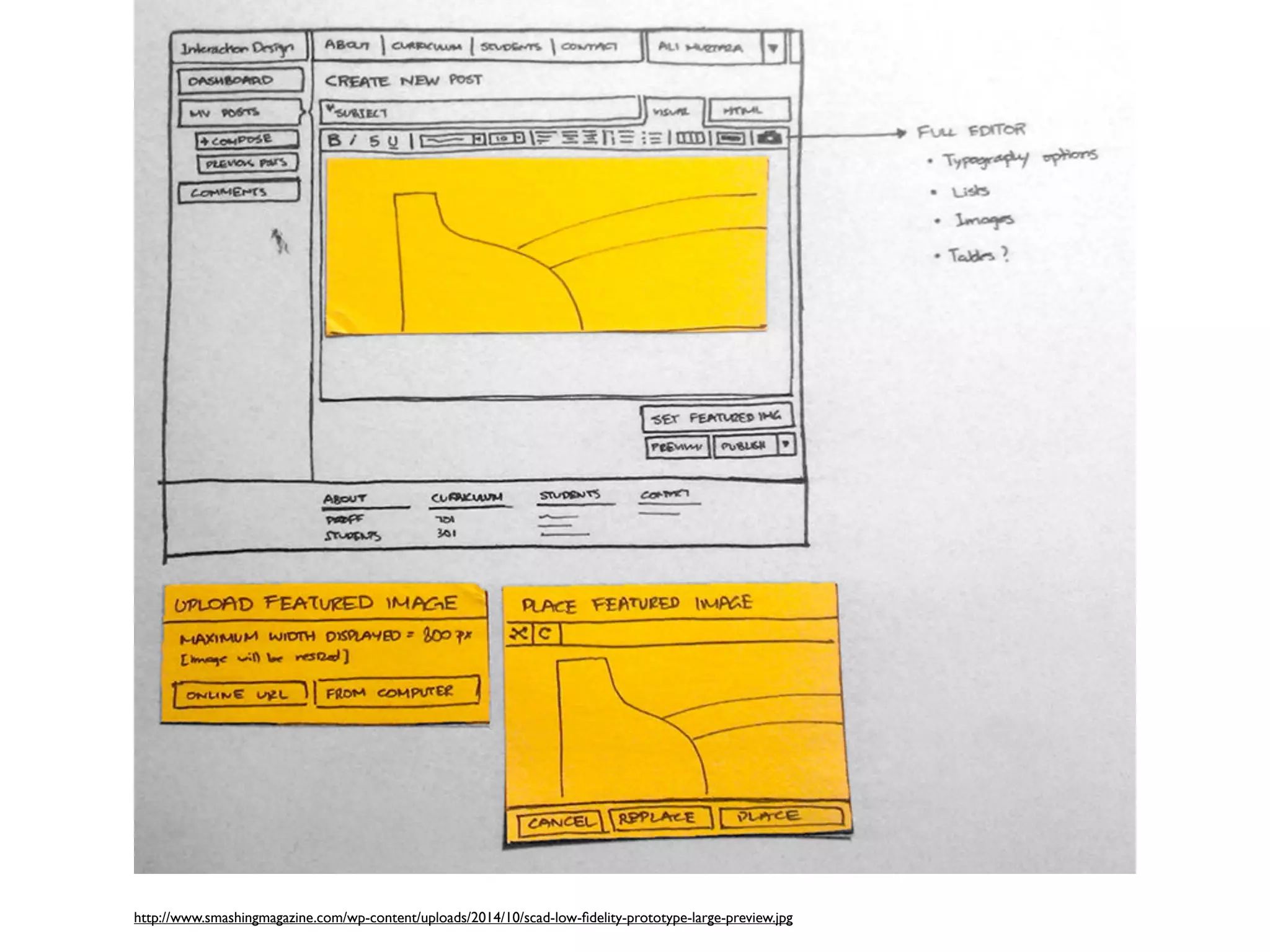
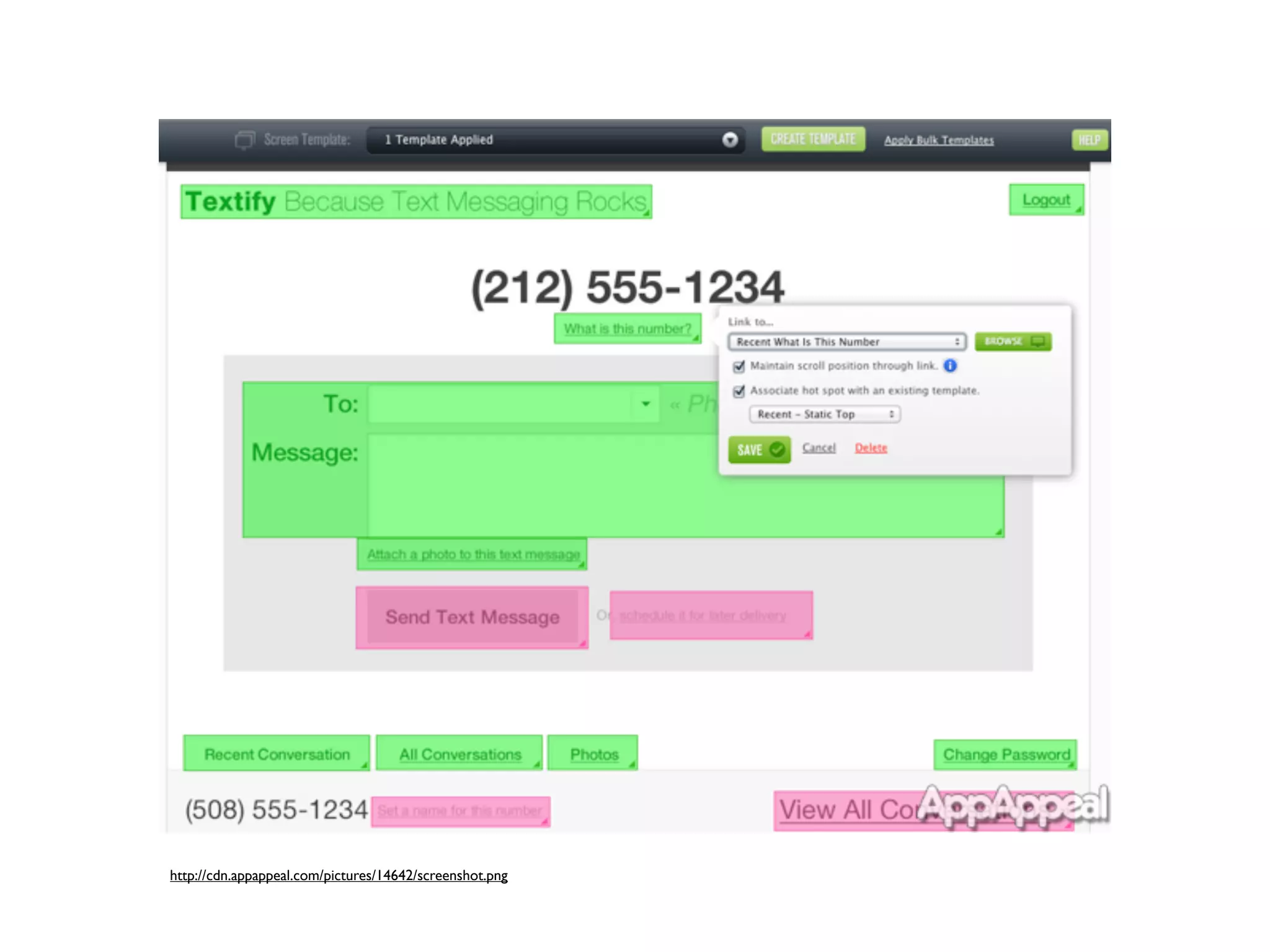
The document describes a workshop on open design. The morning session includes introductions, case studies, design tools, and activities to understand users. The afternoon session includes wrapping up the first activity, presenting derivative design concepts, low-fidelity prototyping, sharing activities, and wrapping up. Participants will learn about the open source ecosystem, levels of configuring open interactive products, open licenses, and skills/knowledge transfer from designers to users. Open products are discussed as platforms that provide information and tools for users to access, produce, modify, and create new products built on the platform. The tasks of designers are to provide user-friendly interfaces and design toolkits to transfer skills and access to openness.