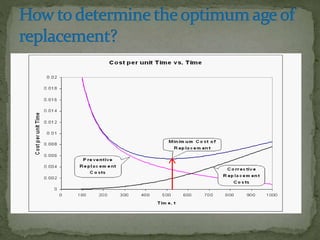
The document discusses various types of maintenance including preventive, corrective, condition-based, predictive, reliability-centered, and value driven maintenance. It explains that preventive maintenance involves maintaining equipment before failures occur to prevent downtime and costs, while corrective maintenance repairs equipment after failures. Condition-based maintenance uses indicators to determine when equipment will fail and prioritizes maintenance. Predictive techniques help determine equipment condition to schedule maintenance. Reliability-centered maintenance aims to improve cost-effectiveness and uptime. The 5S methodology focuses on effective workplace organization through sorting, setting in order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining these practices.