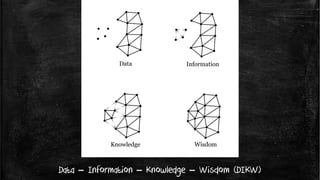
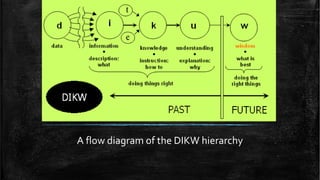
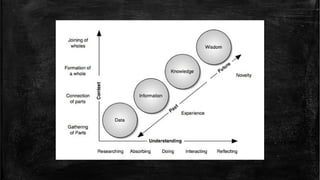
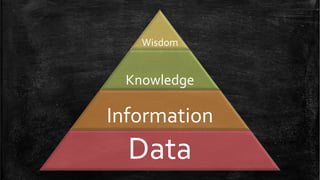
The document introduces the Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom (DIKW) hierarchy. It defines each component as follows:
Data are raw facts without meaning on their own. Information provides meaning to data by relating it contextually. Knowledge transforms information into instructions by combining it with experience. Wisdom adds value through judgment, incorporating ethical and aesthetic considerations to increase effectiveness.
The DIKW hierarchy presents these concepts as a pyramid, with data at the bottom supplying the foundation, and each higher level building upon the lower ones to derive greater meaning and utility - from data to information, knowledge, and ultimately wisdom at the top.