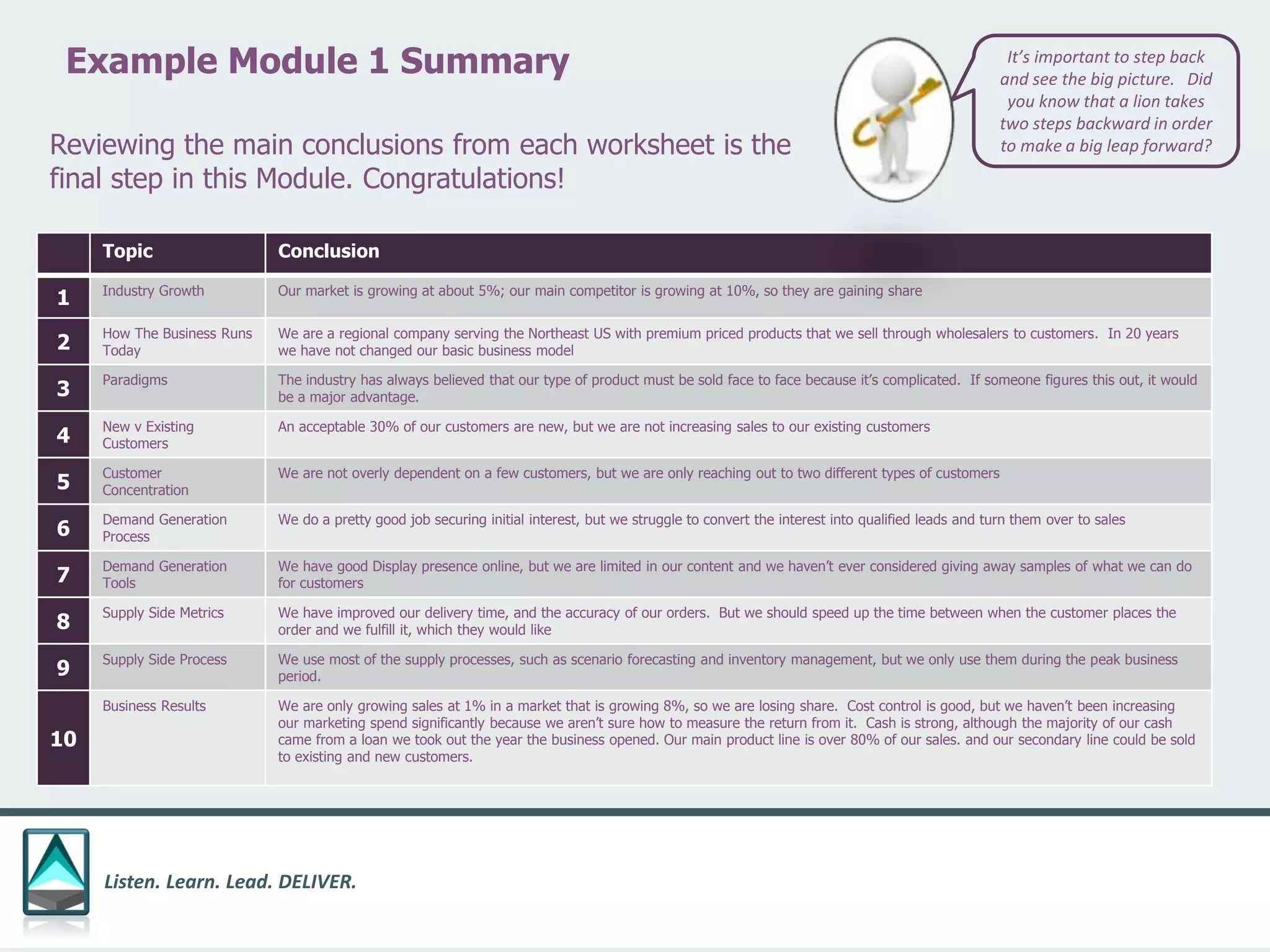
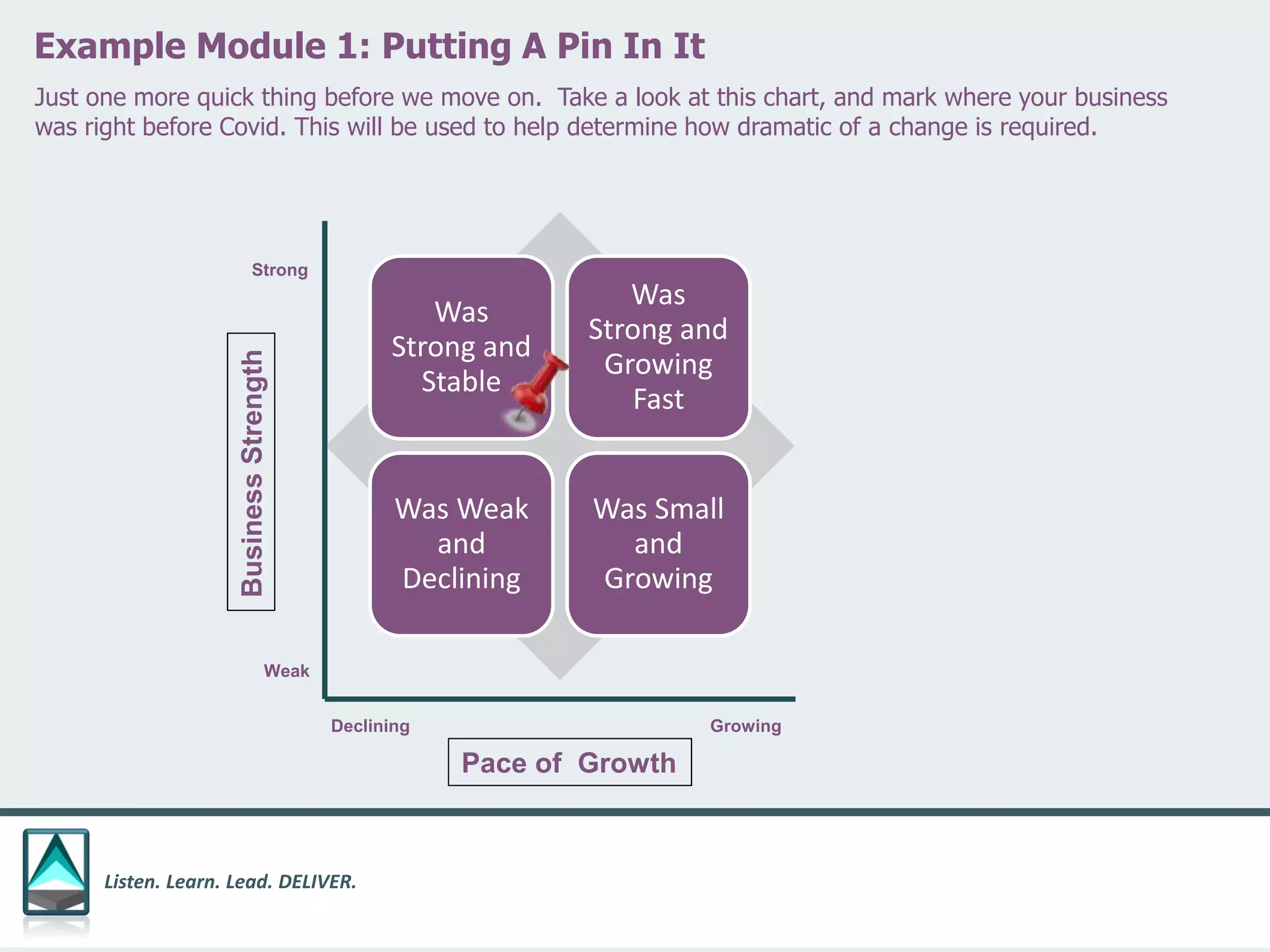
The document outlines a workbook designed to help organizations navigate the challenges posed by COVID-19 through a structured approach titled 'listen. learn. lead. deliver.' This system consists of five modules that facilitate assessment and planning by using practical worksheets to evaluate an organization's pre-COVID health, current impact, future options, and actionable plans. The goal is to offer a flexible, jargon-free framework to empower businesses to determine their own paths forward amidst disruption.