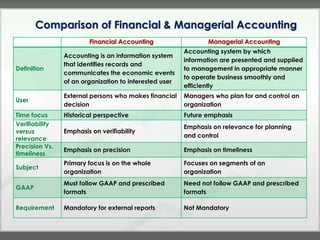
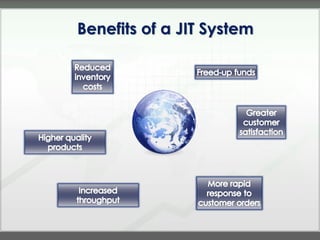
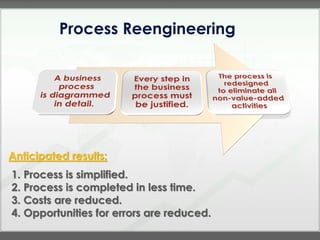
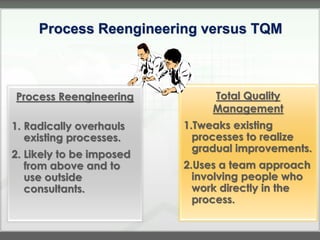
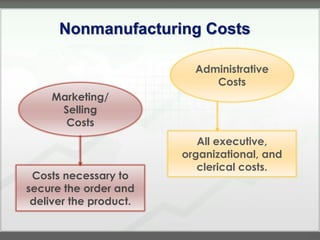
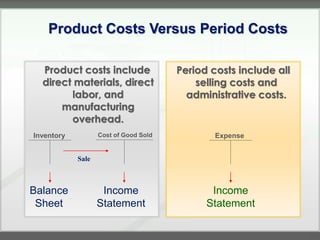
The document discusses key concepts in management accounting such as direct and indirect costs, product versus period costs, cost behavior analysis of variable, fixed, and mixed costs, and how managerial accounting differs from financial accounting in focusing on future decisions rather than past financial reporting. It also covers management accounting tools like just-in-time production, total quality management, process reengineering, and the theory of constraints.