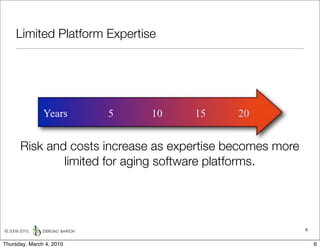
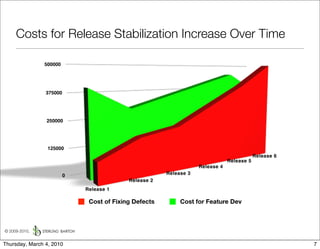
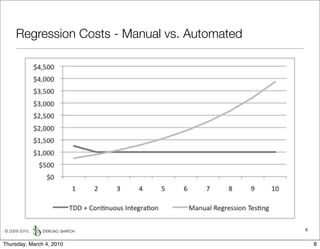
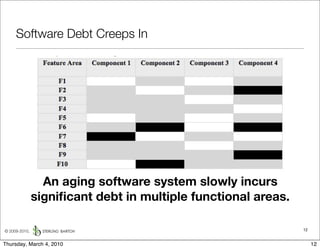
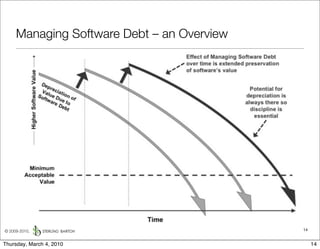
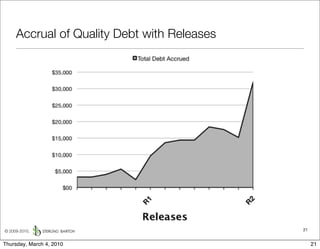
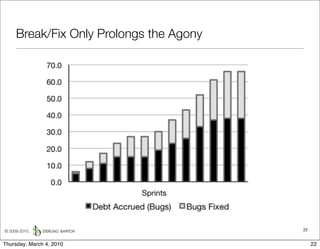
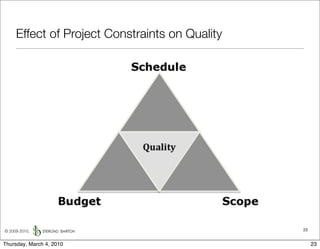
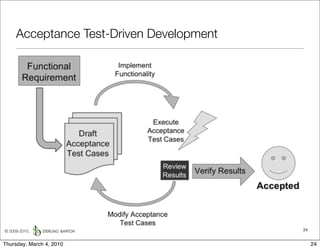
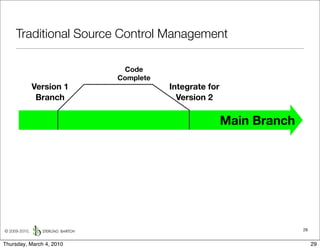
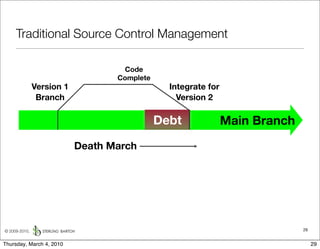
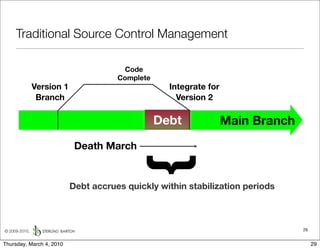
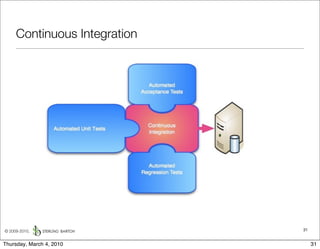
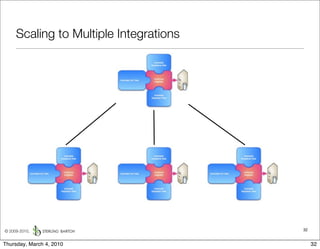
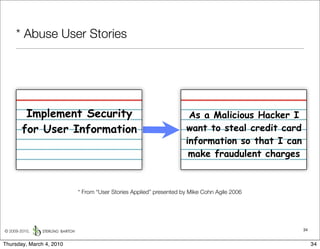
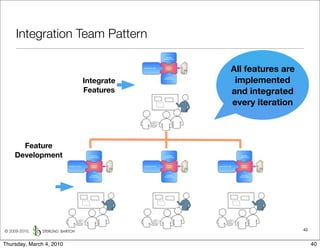
The document discusses managing software debt as systems age. It describes different types of software debt including technical debt, quality debt, configuration management debt, design debt, and platform experience debt. It explains how software debt accrues over time and provides examples of how feedback mechanisms can help manage debt in aging software.