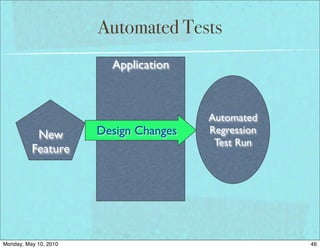
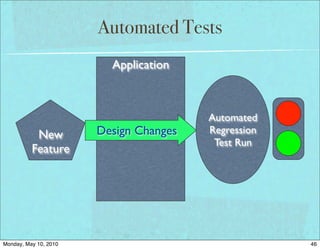
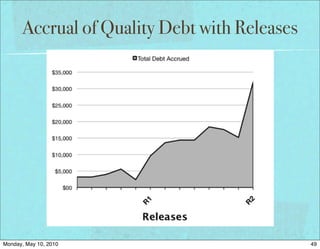
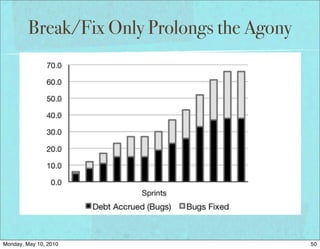
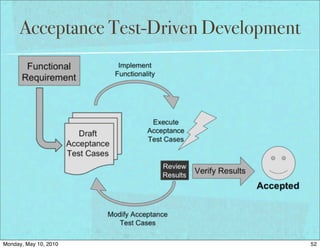
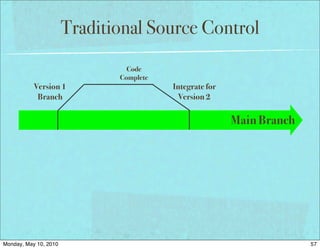
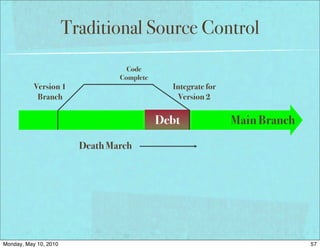
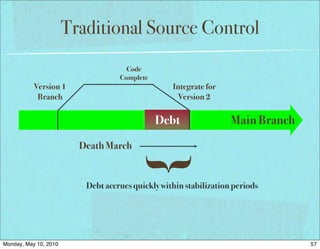
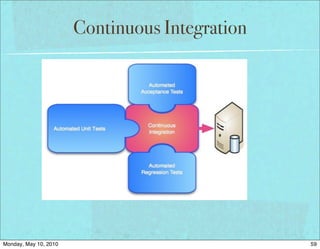
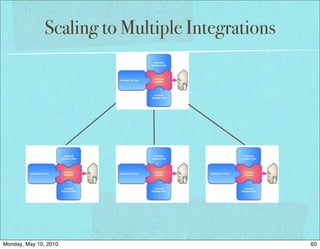
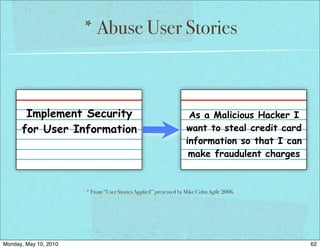
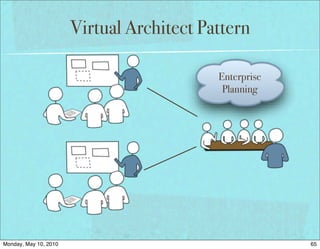
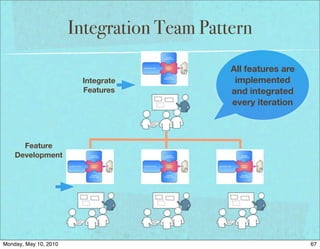
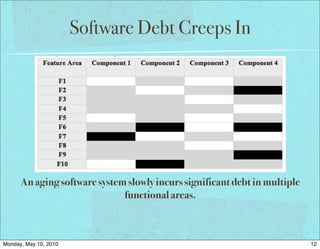
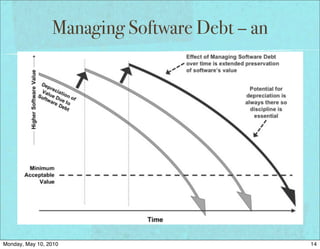
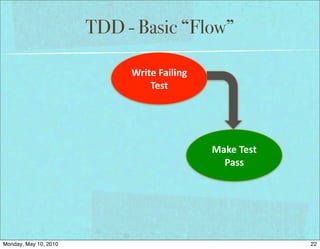
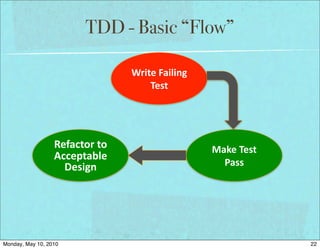
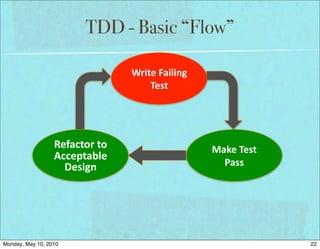
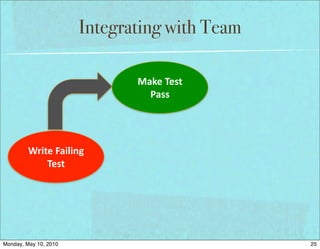
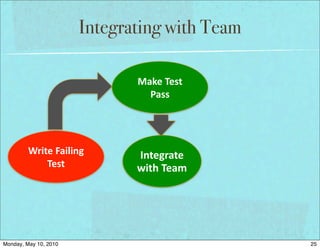
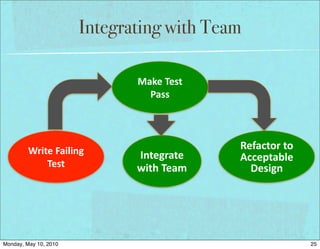
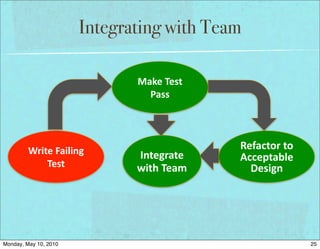
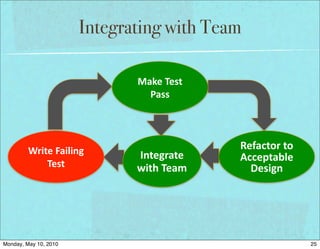
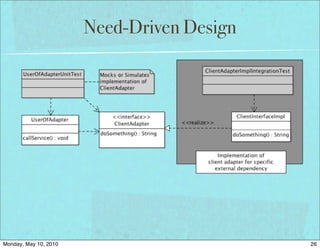
The document discusses managing software debt as systems age. It covers different types of software debt including technical debt, quality debt, configuration management debt, design debt, and platform experience debt. The document provides examples of how software debt can creep into systems over time if not properly managed through frequent feedback mechanisms and refactoring code as needed.





































![Merciless Refactoring
Refactoring: a disciplined technique for restructuring an existing
body of code, altering its internal structure without changing its
external behavior.*
Merciless: having or showing no [mercy - showing great kindness
toward the distressed]
Relieve your distressed code through kindness and disciplined
restructuring
* From http://www.refactoring.com/
Monday, May 10, 2010 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class3-managingsoftwaredebttdd-100510160321-phpapp02/85/UW-Agile-CP202-Class-3-Managing-Software-Debt-52-320.jpg)