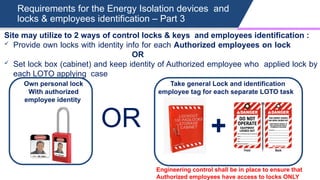
The document outlines Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) training provided by Parabakaran Balasubramaniam, an expert with over 15 years in health and safety training. It emphasizes the importance of understanding hazardous energy control methods and detailed procedures for safely working on machinery, including specific responsibilities for authorized employees, the use of energy isolation devices, and verification steps to ensure safety. Key training components involve identifying energy sources, applying lockout devices, and performing maintenance under controlled conditions to prevent accidents.