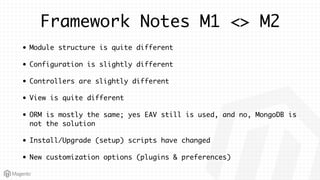
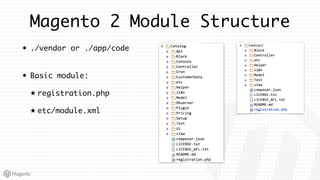
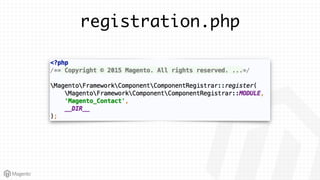
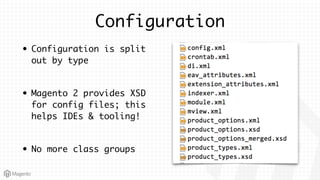
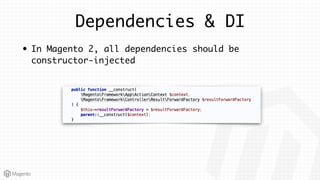
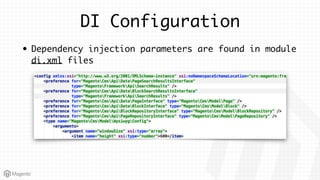
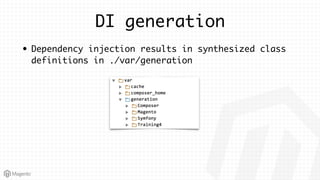
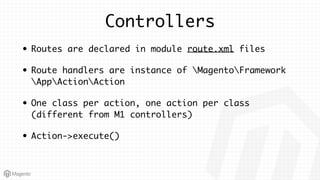
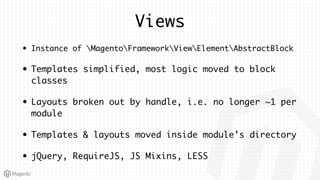
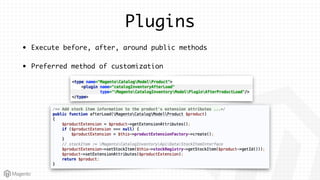
This document summarizes some of the key differences between Magento 1 and Magento 2. It notes that Magento 2 has improved support for modern technologies like PHP 7, Composer, and PSR standards. The module and configuration structure is redesigned in Magento 2. Dependencies are injected through DI configuration files rather than being hardcoded. Controllers are now based on actions rather than having one controller per class. Views use updated frontend technologies and a separated layout system. Setup and customization approaches like plugins and preferences replace some Magento 1 patterns. Resources listed can help developers learn Magento 2.