Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX





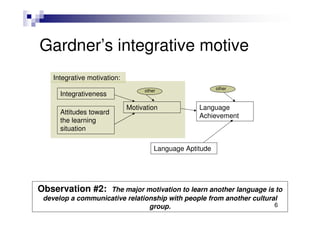





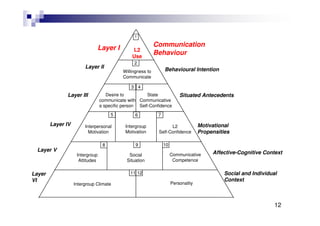



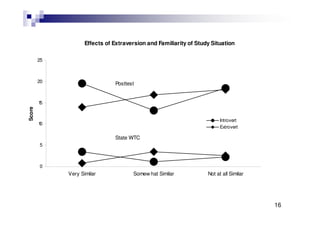














This document summarizes a workshop on understanding and developing willingness to communicate (WTC). The workshop included a brief review of WTC theory and studies, an activity demonstrating situational variation in WTC, and a group discussion on factors affecting WTC. Key points from WTC research presented were that the decision to communicate reflects the intersection of motivation and language anxiety, involves voluntary action, and may be mindful or mindless.





























