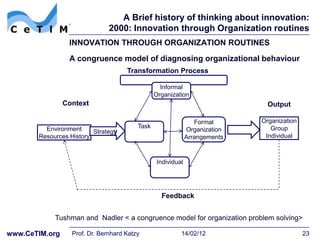
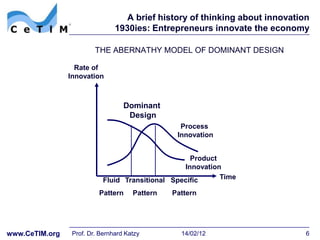
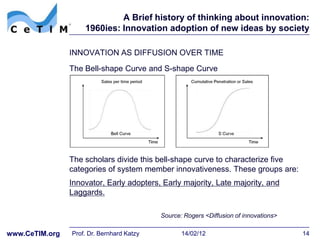
This document provides an overview of a session on basic innovation concepts and the history of innovation theory. It discusses early thinkers like Schumpeter who viewed entrepreneurs as the drivers of innovation through "creative destruction". It also outlines models of technology cycles and dominant design. Later sections describe the rise of dedicated R&D departments in the 1950s and innovation diffusion research in the 1960s which examined how new ideas spread through social systems over time. The document is intended to give context on the major themes and theorists that have shaped the field of innovation management.




![A brief history of thinking about innovation
1930ies: Entrepreneurs innovate the economy
THE S MODEL OF TECHNOLOGY CYCLE
Maturity of
Technology
T
2
Substitution
T
1
Time
Initiation Take-off Maturity
[Source: Foster,1986]
www.CeTIM.org Prof. Dr. Bernhard Katzy 14/02/12 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2innovationconcepts-120214152919-phpapp02/85/Managing-Innovation_innovation-concepts-6-320.jpg)


![A brief history of thinking about innovation
1930ies: Entrepreneurs innovate the economy
ARCHITECTURAL INNOVATION
[Source: Henderson, Clark]
www.CeTIM.org Prof. Dr. Bernhard Katzy 14/02/12 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2innovationconcepts-120214152919-phpapp02/85/Managing-Innovation_innovation-concepts-10-320.jpg)




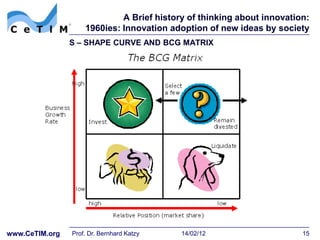
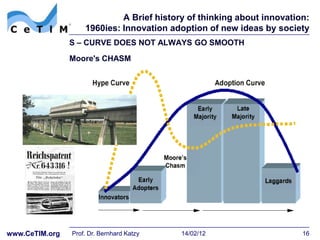

![A Brief history of thinking about innovation:
1980ies: Innovation as a profession and competence
INNOVATION AS A DISCIPLINE - DRUCKER
Innovation
is an effect in economy
Innovation and society Innovators
is work
Principles must build
on their strength
The practice (discipline) of innovation:
„90% of Innovation is Transpiration‟
1 Analysis for 5
opportunities
2 Do‟s Gain
Go out, 4 leadership
3
look and listen Start small
conception & perception Be effective,
simple
and focused
[Drucker, 1996]
www.CeTIM.org Prof. Dr. Bernhard Katzy 14/02/12 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2innovationconcepts-120214152919-phpapp02/85/Managing-Innovation_innovation-concepts-19-320.jpg)

![A Brief history of thinking about innovation
1990ies: Innovation through collaboration in network
INNOVATION SYSTEM
Sectoral
Innovation
Regional
System
Cluster
Industry and
Company Research
Research
Centre
Entities
Publi
c VPC VPC
Instit
ution
University
National
Innovation
System
Living Lab LL client
community
Social
New
Comm product/
Territory unity service
Social Co-
Settings LL Collaborative creation
Infrastructure
Innovation system
[Katzy and Crownston 2008; Schuh, Katzy, Eisen 1997]
www.CeTIM.org Prof. Dr. Bernhard Katzy 14/02/12 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2innovationconcepts-120214152919-phpapp02/85/Managing-Innovation_innovation-concepts-21-320.jpg)
![A Brief history of thinking about innovation:
2000: “open” Innovation in cooperation with the user
INNOVATION THROUGH OPEN INNOVATION
Research licensing Development
Other firms’
Market
New Market
Spin-off
Internal
Technology Base Current Market
External
Technology Base Technology
insourcing
Labor mobility/ Venture Capital/ Numerous Start-ups/ research
conducted at Universities/……
[Source: Henry Chesbrough 2003]
www.CeTIM.org Prof. Dr. Bernhard Katzy 14/02/12 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2innovationconcepts-120214152919-phpapp02/85/Managing-Innovation_innovation-concepts-22-320.jpg)