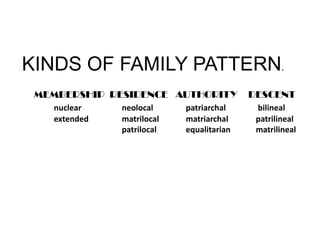
The functions of the family include: 1) reproduction and rearing of children, 2) cultural transmission from parents to children, 3) socialization of children through teaching them roles and status, 4) providing love and security for its members, and 5) facilitating personality development through relationships. There are different types of family structures defined by membership, residence, authority, and lineage descent. Nuclear families consist of parents and children while extended families include other relatives. Authority can be patriarchal, matriarchal, or equal. Descent can trace through the father's, mother's, or both parental lines.