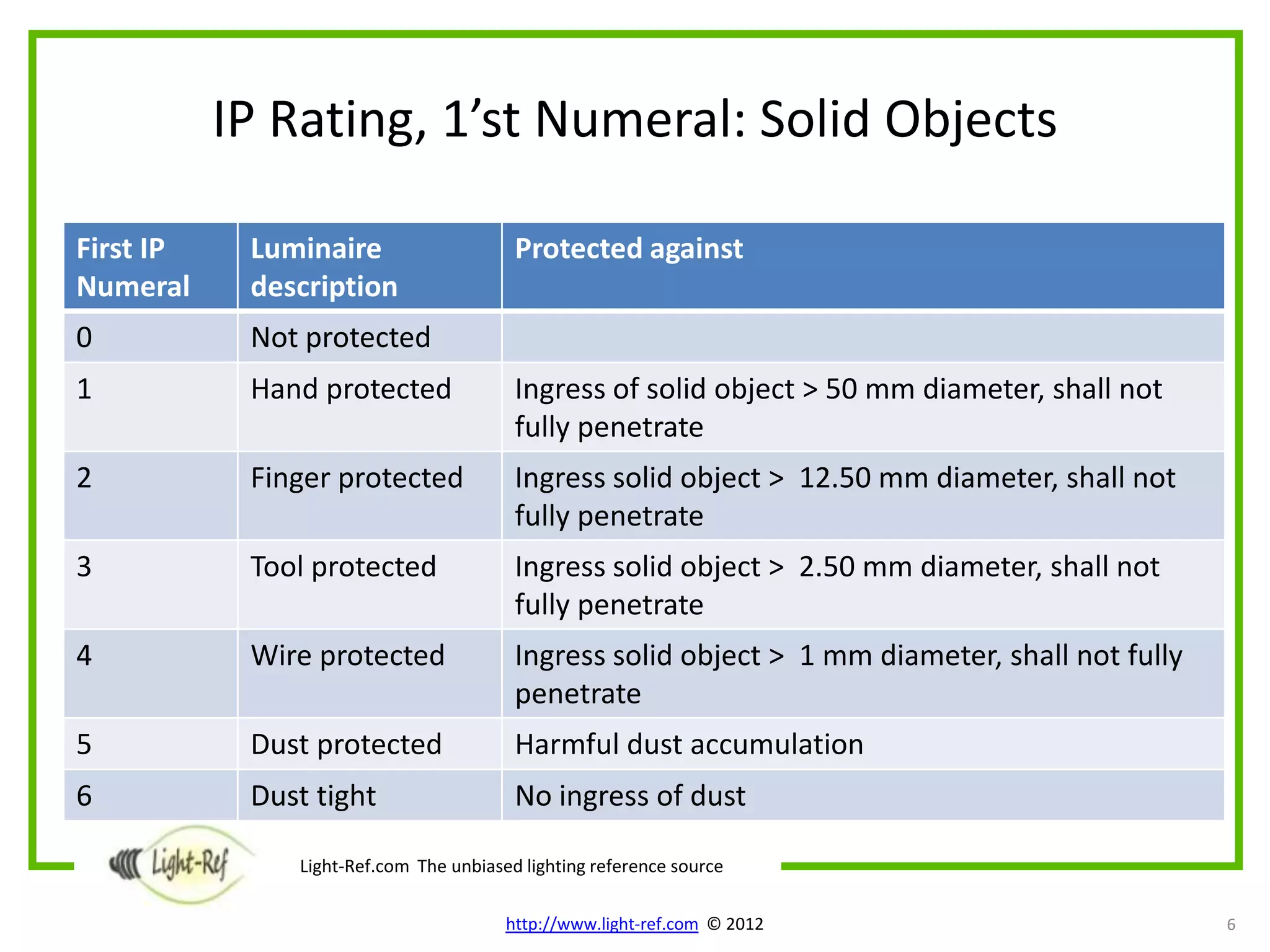
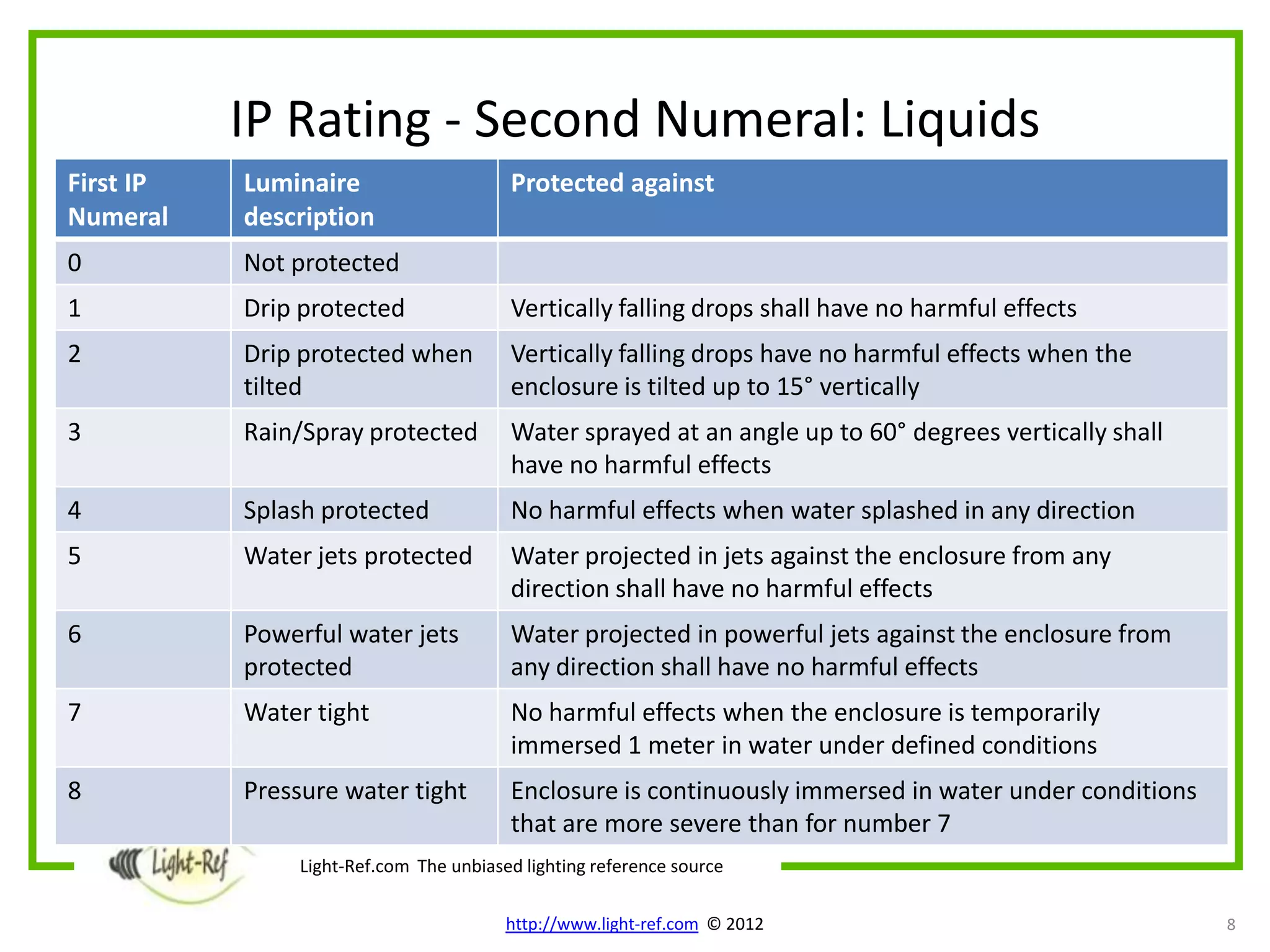
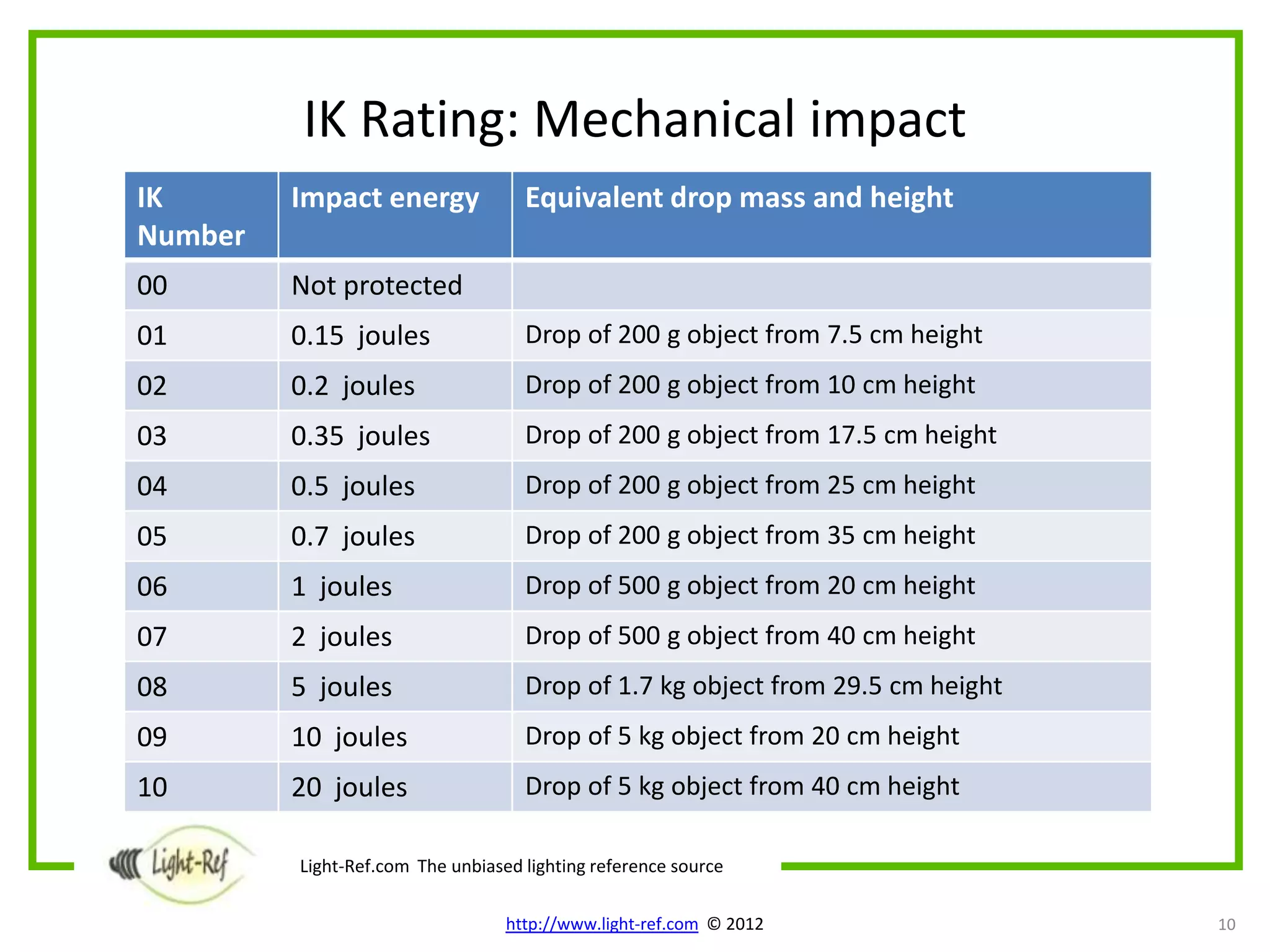
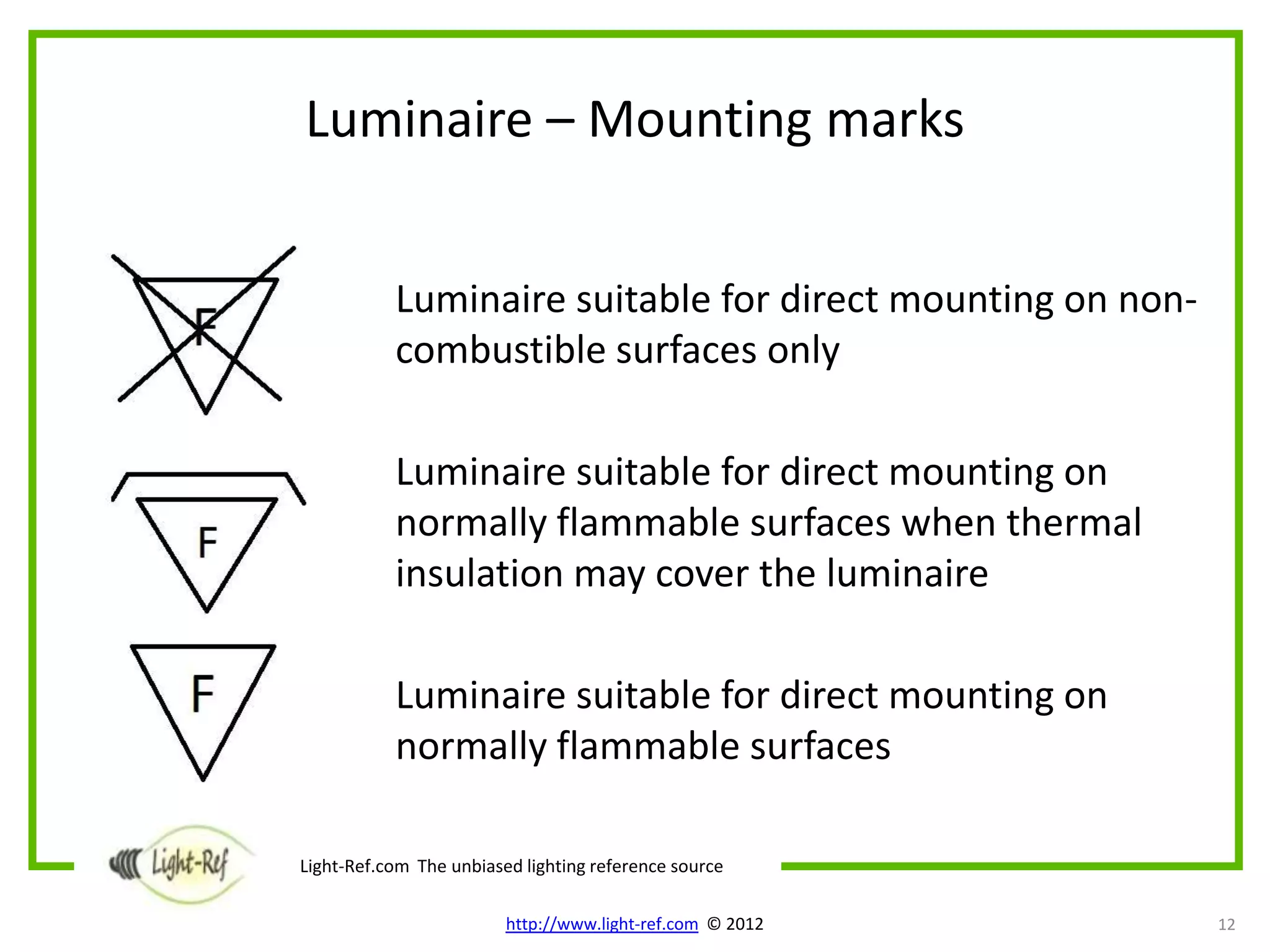
The document provides an overview of key luminaire technical aspects that decision makers should consider when evaluating lighting solutions. It discusses luminaire classification standards, as well as technical attributes like IP ratings for protection from solids and liquids, IK ratings for mechanical impact protection, maximum operating temperatures, mounting requirements, electrical protection classes, and relevant IEC standards. The purpose is to familiarize readers with important technical specifications of luminaires.