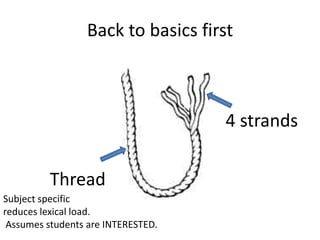
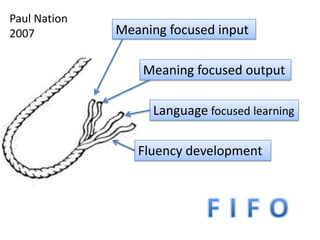
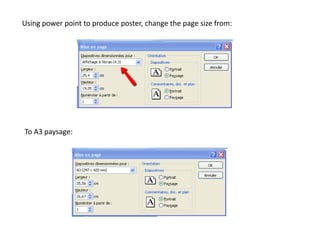
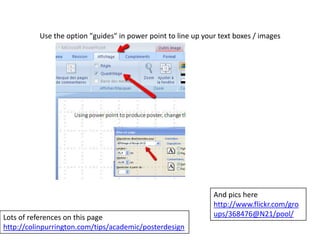
This document provides guidance on teaching English language skills. It discusses four strands of language learning: thread, subject specific, reduces lexical load, and assumes student interest. It also references the work of Paul Nation and his framework of meaning focused input, meaning focused output, language focused learning, and fluency development. Specific techniques are recommended for each strand, including using large quantities of input, encouraging student output through speaking and writing, deliberate practice of language features, and developing language learning strategies. The document also provides advice on vocabulary learning, using computer programs to practice listening and receive feedback, making posters, and using course logs for assessment.