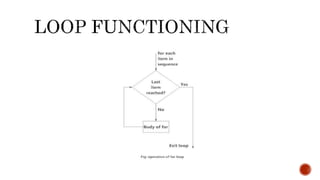
This document discusses different types of loops in computer programming including for loops, nested for loops, while loops, repeat loops, and the break and next keywords. For loops are entry-controlled and iterate over a known sequence. Nested for loops run multiple inner loops within an outer loop. While loops are also entry-controlled but are used when the number of iterations is unknown. The break keyword exits a loop entirely, while next skips the current iteration. Repeat loops run continuously until a break condition is encountered.