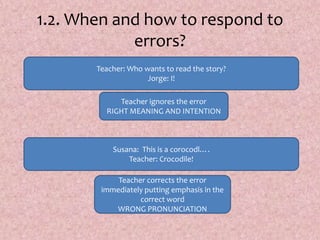
The document provides guidance for teachers on effectively planning and teaching English in the classroom, including maintaining proficiency in English, using a course book and other resources to supplement lessons, and planning lessons with clear routines, sequencing of activities, and opportunities for students to practice listening, speaking, reading and writing skills.