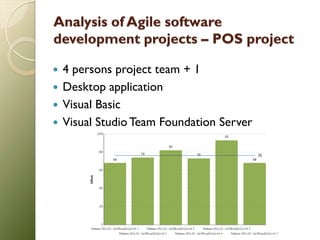
This document is a master's thesis that examines best practices for managing agile software development projects. It discusses traditional and agile development methodologies like Scrum and Extreme Programming (XP). It also analyzes three case studies of agile projects and evaluates tools to support agile development. The thesis concludes that adopting a methodology fully and using communication tools are keys to agile success.



![Software development
methodologies
According to Sommerville [ (5), page 13]
there are three key challenges facing
software engineering nowadays:
The heterogeneity challenge
The delivery challenge
The trust challenge
(5) Sommerville, Ian. Software engineering - 8th edition. s.l. : Addison Wesley, June 4, 2006.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-5-320.jpg)
![Software development
methodologies - Traditional
According to Awad [ (7), page 6] there are
four main characteristics of heavyweight
methodologies:
Predictive approach
Comprehensive documentation
Process oriented
Tool oriented
(7) Awad, Mohamed. Comparison between Agile and Traditional Software Development
Methodologies. [Online] [Cited: 25 February 2011.]
http://pds10.egloos.com/pds/200808/13/85/A_comparision_between_Agile_and_Traditional_SW
_development_methodologies.pdf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-6-320.jpg)
![Software development
methodologies - Agile
Agile methodologies are introduced by four
basic values [ (10)]:
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive
documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
(10) Agile values. Agile manifesto official web page. [Online] [Cited: 2 March 2011.]
http://agilemanifesto.org/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-7-320.jpg)
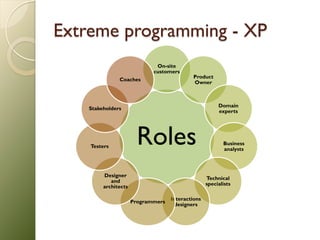
![Software development
methodologies - Agile
Agile process Modularity
Collaborative Iterative
People-
Time-Bound
Oriented
Convergent Parsimony
Incremental Adaptive
Granville, Miller G. The Characteristics of Agile Software Processes. [Online] [Cited: 2 March 2011.]
http://faculty.salisbury.edu/~xswang/Research/Papers/SERelated/Agile/12510385.pdf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-8-320.jpg)



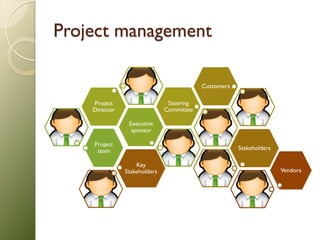
![Scrum Product
Owner
Smaller teams
Roles
For bigger - Scrum
Project Scrum
of Scrums team Master
(17) Waters, Kelly. Using Scrum on Larger Projects: "Scrum of Scrums". [Online] [Cited: 22
February 2011.] http://www.allaboutagile.com/using-scrum-on-larger-projects-scrum-of-
scrums/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-13-320.jpg)
![Scrum
(18) Eclipse. Eclipse organization. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.]
http://epf.eclipse.org/wikis/scrumpt/Scrum/guidances/supportingmaterials/resources/ScrumLarge
Labelled.png](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-14-320.jpg)


















![Literature
1. The Standish Group. The Standish Group Report CHAOS. [Online] [Cited: 12 September 2011.] http://www.projectsmart.co.uk/docs/chaos-report.pdf.
2. —. CHAOS Report Press Release. The Standish Group. [Online] [Cited: 12 September 2011.] http://www1.standishgroup.com/newsroom/chaos_2009.php.
3. PMI, Project management institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide)- 4th edition. s.l. : Project management institute, December 31,
2008.
4. Barry, Timothy R. Top 10 Qualities of a Project Manager. Project Smart. [Online] 2010. [Cited: 22 March 2011.] http://www.projectsmart.co.uk/top-10-qualities-project-
manager.html.
5. Sommerville, Ian. Software engineering - 8th edition. s.l. : Addison Wesley, June 4, 2006.
6. Abran, Alain, et al. Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge (SWEBOK). s.l. : IEEE, 2004.
7. Awad, Mohamed. Comparison between Agile and Traditional Software Development Methodologies. [Online] [Cited: 25 February 2011.]
http://pds10.egloos.com/pds/200808/13/85/A_comparision_between_Agile_and_Traditional_SW_development_methodologies.pdf.
8. IBM Rational Unified Process. Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopaedia. [Online] [Cited: 1 March 2011.] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_Rational_Unified_Process.
9. IBM Rational Unified Process (RUP). IBM Official Web Pages. [Online] [Cited: 1 March 2011.] http://www-01.ibm.com/software/awdtools/rup/.
10. Agile values. Agile manifesto official web page. [Online] [Cited: 2 March 2011.] http://agilemanifesto.org/.
11. Granville, Miller G. The Characteristics of Agile Software Processes. [Online] [Cited: 2 March 2011.]
http://faculty.salisbury.edu/~xswang/Research/Papers/SERelated/Agile/12510385.pdf.
12. Rittenbruch, Markus, et al. Official web pages of Linkoping University. [Online] June 2002. [Cited: 25 February 2011.]
http://www.ida.liu.se/~TDDD26/material/extremeparticipation.pdf.
13. Shore, James and Warden, Shane. The Art of Agile Development. s.l. : O'Reilly Media, Inc., 2008.
14. Bachan & Catherine. Essence of Scrum. Conscires Agile Practices. [Online] [Cited: 17 September 2011.] http://agile.conscires.com/2010/09/18/essence-of-scrum/.
15. Cohn, Mike. Mountain Goat Software. [Online] [Cited: 18 February 2011.] http://www.mountaingoatsoftware.com/topics/scrum.
16. Watts, Geoff. Scrum Alliance. [Online] 11 January 2010. http://www.scrumalliance.org/articles/321-getting-retrained-to-be-a-scrummaster.
17. Waters, Kelly. Using Scrum on Larger Projects: "Scrum of Scrums". [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.] http://www.allaboutagile.com/using-scrum-on-larger-projects-
scrum-of-scrums/.
18. Eclipse. Eclipse organization. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.]
http://epf.eclipse.org/wikis/scrumpt/Scrum/guidances/supportingmaterials/resources/ScrumLargeLabelled.png.
19. Brothersoft. Brothersoft. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.] http://img.brothersoft.com/screenshots/softimage/v/virtual_scrum_board-180890-1.jpeg.
20. InfoQ. InfoQ. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.] http://www.infoq.com/resource/articles/agile-kanban-boards/en/resources/Fig1_task-board.jpg.
21. Scrum Alliance.org. Glossary of Scrum Terms. Scrum alliance. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.] http://www.scrumalliance.org/articles/39-glossary-of-scrum-
terms#1113.
22. Demeer, Peter and Benefield, Gabrielle. An introduction to Project Management with Scrum. Rally Dev. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.]
http://www.rallydev.com/documents/scrumprimer.pdf
23. Team Foundation Server. Microsoft Visual Studio. [Online] [Cited: 18 June 2011.] http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/vstudio/ff637362 .
24. Pivotal Tracker. Pivotal Tracker. [Online] [Cited: 18 June 2011.] http://www.pivotaltracker.com/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-34-320.jpg)
![Literature
26. The Exia Process. The Exia Process. [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://www.exiaprocess.com/.
27. Acunote. Acunote. [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://www.acunote.com/promo.
28. Banana Scrum. Banana Scrum. [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://www.bananascrum.com/.
29. ThoughtWorks. Mingle . [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://www.thoughtworks-studios.com/mingle-agile-project-management.
30. BrixHQ. BrixHQ. [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://www.brixhq.com/.
31. VersionOne. VersionOne. [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://versionone.com/.
32. TargetProcess. TargetProcess. [Online] [Cited: 19 June 2011.] http://www.targetprocess.com/.
33. Finance portal of Portugal. Finance portal of Portugal. [Online] [Cited: 17 February 2011.] http://info.portaldasfinancas.gov.pt/pt/dgci/.
34. Lewison, Mark. Can Product Owner and Scrum Master be combined? InfoQ. [Online] [Cited: 24 February 2011.] http://www.infoq.com/news/2008/12/scrum-master-
product-owner.
35. Nelson, Barbara. Scrum and the Product Owner. Pragmatic Marketing. [Online] [Cited: 24 February 2011.] http://www.pragmaticmarketing.com/resources/ask/scrum-
and-the-product-owner.
36. Marchenko, Artem. Product Manager VS. Scrum Product Owner. Agile Software Development. [Online] [Cited: 24 February 2011.]
http://agilesoftwaredevelopment.com/blog/artem/product-manager-vs-scrum-product-own.
37. FiscoLex. Portuguese collection of fiscal and trade data. FiscoLex. [Online] [Cited: 22 February 2011.]
http://www.fiscolex.com.br/dest_18796967_NOVAS_REGRAS_IRPF_2011.aspx.
38. Milunsky, Jack. Switching user stories mid sprint. The Agile Buddy Blog. [Online] [Cited: 24 February 2011.] http://blog.agilebuddy.com/2009/07/switching-user-stories-mid-
sprint.html.
39. Cohn, Mike. Succeeding with agile; Bugs on the product blog. Mountain Goat Software. [Online] [Cited: 24 February 2011.] http://blog.mountaingoatsoftware.com/tag/user-
stories.
40. DokuWiki. DokuWiki. [Online] [Cited: 14 July 2011.] http://www.dokuwiki.org/dokuwiki.
41. Cockburn, Alistair. Agile Software Development Joins the "Would-be" Crowd. Agile Alliance. [Online] [Cited: 13 September 2011.]
http://cf.agilealliance.org/articles/system/article/file/782/file.pdf.
42. Cleland, David I. and Ireland, Lewis R. Project management. strategic design and implementation- 5th edition. s.l. : The McGraw-Fill Companies Inc., 2007.
43. McMahon, Paul E. Bridging Agile & Traditional Development Methods: A Project Management Perspective. [Online] [Cited: 25 February 2011.] : http://www.sstc-
online.org/proceedings/2004/PDFFiles/PEM972.pdf.
44. Viliet, Hans van. Software Engineering. Principles and Practice. s.l. : Wiley, 2007.
45. Scrum (development). Wikipedia The Free Encylopaedia. [Online] [Cited: 16 February 2011.] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrum_(development).
46. Miller, Grancille G. The Characteristics of Agile Software Processes. Official pages of Alisbury university. [Online] [Cited: 18 5 2011.]
http://faculty.salisbury.edu/~xswang/Research/Papers/SERelated/Agile/12510385.pdf.
47. Hazrati, Vikas. Slide Share. [Online] [Cited: 25 February 2011.] http://www.slideshare.net/nashjain/introduction-to-extreme-programming.
48. Microsoft. Microsoft MSDN. [Online] [Cited: 21 February 2011.] http://i.msdn.microsoft.com/dd347827.fig09_L(en-us).gif.
49. The Standish Group. The Standish Group Report. CHAOS. 1995.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentacijadipl-111124171505-phpapp01/85/Managing-Agile-Software-Development-Projects-35-320.jpg)