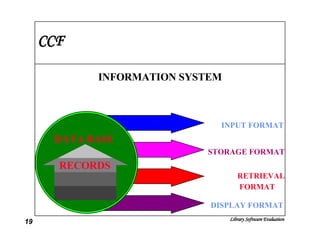
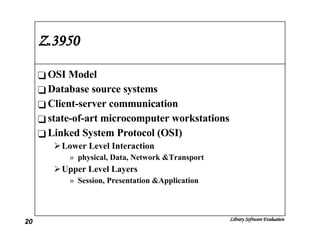
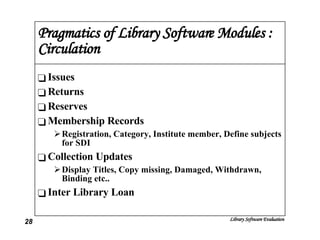
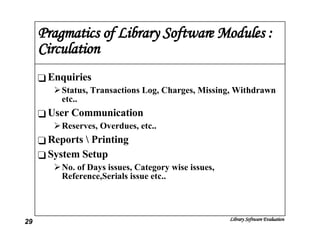
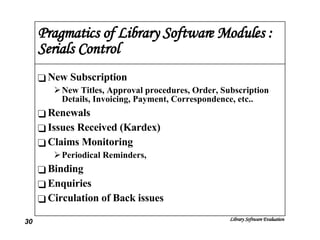
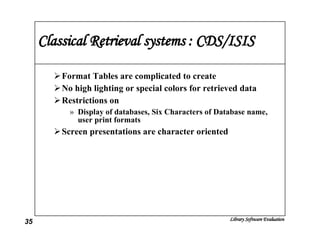
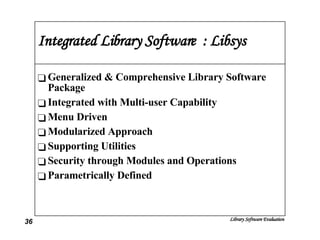
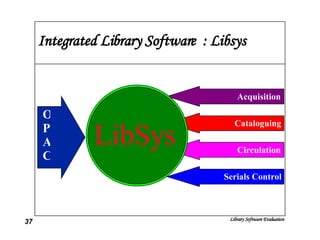
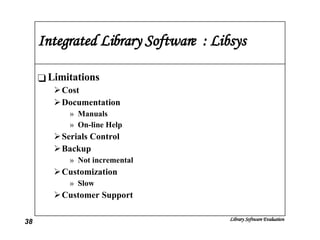
The document discusses the evaluation of library software and its impact on library services. It outlines the scope of library automation and technological trends affecting libraries. The key aspects of library software modules for acquisition, cataloguing, circulation and serials control are described. Classical retrieval systems like CDS/ISIS and integrated library software packages like Libsys are compared, along with their advantages and limitations. The conclusion states that no software can meet all requirements of a library and some customization or compromise is usually needed.