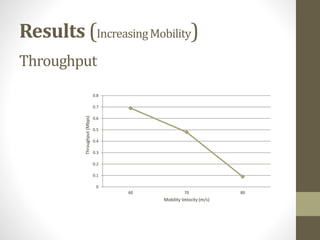
The document outlines a lab experiment on Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANETs) focusing on developing and analyzing MAC protocols using NetSim. It discusses the impact of node density and mobility on network performance metrics like throughput, average delay, and packet delivery ratio. The findings indicate that while increased node density can enhance throughput up to a point, and increased mobility negatively affects performance, highlighting the complexities in networking within MANETs.