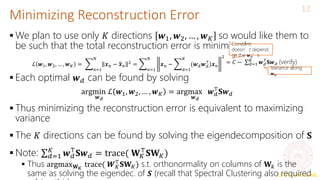
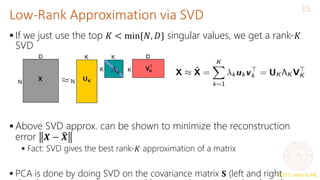
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a technique for dimensionality reduction that projects high-dimensional data onto a lower-dimensional space in a way that maximizes variance. It works by finding the directions (principal components) along which the variance of the data is highest. These principal components become the new axes of the reduced space. PCA involves computing the covariance matrix of the data, performing eigendecomposition on the covariance matrix to obtain its eigenvectors, and projecting the data onto the top K eigenvectors corresponding to the largest eigenvalues, where K is the target dimensionality. This projection both reduces dimensionality and maximizes retained variance.
![CS771: Intro to ML
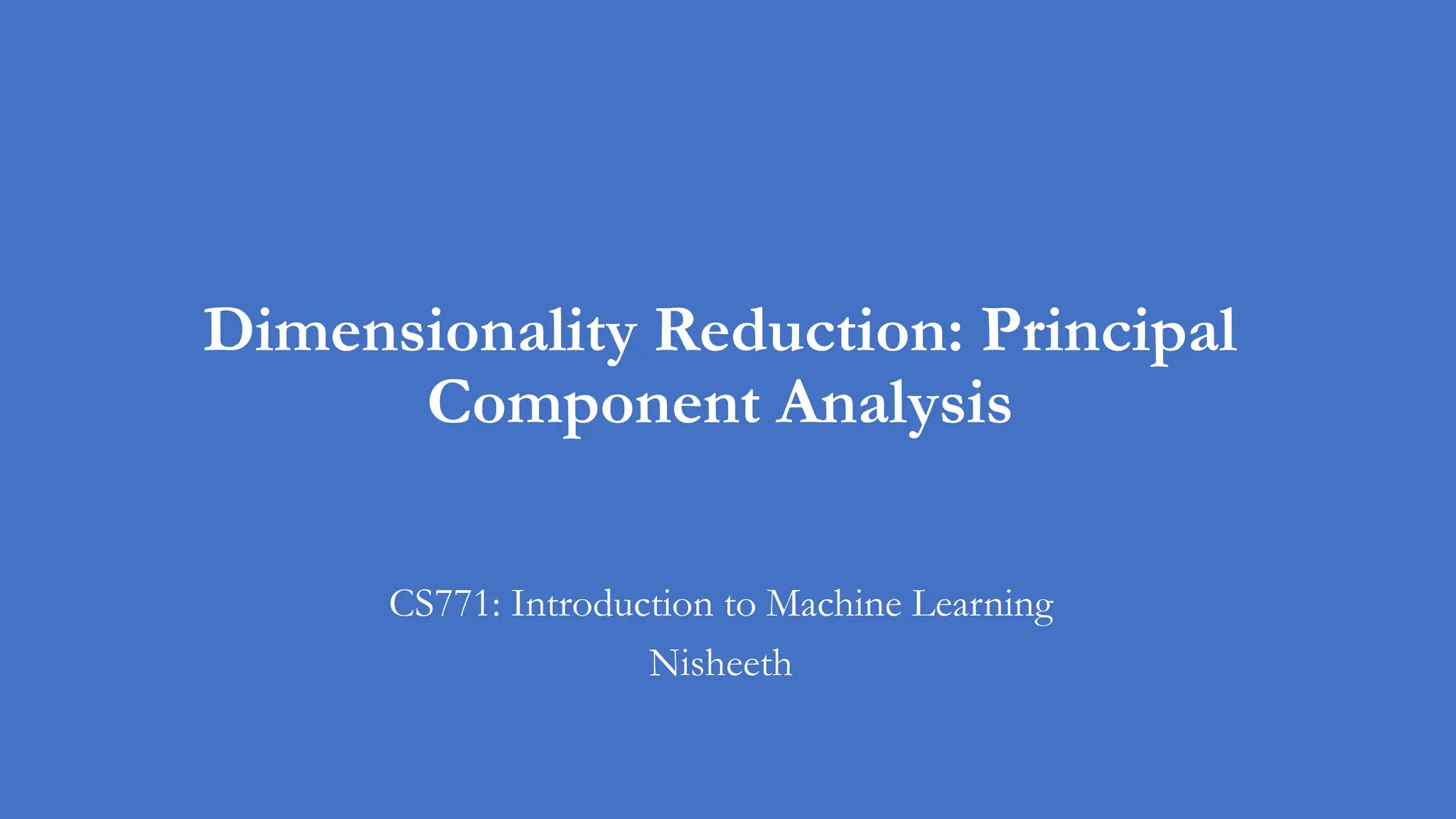
K-means loss function: recap
2
X Z
N
K
K
𝒛𝑛 = [𝑧𝑛1, 𝑧𝑛2, … , 𝑧𝑛𝐾]
denotes a length 𝐾 one-
hot encoding of 𝒙𝑛
• Remember the matrix factorization view of the k-means loss function?
• We approximated an N x D matrix with
• An NxK matrix and a
• KXD matrix
• This could be storage efficient if K is much smaller than D
D
D](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec22-240316134342-4ee6b7af/85/Machine-learning-ppt-and-presentation-code-2-320.jpg)

![CS771: Intro to ML
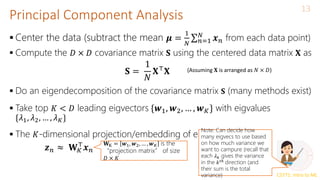
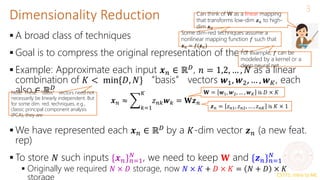
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
5
A classic linear dim. reduction method (Pearson, 1901; Hotelling, 1930)
Can be seen as
Learning directions (co-ordinate axes) that capture maximum variance in data
Learning projection directions that result in smallest reconstruction error
PCA also assumes that the projection directions are orthonormal
argmin
𝑾,𝒁 𝑛=1
𝑁
𝒙𝑛 − 𝑾𝒛𝑛
2 = argmin
𝑾,𝒁
𝑿 − 𝒁𝑾 2
𝑤2
𝑤1
PCA is essentially doing a change of
axes in which we are representing the
data
𝑒1
𝑒2
𝑒1, 𝑒2: Standard co-ordinate axis (𝒙 = [𝑥1, 𝑥2])
𝑤1, 𝑤2: New co-ordinate axis (𝒛 = [𝑧1, 𝑧2])
Each input will still have 2 co-
ordinates, in the new co-ordinate
system, equal to the distances
measured from the new origin
To reduce dimension, can only keep the co-
ordinates of those directions that have largest
variances (e.g., in this example, if we want to
reduce to one-dim, we can keep the co-
ordinate 𝑧1 of each point along 𝑤1 and throw
away 𝑧2). We won’t lose much information Subject to
orthonormality
constraints: 𝒘𝑖
⊤
𝒘𝑗 =
0 for 𝑖 ≠ 𝑗 and 𝒘𝑖
2
=
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec22-240316134342-4ee6b7af/85/Machine-learning-ppt-and-presentation-code-5-320.jpg)




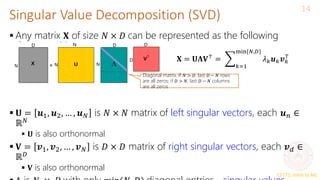
![CS771: Intro to ML
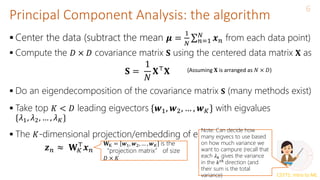
Alternate Basis and Reconstruction
11
Representing a data point 𝒙𝑛 = [𝑥𝑛1, 𝑥𝑛2, … , 𝑥𝑛𝐷] ⊤
in the standard
orthonormal basis 𝒆1, 𝒆2, … , 𝒆𝐷
Let’s represent the same data point in a new orthonormal basis
𝒘1, 𝒘2, … , 𝒘𝐷
Ignoring directions along which projection 𝑧𝑛𝑑 is small, we can approximate
𝒙𝑛 as
Now 𝒙𝑛 is represented by 𝐾 < 𝐷 dim. rep. 𝒛𝑛 = [𝑧𝑛1, 𝑧𝑛2, … , 𝑧𝑛𝐾] and
(verify)
𝒙𝑛 =
𝑑=1
𝐷
𝑥𝑛𝑑𝒆𝑑
𝒆𝑑 is a vector of all zeros except a single 1
at the 𝑑𝑡ℎ
position. Also, 𝒆𝑑
⊤
𝒆𝑑′ = 0 for
𝑑 ≠ 𝑑’
𝒙𝑛 =
𝑑=1
𝐷
𝑧𝑛𝑑𝒘𝑑
𝒛𝑛 = [𝑧𝑛1, 𝑧𝑛2, … , 𝑧𝑛𝐷] ⊤
denotes
the co-ordinates of 𝒙𝑛 in the new
basis
𝑧𝑛𝑑 is the projection of 𝒙𝑛 along the
direction 𝒘𝑑 since 𝑧𝑛𝑑 = 𝒘𝑑
⊤
𝒙𝑛 =
𝒙𝑛
⊤
𝒘𝑑(verify)
𝒙𝑛 ≈ 𝒙𝑛 =
𝑑=1
𝐾
𝑧𝑛𝑑𝒘𝑑 =
𝑑=1
𝐾
(𝒙𝑛
⊤𝒘𝑑)𝒘𝑑 =
𝑑=1
𝐾
(𝒘𝑑𝒘𝑑
⊤
)𝒙𝑛
𝒛𝑛 ≈ 𝐖𝐾
⊤
𝒙𝑛
𝐖K = 𝒘1, 𝒘2, … , 𝒘𝐾 is the
“projection matrix” of size
𝐷 × 𝐾
Note that 𝒙𝑛 −
Also, 𝒙𝑛 ≈ 𝐖𝐾𝒛𝑛](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec22-240316134342-4ee6b7af/85/Machine-learning-ppt-and-presentation-code-11-320.jpg)