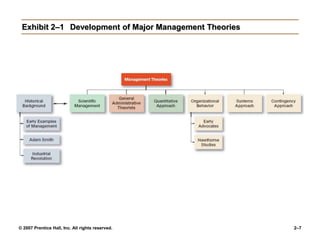
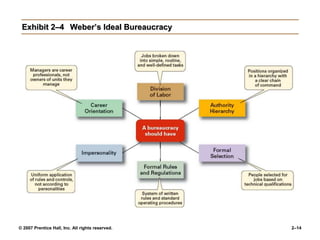
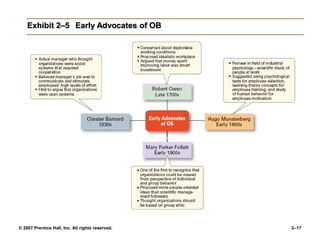
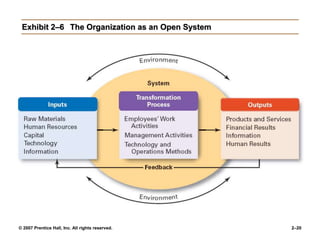
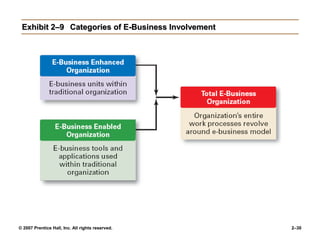
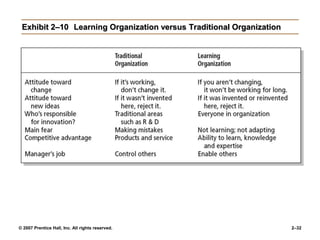
The document outlines the historical development of management theories from early practices like those seen in ancient Egypt and China, to modern approaches. It discusses scientific management developed by Taylor which emphasized standardized work methods. Henri Fayol established 14 principles of general administrative theory while Weber advocated for rational-legal authority. Quantitative approaches apply models and statistics to improve decision making. Organizational behavior emerged from the Hawthorne Studies which showed social factors strongly influence work. The systems approach views organizations as open systems interacting with their environment. Contingency theory states there is no universal set of management rules and the approach must fit the situation. Current trends discussed include globalization, ethics, diversity, e-business, knowledge management and quality.