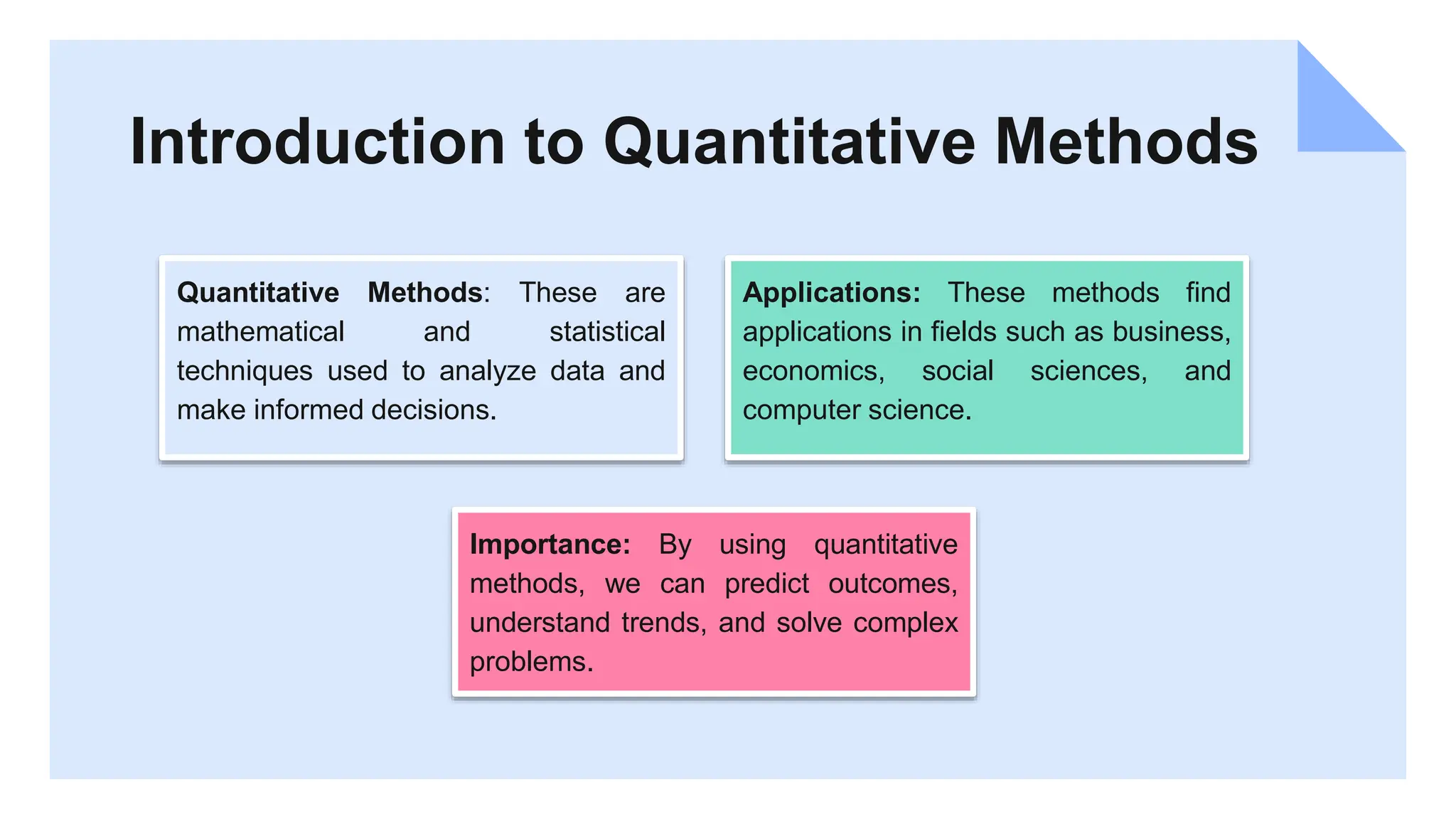
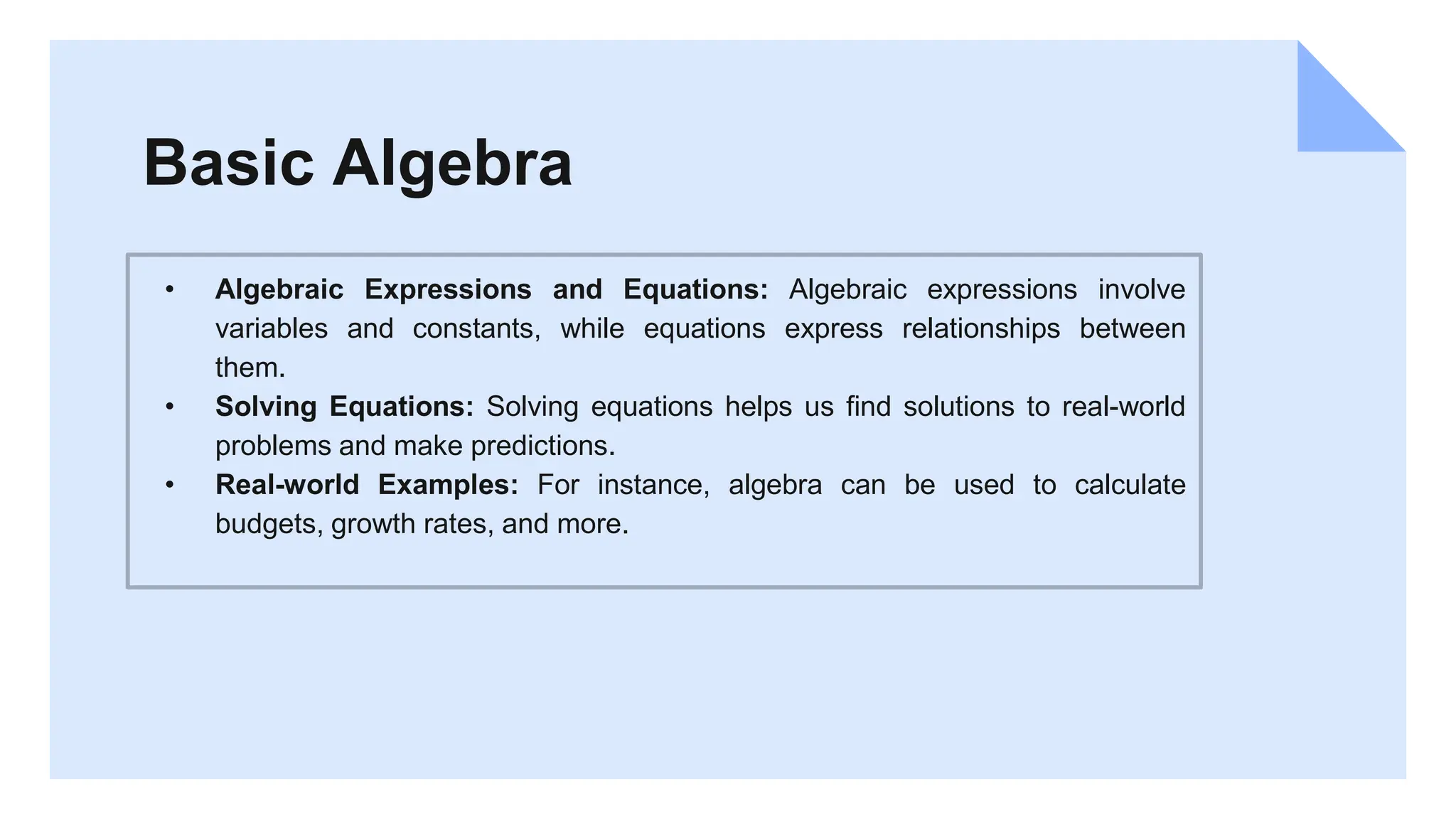
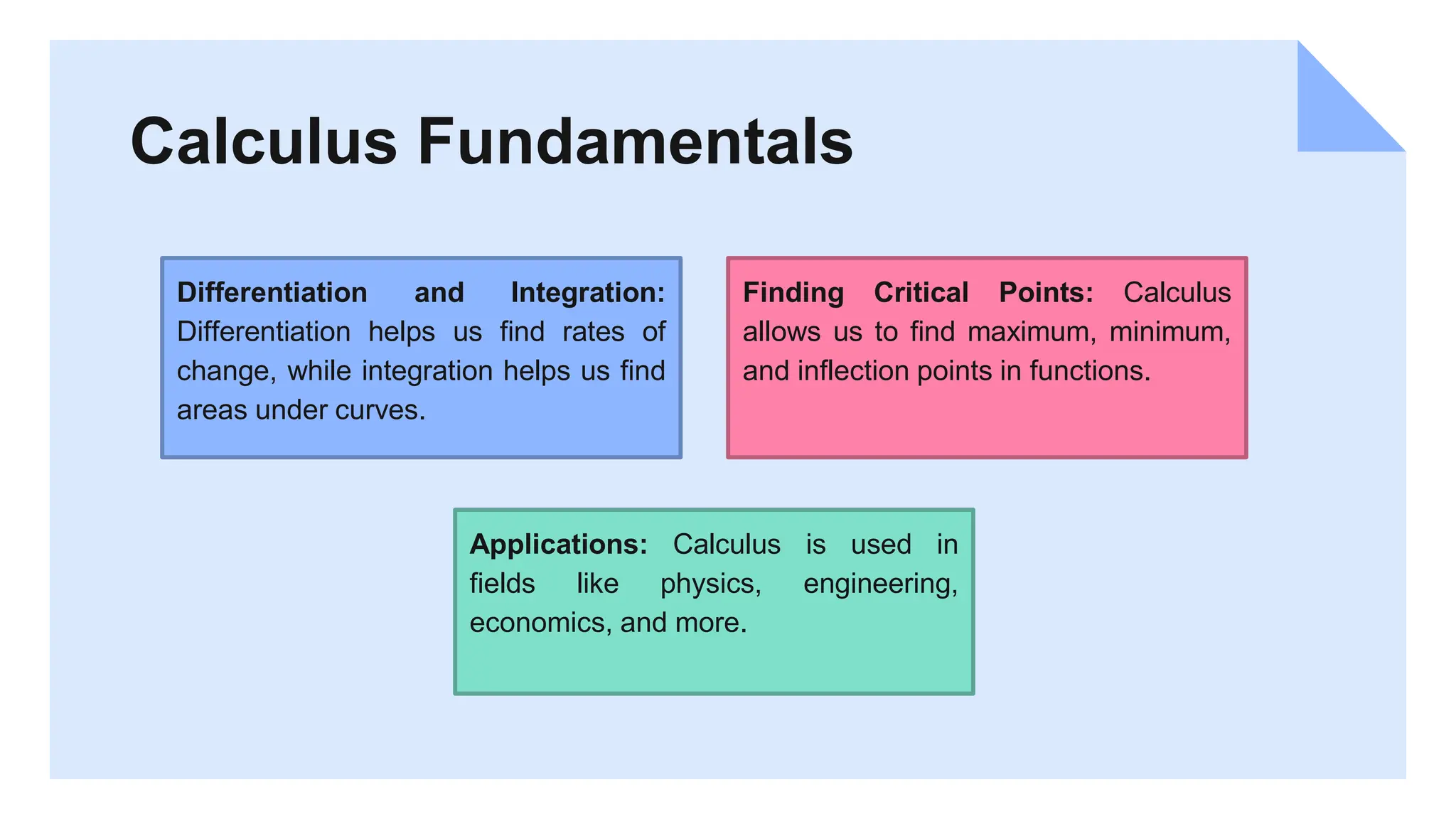
This document provides an overview and introduction to quantitative methods. It discusses key concepts in algebra, calculus, statistics, and Python programming. Various quantitative analysis techniques are explained, including descriptive statistics, hypothesis testing, and data visualization. The course covers manipulating and analyzing data with Python libraries like NumPy, pandas, and Matplotlib. The goal is to equip students with essential quantitative skills and encourage practicing these skills by exploring datasets and creating their own analyses. Additional learning resources are recommended for continuing education in quantitative methods.