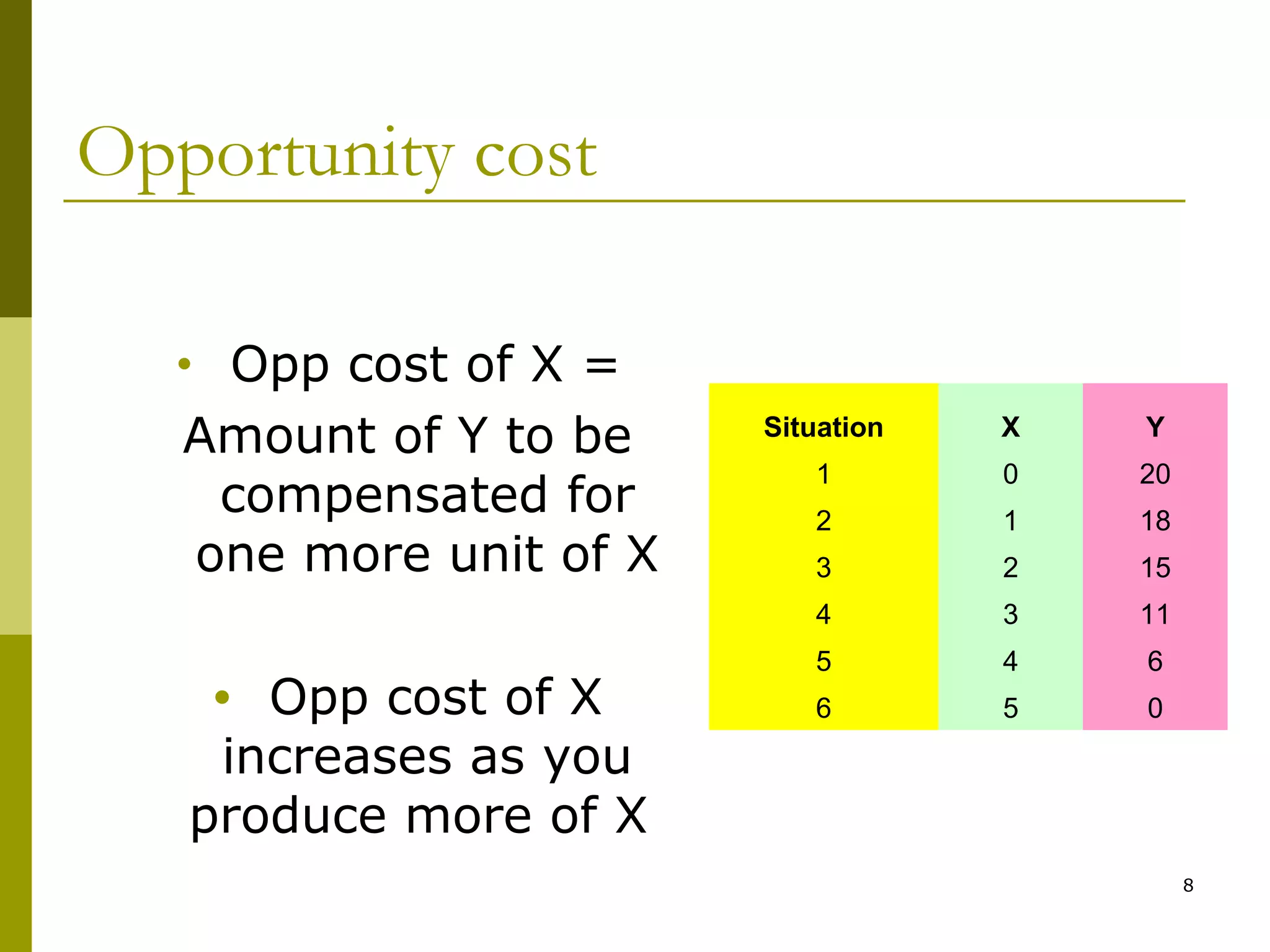
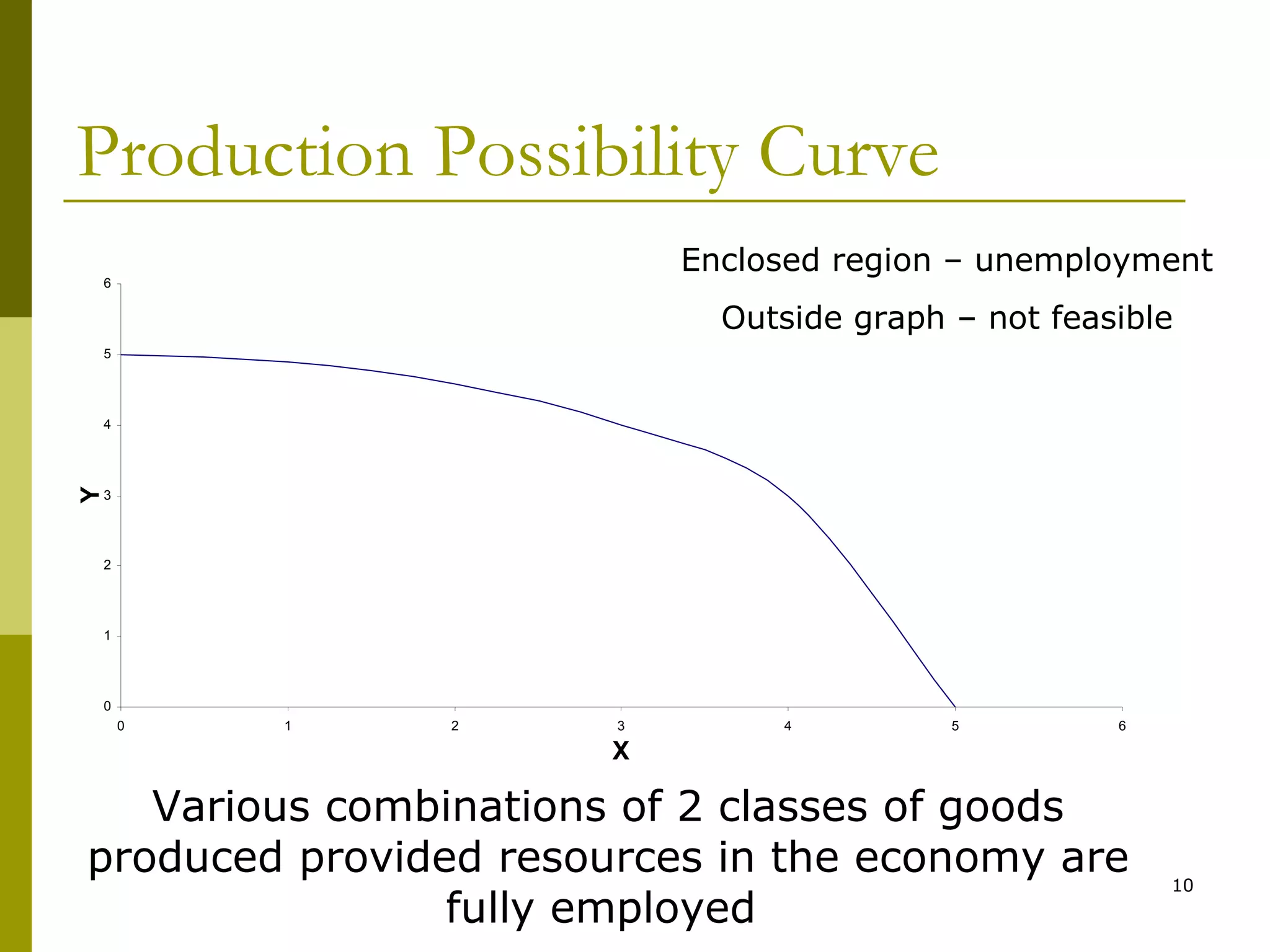
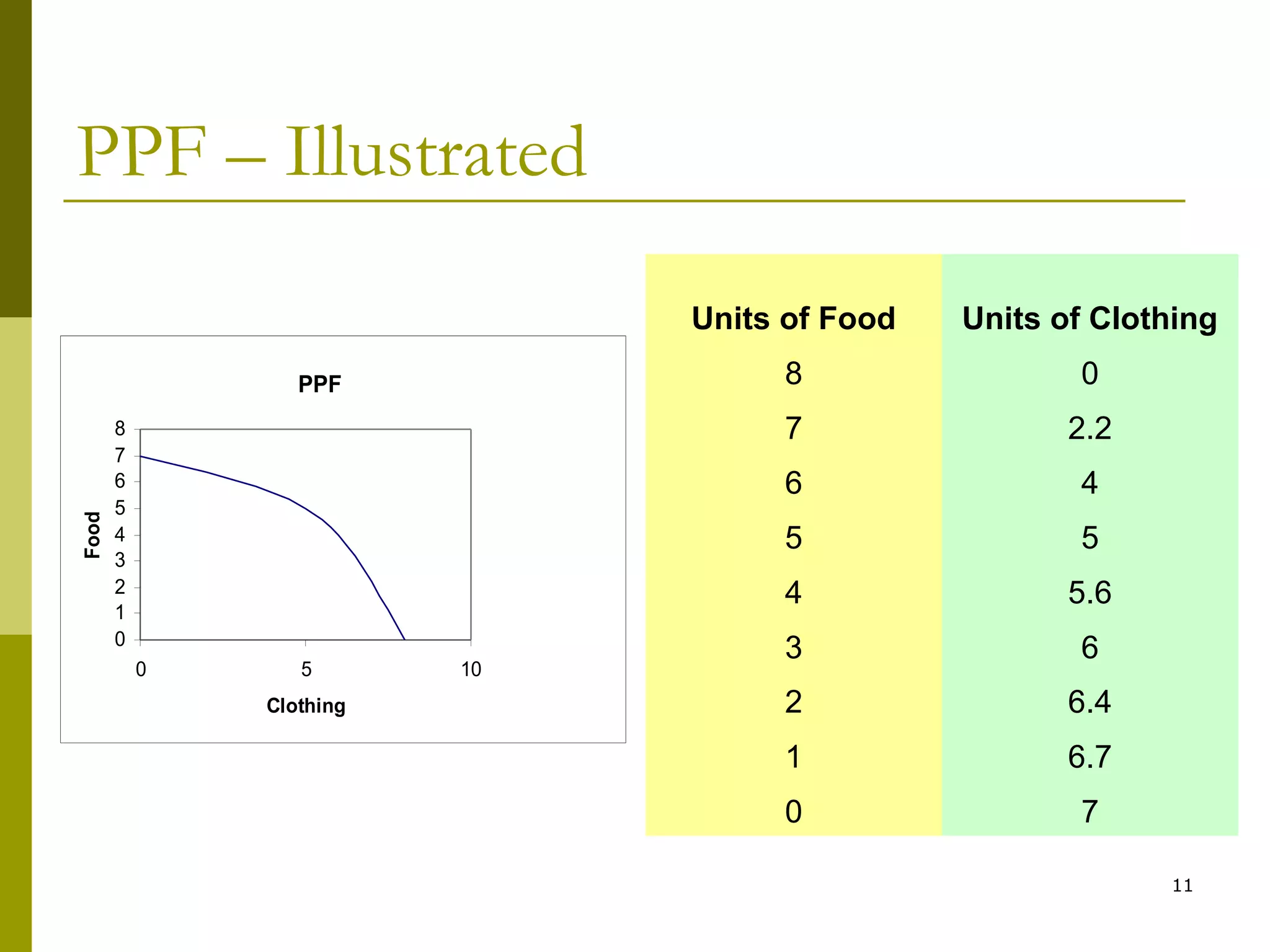
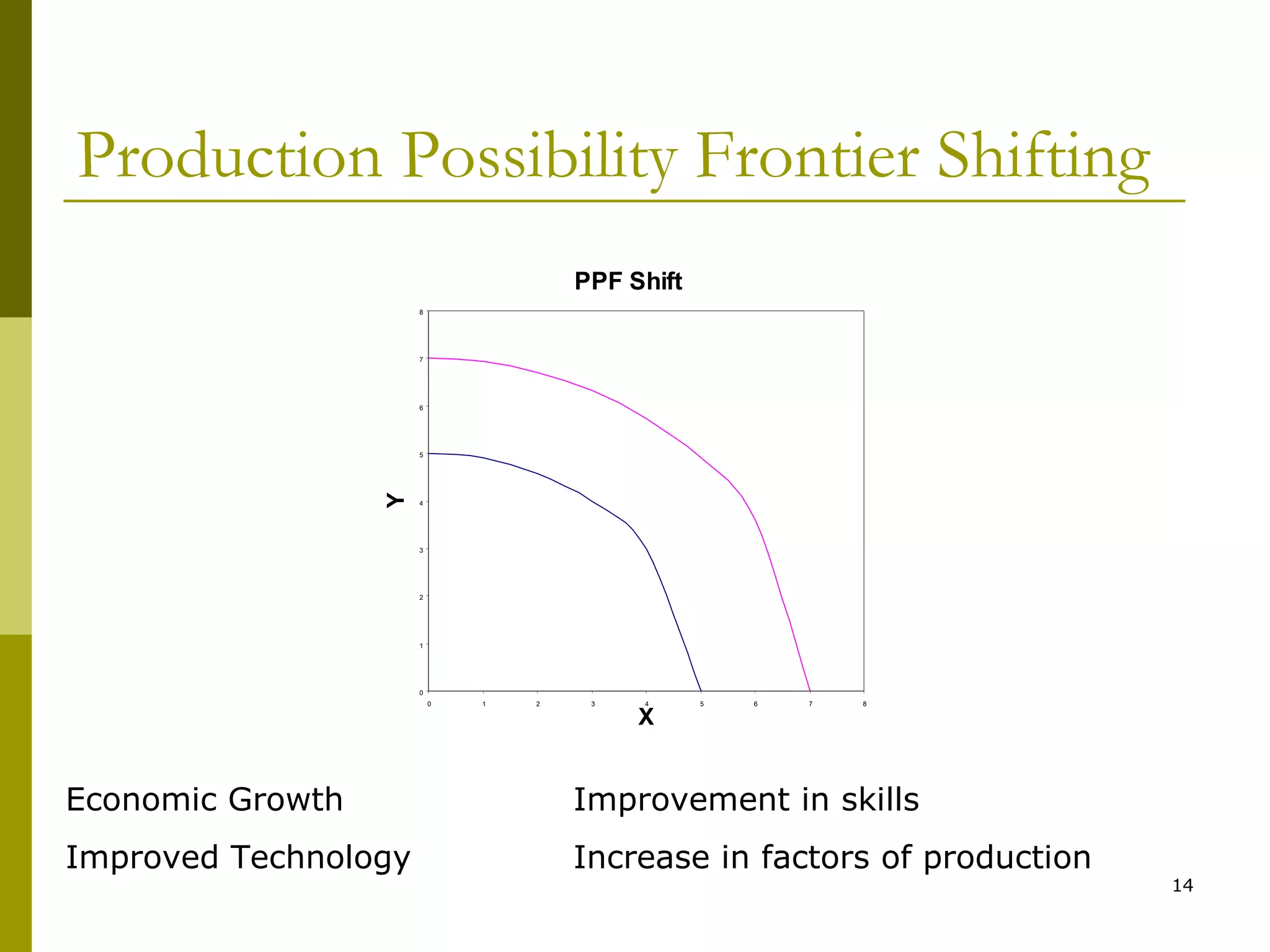
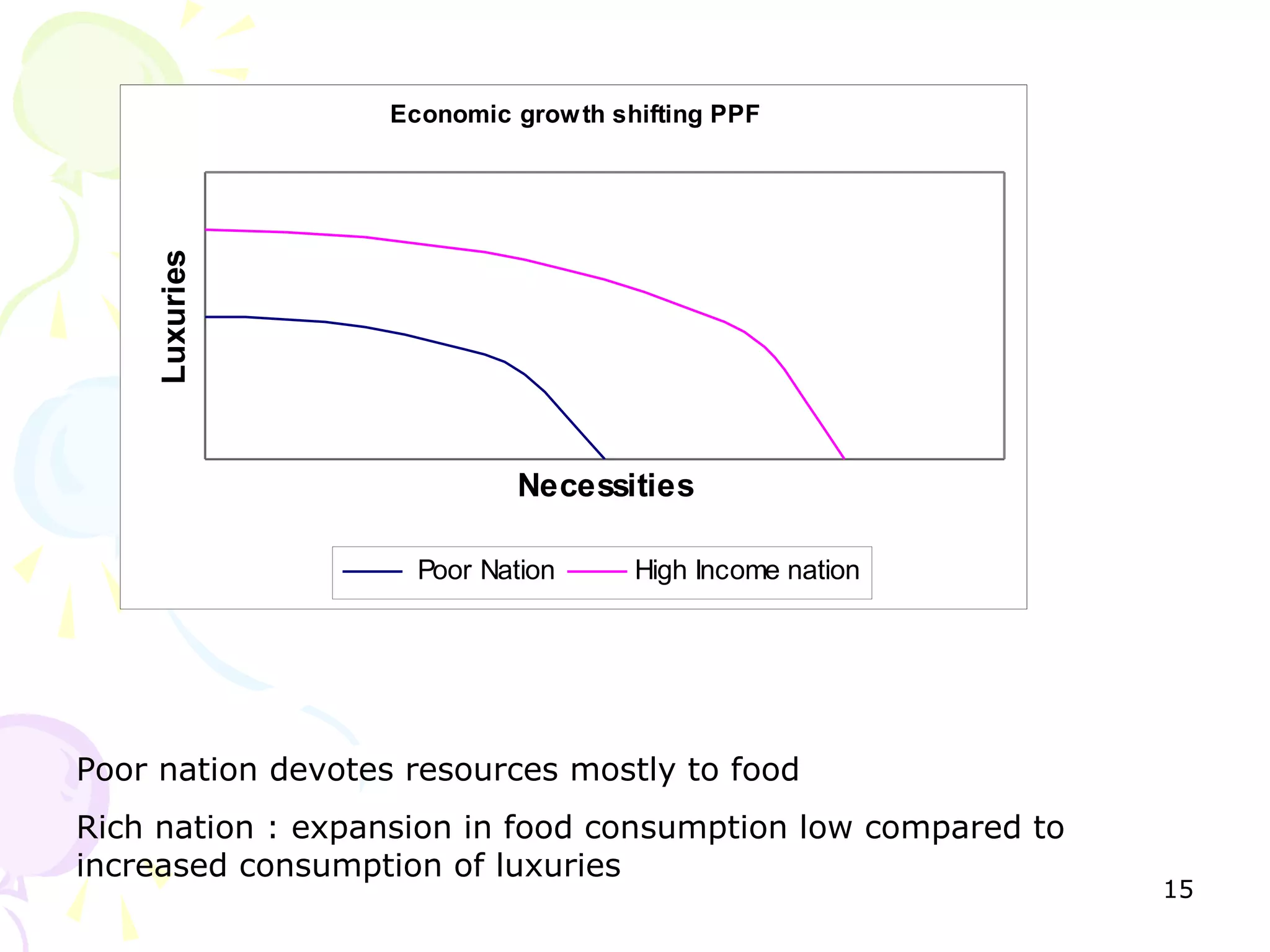
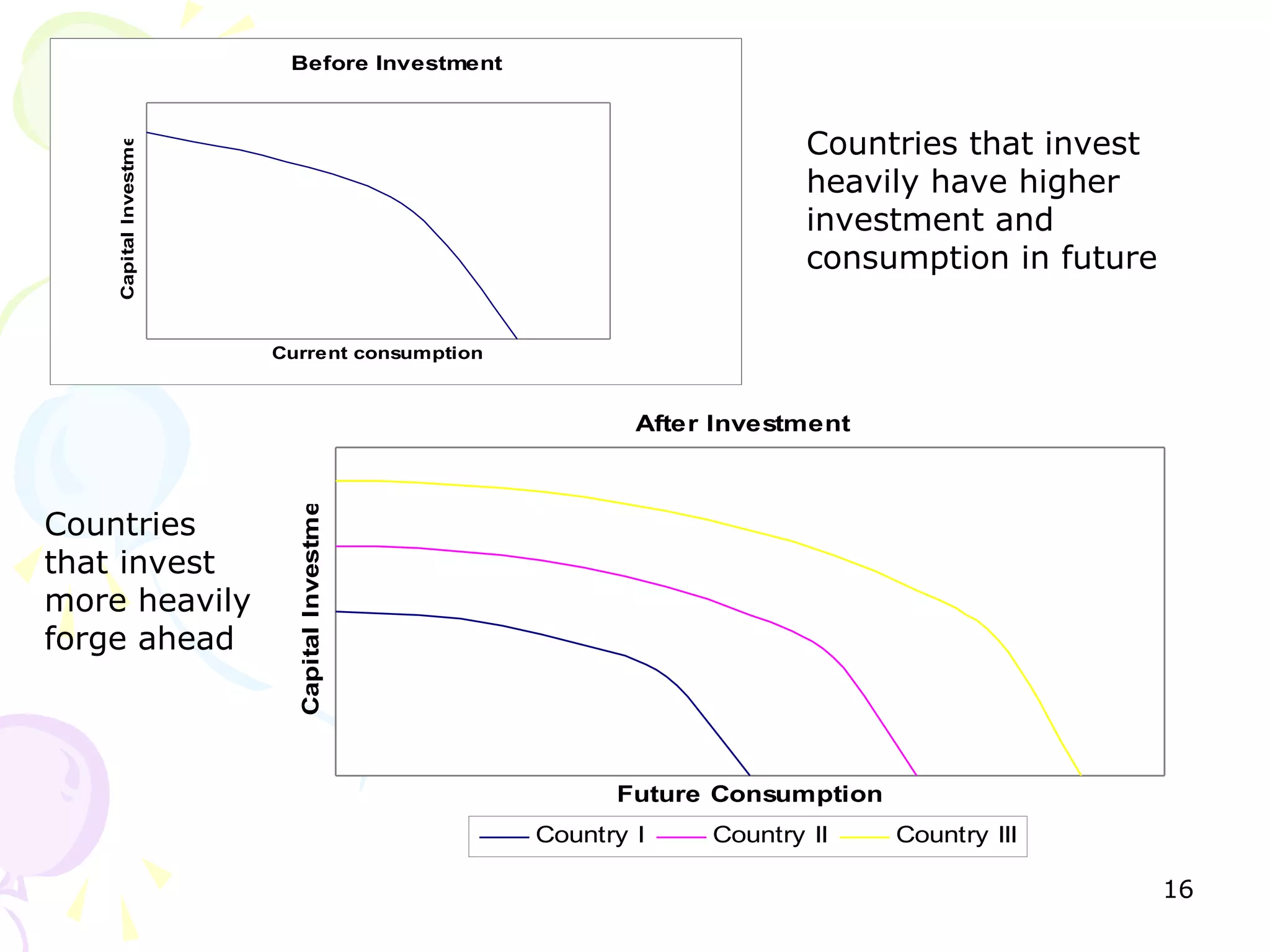
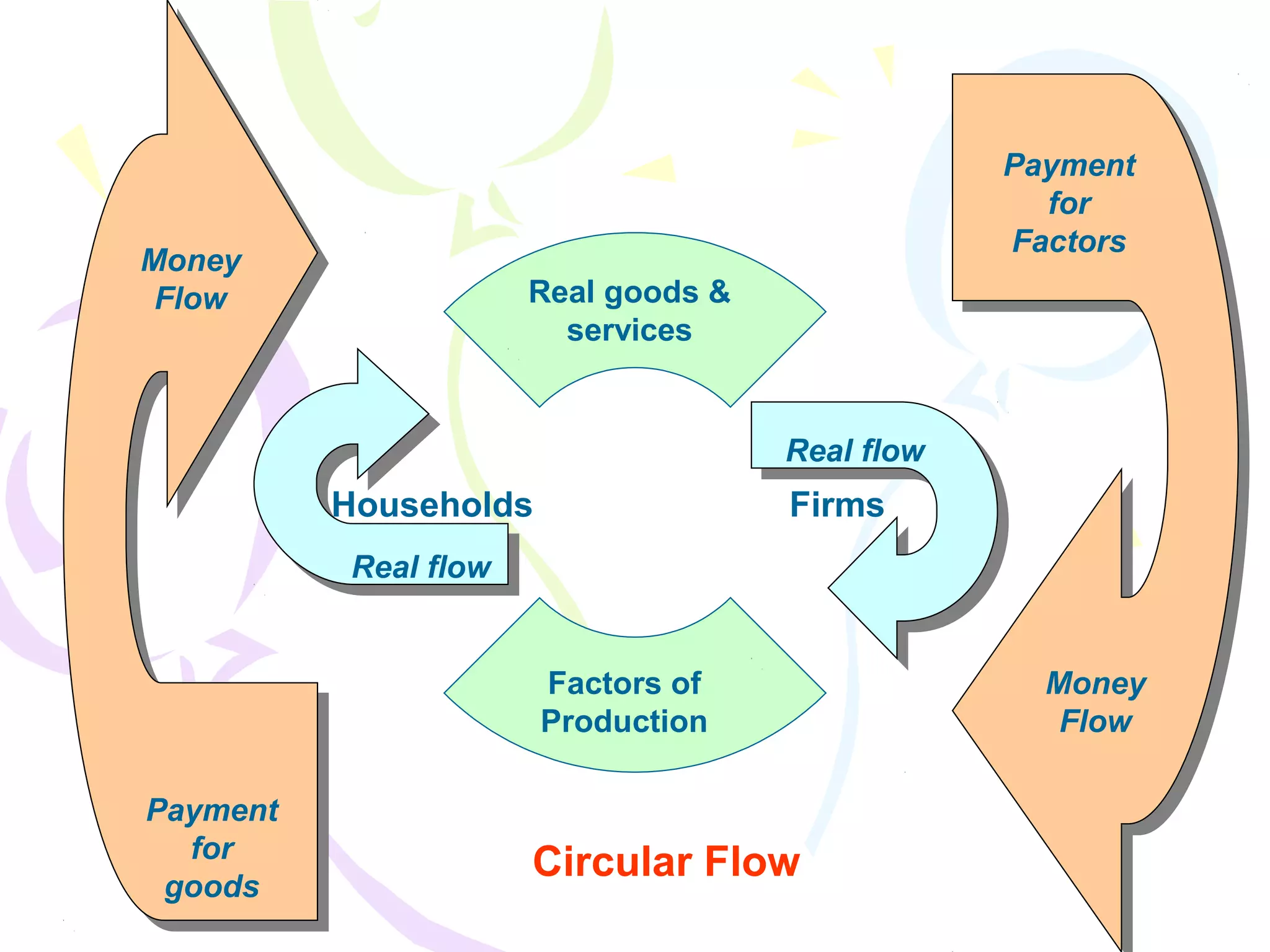
This document provides an outline for a macro-economic framework course taught by Professor Swaha Shome in Mumbai. It covers key topics like measuring national income, economic growth, unemployment, inflation, monetary and fiscal policy, international trade, and the balance of payments. It also defines important macroeconomic concepts like stock and flow variables, opportunity cost, production possibility curves, the circular flow of income, and leakages and injections in the economy.