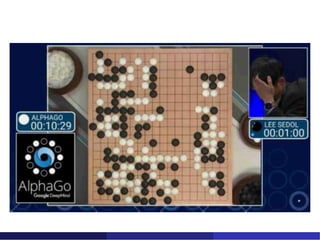
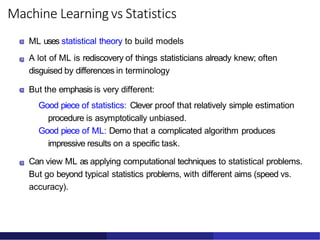
The document introduces machine learning, describing how it involves developing algorithms that can learn from examples or experiences to perform tasks like classification, recognition, and prediction, rather than being explicitly programmed. A variety of applications are discussed, including computer vision, robotics, games, and more. The document also compares machine learning to statistics, noting differences in terminology, emphasis on results over theory, and the scale of machine learning problems and datasets.

























![Computer Vision
[Gatys, Ecker, Bethge. A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style. Arxiv’15.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-1-240126094626-313b7c9e/85/Machine-Learning-pptx-29-320.jpg)