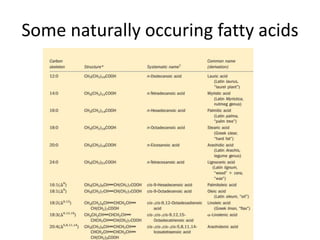
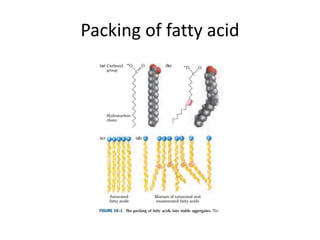
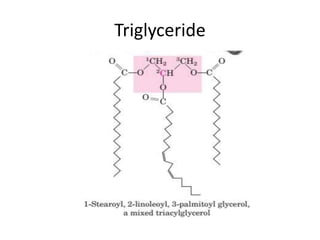
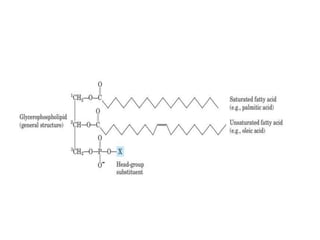
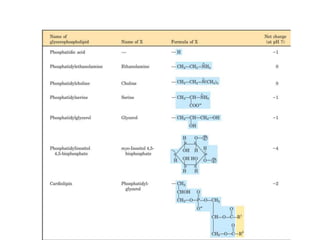
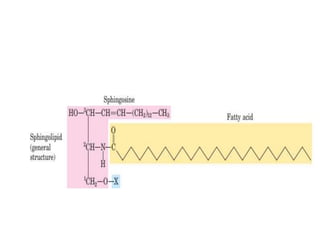
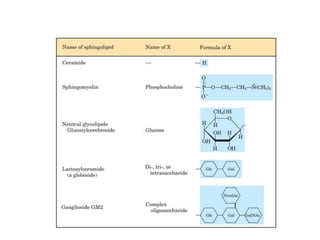
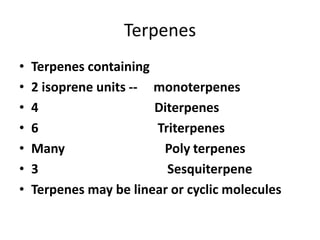
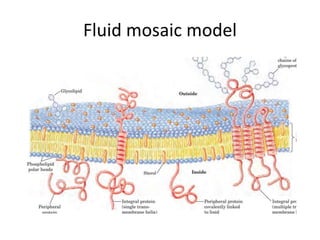
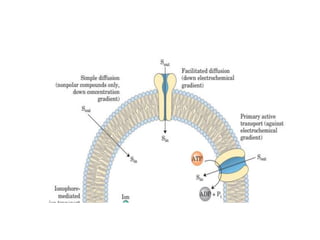
Lipids are water-insoluble biomolecules with functions including cell membrane structure, energy storage, and protection. They are categorized into complex and simple lipids, with triglycerides being the most abundant storage form. Biological membranes consist mainly of lipids and proteins, following the fluid mosaic model, and transport mechanisms include passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.