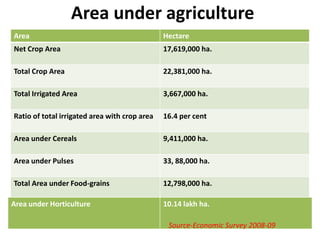
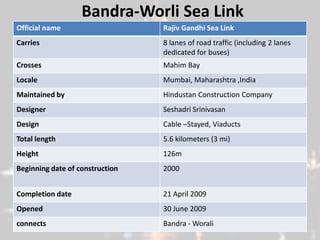
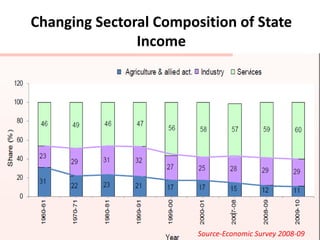
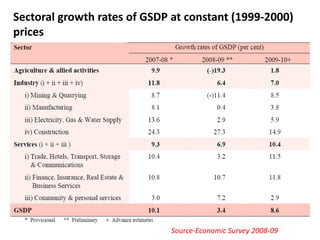
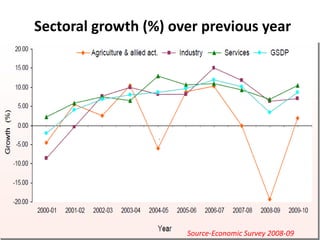
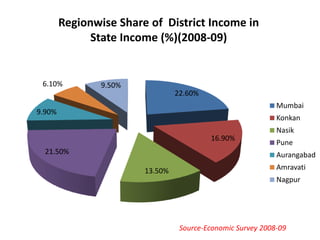
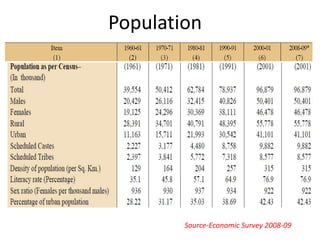
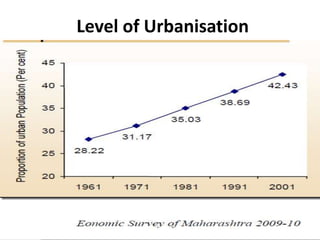
This document provides an overview of Maharashtra, India. It discusses the history of the Maratha empire and Peshwa dynasty. It highlights important figures in Maharashtra's history like Chhatrapati Shivaji and Dr. B. R. Ambedkar. It also summarizes the state's geography, politics, agriculture, culture and food. Important cities like Mumbai, Pune, Kolhapur and Aurangabad are mentioned for their historical sites. Mumbai is described as the commercial capital of India and for institutions like the dabbawalas lunch delivery system.