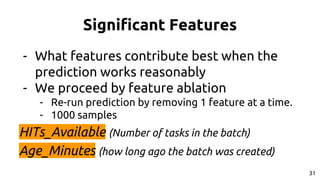
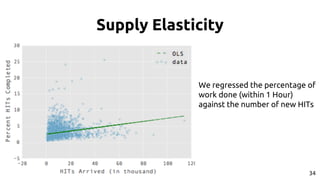
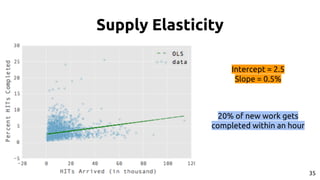
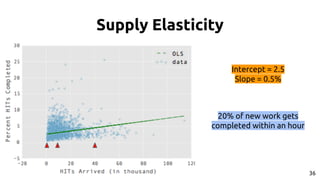
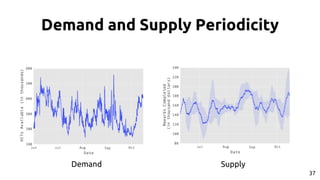
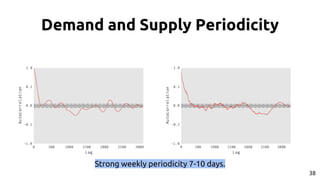
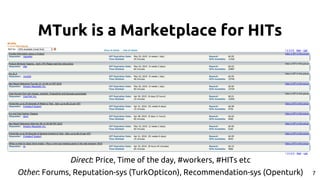
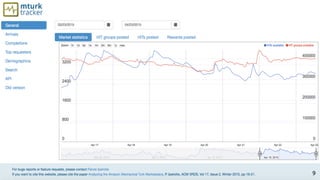
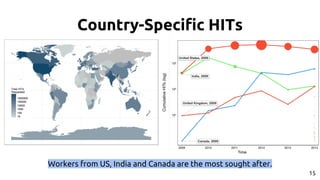
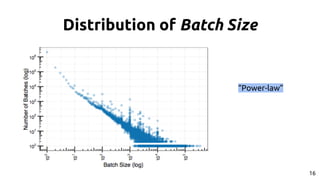
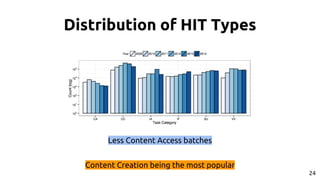
The document discusses the dynamics of micro-task crowdsourcing on Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk), presenting findings from a large-scale analysis of 2.5 million batches and 130 million hits collected over five years. Key insights include classification of hit types, factors affecting batch throughput, and the elasticity of supply and demand in the marketplace, highlighting a periodicity in task availability. The research emphasizes significant features for predicting batch performance, suggesting that crowdsourcing can be efficient if optimized appropriately.






![...Five Years Later
[2009 - 2014]
mturk-tracker collected
2.5Million different batches
with over 130Million HITs
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mturkdynamics-150520213413-lva1-app6892/85/The-Dynamics-of-Micro-Task-Crowdsourcing-10-320.jpg)









![Batch Throughput Prediction
T
time
delta
- Predict batch throughput at time T by training a Random Forest
Regression model with samples taken in [T-delta, T) time span
- 29 Features (including the Type of the Batch)
- Hourly Data in range [June-October] 2014
- We sampled 50 times points for evaluation purposes
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mturkdynamics-150520213413-lva1-app6892/85/The-Dynamics-of-Micro-Task-Crowdsourcing-27-320.jpg)
![Batch Throughput Prediction
T
time
delta
- Predict batch throughput at time T by training a Random Forest
Regression model with samples taken in [T-delta, T) time span
- 29 Features (including the Type of the Batch)
- Hourly Data in range [June-October] 2014
- We sampled 50 times points for evaluation purposes
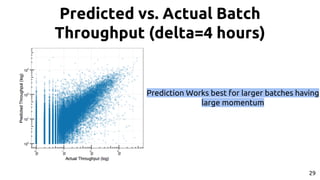
We are interested in cases where prediction works reasonably 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mturkdynamics-150520213413-lva1-app6892/85/The-Dynamics-of-Micro-Task-Crowdsourcing-28-320.jpg)