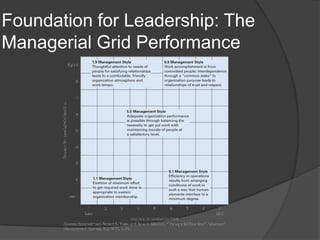
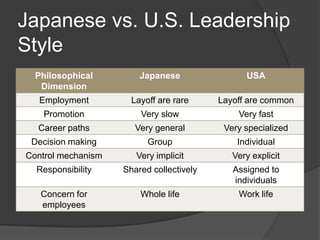
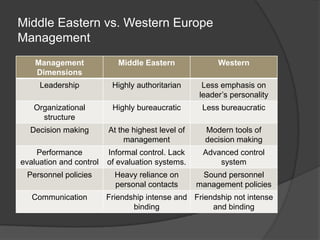
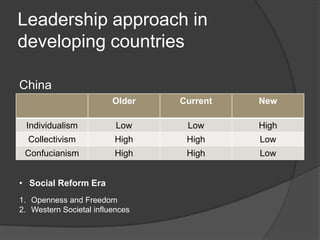
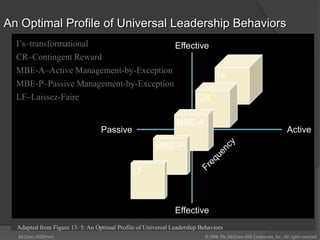
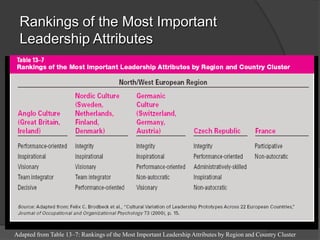
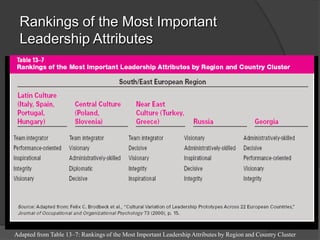
This document discusses leadership across different cultures. It begins by defining leadership and examining philosophical approaches to management like Theory X, Y and Z. It then explores leadership styles, behaviors and how they vary across cultures like the US, Europe, Middle East, developing countries, Japan and more. Transformational leadership is discussed as an effective universal style. The document concludes with a hypothetical case study about an American retailer expanding internationally and the leadership challenges that may arise.