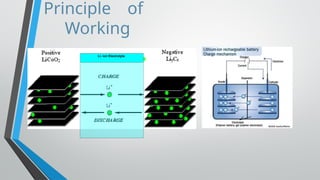
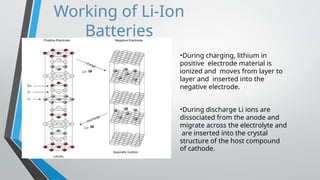
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices that utilize lithium compounds as anode materials, providing high energy density and low self-discharge rates. These batteries have a four-layer structure, with a unique intercalation mechanism allowing lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge cycles. They are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and various applications due to their lightweight and safety features.