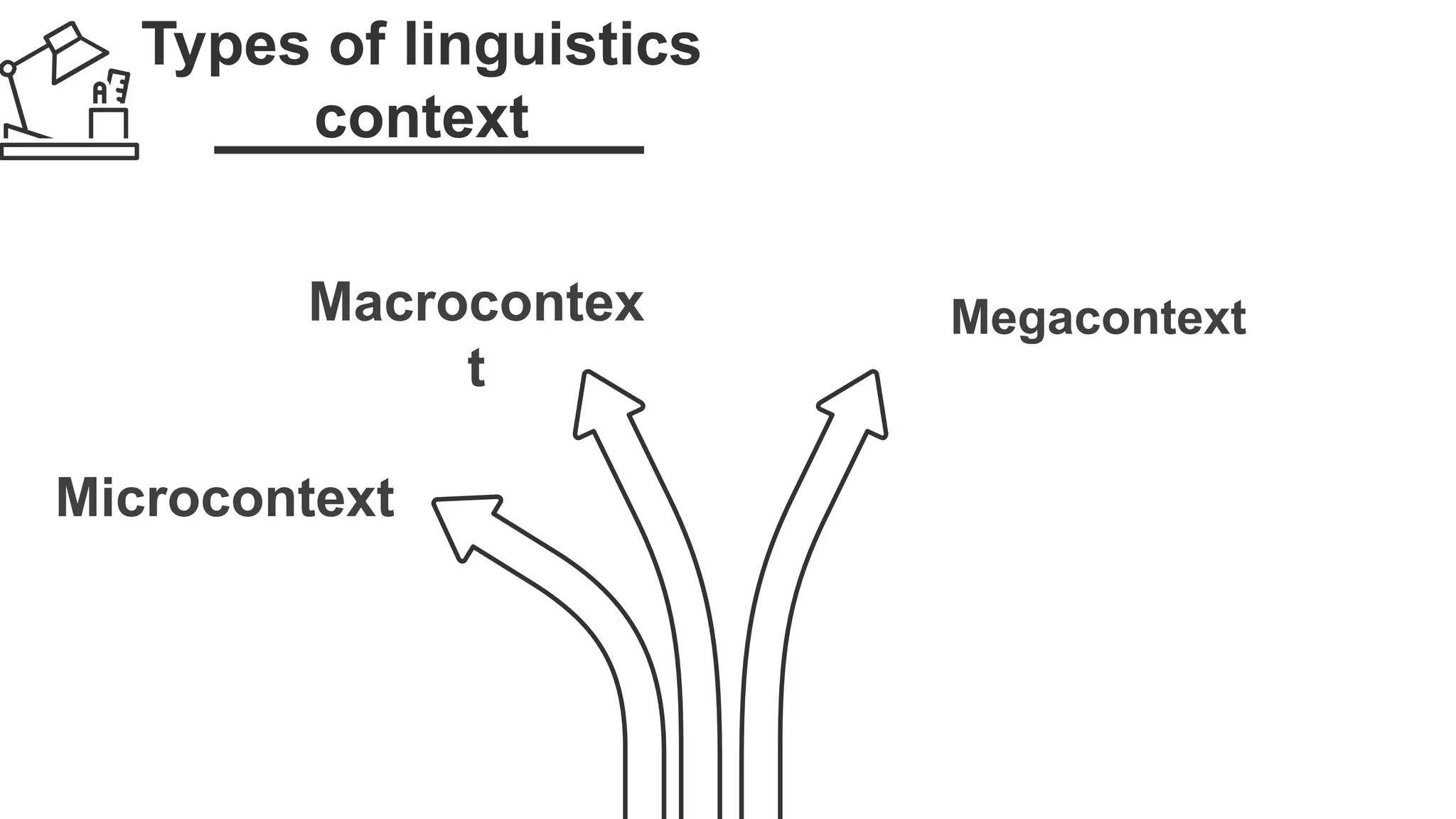
Linguistic context refers to the language surrounding a word or phrase that provides meaning, including deictic expressions, co-text, and collocation. Extralingual context comprises non-linguistic factors that influence communication, such as the physical environment. Context can be examined at different levels: microcontext analyzes a single utterance; macrocontext considers a paragraph in relation to a full text; and megacontext looks at chapters or an entire book. Both linguistic and extralingual context are important for fully understanding any communication.